
Carolina is a city and municipality located on the northeast coast of Puerto Rico. It lies immediately east of the capital San Juan and Trujillo Alto; north of Gurabo and Juncos; and west of Canóvanas and Loíza. Carolina is spread over 12 barrios plus Carolina Pueblo. It is part of the San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo Metropolitan Statistical Area, and home to Puerto Rico's main airport, the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport.

Sabana Grande is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located north of Lajas and Guánica; south of Maricao; east of San Germán; and west of Yauco. Sabana Grande is spread over seven barrios and Sabana Grande Pueblo. It is part of the San Germán-Cabo Rojo Metropolitan Statistical Area.
AeroTACA was an airline based in Bogotá, Colombia. It operated charter flights within Colombia and to neighboring countries. Its main base was El Dorado International Airport.

Sincelejo is the capital and largest city of the Colombian department of Sucre in the Caribbean region. It is also the capital of the department's subregion, Sabanas, and is the 25th largest city by population of the country. It is located 30 kilometers from the Caribbean Sea at the Gulf of Morrosquillo, 125 kilometers from Cartagena, and 200 kilometers from Barranquilla.

Cruces is a municipality and town in Cienfuegos Province, Cuba. It is the home of the Mal Tiempo National Park which commemorates a battle in the 1895 War of Independence.

Sabana de Torres is a town and municipality in the Santander Department in northeastern Colombia.

El Abra is the name given to an extensive archeological site, located in the valley of the same name. El Abra is situated in the east of the municipality Zipaquirá extending to the westernmost part of Tocancipá in the department of Cundinamarca, Colombia. The several hundred metres long series of rock shelters is in the north of the Bogotá savanna on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes at an altitude of 2,570 metres (8,430 ft). The rock shelter and cave system is one of the first evidences of human settlement in the Americas, dated at 12,400 ± 160 years BP. The site was used by the hunter-gatherers of the Late Pleistocene epoch.

The Bogotá savanna is a montane savanna, located in the southwestern part of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in the center of Colombia. The Bogotá savanna has an extent of 4,251.6 square kilometres (1,641.6 sq mi) and an average altitude of 2,650 metres (8,690 ft). The savanna is situated in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes.

Piedras del Tunjo is an important archaeological park established on a natural rock shelter 40 kilometres (25 mi) west of Bogotá in the municipality of Facatativá.
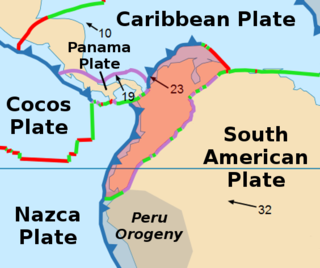
The North Andes Plate or North Andes Block is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located in the northern Andes. It is squeezed between the faster moving South American Plate and the Nazca Plate to the southwest. Due to the subduction of the Coiba and Malpelo plates, this area is very prone to volcanic and seismic activity, with many historical earthquakes.
San Antonio de Areco Airport is an airport 3 kilometres (2 mi) northeast of San Antonio de Areco, a town in the Buenos Aires Province of Argentina.

Jaboque is a wetland, part of the Wetlands of Bogotá, located in the locality Engativá, Bogotá, Colombia. The wetland, close to the Bogotá River on the Bogotá savanna covers an area of 148 hectares. The wetland is close to El Dorado International Airport in the Juan Amarillo River basin.

Thomas van der Hammen was a Dutch palaeontologist, botanist and geologist. He had published more than 160 works in five languages.

The Tunjuelo or Tunjuelito River is a river on the Bogotá savanna and a left tributary of the Bogotá River. The river, with a length of 73 kilometres (45 mi) originates in the Sumapaz Páramo and flows northward through the Usme Synclinal to enter the Colombian capital Bogotá. There, the river is mostly canalised flowing westward into the Bogotá River. It is one of the three main rivers of the city, together with the Fucha and Juan Amarillo Rivers.
The Soacha River is a river on the Bogotá savanna and a left tributary of the Bogotá River.

The Guadalupe Group (Spanish: Grupo Guadalupe, K2G, Ksg) is a geological group of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The group, a sequence of shales and sandstones, is subdivided into three formations; Arenisca Dura, Plaeners and Arenisca Labor-Tierna, and dates to the Late Cretaceous period; Campanian-Maastrichtian epochs and at its type section has a thickness of 750 metres (2,460 ft).

The Tunjuelo Formation, Río Tunjuelo or Río Tunjuelito Formation is a geological formation of the Bogotá savanna, Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consists mainly of conglomerates with intercalating shales and sandstones. The Tunjuelo Formation dates to the Quaternary period; covering the complete Pleistocene epoch, and has a maximum thickness of 150 metres (490 ft). It is a formation of the lacustrine and fluvio-glacial sediments of Lake Humboldt.
The Río Frío is a river on the Bogotá savanna and a right tributary of the Bogotá River. The river, in a basin of 6,008.69 hectares (23.1997 sq mi), originates on the Páramo de Guerrero in Zipaquirá at an altitude of 3,700 metres (12,100 ft). It flows through the municipalities Tabio and Cajicá and into the Bogotá River in the south of Chía, at 2,650 metres (8,690 ft) above sea level.

The Bogotá Fault is a major inactive slightly dextral oblique thrust fault in the department of Cundinamarca in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of 79.3 kilometres (49.3 mi), while other authors designate a length of 107 kilometres (66 mi), and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 013.5 ± 7 across the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, central part of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes.















