Mesotherapy is a form of alternative medicine which involves intradermal or subcutaneous injections of pharmaceutical preparations, enzymes, hormones, plant extracts, vitamins, and/or other ingredients such as hyaluronic acid. It has no proven clinical efficacy and poor scientific backing. Mesotherapy injections allegedly target adipose fat cells, apparently by inducing lipolysis, rupture and cell death among adipocytes. The stated aim of mesotherapy is to provide the skin with essential nutrients, hydration, and other beneficial compounds to rejuvenate and revitalize its appearance.
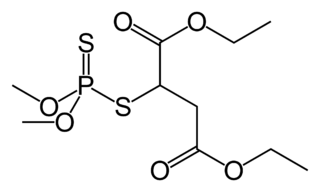
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In the USSR, it was known as carbophos, in New Zealand and Australia as maldison and in South Africa as mercaptothion.
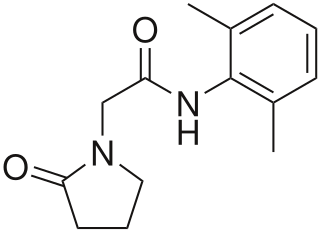
Nefiracetam is a nootropic drug of the racetam family. Preliminary research suggests that it may possess certain antidementia properties in rats.

Methylcholanthrene is a highly carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon produced by burning organic compounds at very high temperatures. Methylcholanthrene is also known as 3-methylcholanthrene, 20-methylcholanthrene or the IUPAC name 3-methyl-1,2-dyhydrobenzo[j]aceanthrylene. The short notation often used is 3-MC or MCA. This compound forms pale yellow solid crystals when crystallized from benzene and ether. It has a melting point around 180 °C and its boiling point is around 280 °C at a pressure of 80 mmHg. Methylcholanthrene is used in laboratory studies of chemical carcinogenesis. It is an alkylated derivative of benz[a]anthracene and has a similar UV spectrum. The most common isomer is 3-methylcholanthrene, although the methyl group can occur in other places.

The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are utilized in cosmetic formulations, clinical dermatology, and the treatment of some forms of cancer.

1,4-Dioxane is a heterocyclic organic compound, classified as an ether. It is a colorless liquid with a faint sweet odor similar to that of diethyl ether. The compound is often called simply dioxane because the other dioxane isomers are rarely encountered.

Aldrin is an organochlorine insecticide that was widely used until the 1990s, when it was banned in most countries. Aldrin is a member of the so-called "classic organochlorines" (COC) group of pesticides. COCs enjoyed a very sharp rise in popularity during and after World War II. Other noteworthy examples of COCs include dieldrin and DDT. After research showed that organochlorines can be highly toxic to the ecosystem through bioaccumulation, most were banned from use. Before the ban, it was heavily used as a pesticide to treat seed and soil. Aldrin and related "cyclodiene" pesticides became notorious as persistent organic pollutants.
Selenium disulfide, also known as selenium sulfide, is a chemical compound and medication used to treat seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, and pityriasis versicolor. It is applied to the affected area as a lotion or shampoo. Symptoms frequently return if treatment is stopped.
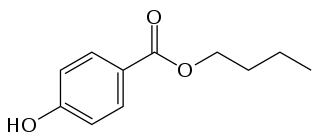
Butylparaben, or butyl p-hydroxybenzoate, is an organic compound with the formula C
4H
9O
2CC
6H
4OH. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It has proven to be a highly successful antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics. It is also used in medication suspensions, and as a flavoring additive in food.

Flutamide, sold under the brand name Eulexin among others, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which is used primarily to treat prostate cancer. It is also used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions like acne, excessive hair growth, and high androgen levels in women. It is taken by mouth, usually three times per day.

Skin care or skincare is a range of practices that support skin integrity, enhance its appearance, and relieve skin conditions. They can include nutrition, avoidance of excessive sun exposure, and appropriate use of emollients. Practices that enhance appearance include the use of cosmetics, botulinum, exfoliation, fillers, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, peels, retinol therapy, and ultrasonic skin treatment. Skin care is a routine daily procedure in many settings, such as skin that is either too dry or too moist, and prevention of dermatitis and prevention of skin injuries.
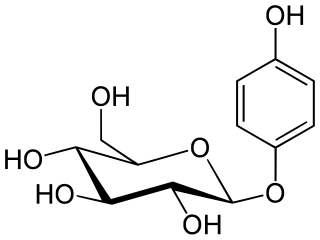
β-Arbutin, also known by its International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) name, arbutin, is a glycosylated derivative of hydroquinone. β-Arbutin is naturally present in the leaves and bark of a variety of plants, notably the bearberry plant, Arctostaphylos uva-ursi. Utilized as a biosynthetic active ingredient in topical treatments for skin lightening, β-arbutin is aimed at addressing hyperpigmentation issues. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase, an essential enzyme for melanin synthesis in the human skin, thereby leading to a reduction in hyperpigmentation. It is important to distinguish β-arbutin from its structurally similar stereoisomer, α-arbutin, which exhibits similar effects in clinical applications.

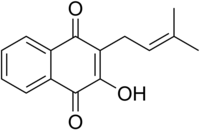
Lapacho or taheebo is herbal tea made from the inner bark of the pau d'arco tree Handroanthus impetiginosus.

Handroanthus impetiginosus, the pink ipê, pink lapacho or pink trumpet tree, is a tree in the family Bignoniaceae, distributed throughout North, Central and South America, from northern Mexico south to northern Argentina. Along with all the other species in the Handroanthus genus, it is the national tree of Paraguay.
Carboxytherapy is a non-surgical cosmetic medicine treatment for dermatology. Carboxytherapy employs injections or transdermal application to infuse gaseous carbon dioxide below the skin into the subcutaneous tissue through a needle or skin. It has a necrotizing effect on fat tissue fat cells, stimulates blood flow, improves the skin's elasticity and reduces the appearance of cellulite. It has also become a popular treatment for stretch marks. It is non-toxic and less invasive than operations like liposuction. Carboxytherapy leads to a temporary decrease in subcutaneous fat but has shown to reoccur again after a 28 week period. It can be applied for those with androgenic alopecia or alopecia areata.

Tabebuia rosea, also called pink poui, and rosy trumpet tree is a neotropical tree that grows up to 30 m (98 ft) and can reach a diameter at breast height of up to 100 cm (3 ft). The Spanish name roble de sabana, meaning "savannah oak", is widely used in Costa Rica, probably because it often remains in heavily deforested areas and because of the resemblance of its wood to that of oak trees. It is the national tree of El Salvador, where it is called "Maquilíshuat".

Sodium bisulfite (or sodium bisulphite, sodium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite is not a real compound, but a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions composed of sodium and bisulfite ions. It appears in form of white or yellowish-white crystals with an odor of sulfur dioxide. Regardless of its ill-defined nature, sodium bisulfite is used in many different industries such as a food additive with E number E222 in the food industry, a reducing agent in the cosmetic industry, and a decomposer of residual hypochlorite used in the bleaching industry.
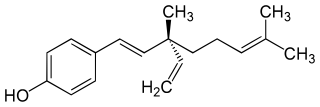
Bakuchiol is a meroterpenoid in the class terpenophenol.

Handroanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae. It consists of 30 species of trees, known in Latin America by the common names poui, pau d'arco, or ipê. The latter sometimes appears as epay or simply ipe (unaccented) in English. The large timber species are sometimes called lapacho or guayacan, but these names are more properly applied to the species Handroanthus lapacho and Handroanthus guayacan, respectively.

A botanical drug is defined in the United States Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as a botanical product that is marketed as diagnosing, mitigating, treating, or curing a disease; a botanical product in turn, is a finished, labeled product that contains ingredients from plants. Chemicals that are purified from plants, like paclitaxel, and highly purified products of industrial fermentation, like biopharmaceuticals, are not considered to be botanical products.