Related Research Articles

The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA, Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and CSA (Canada). The ISS is the largest space station ever built. Its primary purpose is to perform microgravity and space environment experiments.

Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing fusion. Common alternative methods include solvent welding using chemicals to melt materials being bonded without heat, and solid-state welding processes which bond without melting, such as pressure, cold welding, and diffusion bonding.

A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a medium used to connect or "wire" components to one another in a circuit. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with a pattern of traces, planes and other features etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers, generally by means of soldering, which both electrically connects and mechanically fastens the components to the board. Another manufacturing process adds vias, drilled holes that allow electrical interconnections between conductive layers.

Kibō, also known as the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station (ISS) developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module, and is attached to the Harmony module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on Space Shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124. The third and final components were launched on STS-127.

STS-72 was a Space Shuttle Endeavour mission to capture and return to Earth a Japanese microgravity research spacecraft known as Space Flyer Unit (SFU). The mission launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on 11 January 1996.

STS-94 was a mission of the United States Space Shuttle Columbia, launched on 1 July 1997.

STS-105 was a mission of the Space Shuttle Discovery to the International Space Station, launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, 10 August 2001. This mission was Discovery's final mission until STS-114, because Discovery was grounded for a refit, and then all Shuttles were grounded in the wake of the Columbia disaster. The refit included an update of the flight deck to the glass cockpit layout, which was already installed on Atlantis and Columbia.

Peter Jeffrey Kelsay Wisoff is an American physicist and former NASA astronaut. Wisoff qualified as mission specialist and flew in four Space Shuttle missions, with his first launch in 1993 and his last in 2000.

Laser engraving is the practice of using lasers to engrave an object. The engraving process renders a design by physically cutting into the object to remove material. The technique does not involve the use of inks or tool bits that contact the engraving surface and wear out, giving it an advantage over alternative marking technologies, where inks or bit heads have to be replaced regularly.

STS-121 was a 2006 NASA Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space ShuttleDiscovery. The main purposes of the mission were to test new safety and repair techniques introduced following the Columbia disaster of February 2003 as well as to deliver supplies, equipment and German European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Reiter to the ISS.

Space manufacturing or In-space manufacturing is the fabrication, assembly or integration of tangible goods beyond Earth's atmosphere, involving the transformation of raw or recycled materials into components, products, or infrastructure in space, where the manufacturing process is executed either by humans or automated systems by taking advantage of the unique characteristics of space. Synonyms of Space/In-space manufacturing are In-orbit manufacturing, Off-Earth manufacturing, Space-based manufacturing, Orbital manufacturing, In-situ manufacturing, In-space fabrication, In-space production, etc.

The Mir Environmental Effects Payload (MEEP) was a set of four experiments installed on the Russian space station Mir from March 1996 to October 1997 to study the effects of space debris impacts and exposure to the space environment on a variety of materials. The materials used in the experiments were being considered for use on the International Space Station, and by exposing them at a similar orbital altitude to that flown by the ISS, the experiments provided an assessment of the performance of those materials in a similar space environment. MEEP also fulfilled the need to examine the occurrence and effects of man-made debris and natural micrometeoroids through capture and impact studies. The experiments were installed on the Mir docking module during STS-76, and retrieved during STS-86.

STS-123 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was flown by Space Shuttle Endeavour. STS-123 was the 1J/A ISS assembly mission. The original launch target date was February 14, 2008, but after the delay of STS-122, the shuttle was launched on March 11, 2008. It was the twenty-fifth shuttle mission to visit the ISS, and delivered the first module of the Japanese laboratory, Japanese Experiment Module (Kibō), and the Canadian Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, (SPDM) Dextre robotics system to the station. The mission duration was 15 days and 18 hours, and it was the first mission to fully utilize the Station-to-Shuttle Power Transfer System (SSPTS), allowing space station power to augment the shuttle power systems. The mission set a record for a shuttle's longest stay at the ISS.
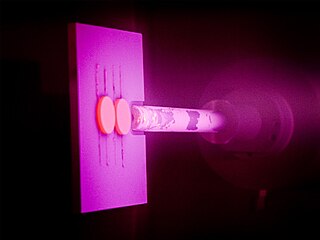
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polymers. PVD is characterized by a process in which the material transitions from a condensed phase to a vapor phase and then back to a thin film condensed phase. The most common PVD processes are sputtering and evaporation. PVD is used in the manufacturing of items which require thin films for optical, mechanical, electrical, acoustic or chemical functions. Examples include semiconductor devices such as thin-film solar cells, microelectromechanical devices such as thin film bulk acoustic resonator, aluminized PET film for food packaging and balloons, and titanium nitride coated cutting tools for metalworking. Besides PVD tools for fabrication, special smaller tools used mainly for scientific purposes have been developed.

The Stykovochnyy Otsek, GRAU index 316GK, otherwise known as the Mir Docking Module or SO, was the sixth module of the Russian space station Mir, launched in November 1995 aboard the Space ShuttleAtlantis. The module, built by RKK Energia, was designed to help simplify space shuttle dockings to Mir during the Shuttle-Mir programme, preventing the need for the periodic relocation of the Kristall module necessary for dockings prior to the compartment's arrival. The module was also used to transport two new photovoltaic arrays to the station, as a mounting point for external experiments, and as a storage module when not in use for dockings.

The Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) is a series of experiments mounted externally on the International Space Station (ISS) that investigates the effects of long-term exposure of materials to the harsh space environment.

STS-134 was the penultimate mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the 25th and last spaceflight of Space ShuttleEndeavour. This flight delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer and an ExPRESS Logistics Carrier to the International Space Station. Mark Kelly served as the mission commander. STS-134 was expected to be the final Space Shuttle mission if STS-135 did not receive funding from Congress. However, in February 2011, NASA stated that STS-135 would fly "regardless" of the funding situation. STS-135, flown by Atlantis, took advantage of the processing for STS-335, the Launch on Need mission that would have been necessary if the STS-134 crew became stranded in orbit.
Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar metals. It is different from fusion welding or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling sheets together under high pressure.

Made In Space, Inc., is an American company specializing in the engineering and manufacturing of three-dimensional printers for use in microgravity. Headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida, Made In Space's 3D printer was the first manufacturing device used in space.
References
- ↑ Patents FR 273917B1,"Method For Laser Marking of s Glass Object", wo 1996032221A1,"Method for laser marking a glass object", EP EP0820363B1,"Method for laser marking a glass object", ES 2146396T3,"Procedure for the Laser Marking of a Glass Object", DE 69607336T2,"Laser Marking Method of a workpiece of glass", and AU 701407B2,"Method for laser marking a glass object".
- ↑ Paul W. Harrison (July 2006), White Paper: "Product Identification in Automated Manufacturing" (PDF), Los Angeles, CA, retrieved 29 January 2015
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ Report: "Marking Tests to Certify Part Identification Marking Processes for use in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)", Roxby, D., Siemens Symbology Research Center, 5000 Bradford Drive NW, Suite A, Huntsville, Alabama 35805, Oct. 11, 2005.
- ↑ MIL-STD 130M DOD Marking Standard, p.24, Table II
- ↑ NASA HDBK-6003 NASA Marking Handbook, Laser Bonding Section 5.1.5, p.15