
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a military order of the Catholic faith, and one of the wealthiest and most popular military orders in Western Christianity. They were founded c. 1119, headquartered on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, and existed for nearly two centuries during the Middle Ages.

The Rule of Saint Benedict is a book of precepts written in Latin c. 530 by St Benedict of Nursia for monks living communally under the authority of an abbot.

Jacques de Molay, also spelled "Molai", was the 23rd and last grand master of the Knights Templar, leading the order sometime before 20 April 1292 until it was dissolved by order of Pope Clement V in 1312. Though little is known of his actual life and deeds except for his last years as Grand Master, he is one of the best known Templars.

Hugues de Payens or Payns was the co-founder and first Grand Master of the Knights Templar. In association with Bernard of Clairvaux, he created the Latin Rule, the code of behavior for the Order.
Omne datum optimum was a papal bull issued by Pope Innocent II on 29 March 1139 that endorsed the Order of the Poor Knights of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, in which the Templar Rule was officially approved, and papal protection given.
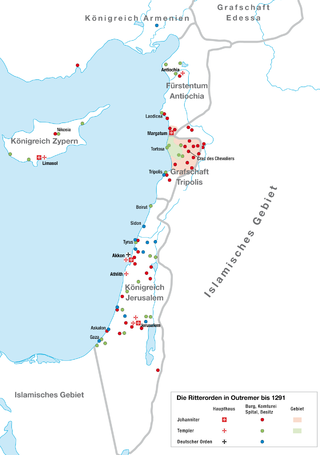
A military order is a Christian religious society of knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades, both in the Holy Land, the Baltics, and the Iberian peninsula; their members being dedicated to the protection of pilgrims and Christians, as well as the defence of the Crusader states. They are the predecessors of chivalric orders.

The Council of Vienne was the fifteenth ecumenical council of the Catholic Church and met between 1311 and 1312 in Vienne, France. One of its principal acts was to withdraw papal support for the Knights Templar at the instigation of Philip IV of France. The Council, unable to decide on a course of action, tabled the discussion. In March 1312 Philip arrived and pressured the Council and Clement to act. Clement passed papal bulls dissolving the Templar Order, confiscating their lands, and labeling them heretics.
Roger de Moulins was the eighth Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller from 1177 until his death in 1187. He succeeded Jobert of Syria. His successors were two interim masters, William Borrel and then Armengol de Aspa, before the permanent Grand Master Garnier of Nablus was selected in 1190.

The Equestrian Order of the Holy Sepulchre of Jerusalem, also called Order of the Holy Sepulchre or Knights of the Holy Sepulchre, is a Catholic order of knighthood under the protection of the Holy See. The Pope is the sovereign of the order. The order creates canons as well as knights, with the primary mission to “support the Christian presence in the Holy Land.” It is an internationally recognised order of chivalry. The order today is estimated to have some 30,000 knights and dames in 60 lieutenancies around the world. The Cardinal Grand Master has been Fernando Filoni since 2019, and the Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem is ex officio the Order's Grand Prior. Its headquarters are situated at the Palazzo Della Rovere and its official church in Sant'Onofrio al Gianicolo, both in Rome, close to Vatican City.

The Military Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz, previously to 1910 Royal Military Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz, previously to 1789 Knightsof Saint Benedict of Aviz or Friars of Santa Maria of Évora, is a Portuguese order of chivalry, founded in Portugal in 1146. It gave its name and coat of arms to the Aviz Dynasty that ruled Portugal between 1385 and 1580.

The Order of Saint Lazarus of Jerusalem, also known as the Leper Brothers of Jerusalem or simply as Lazarists, was a Catholic military order founded by Crusaders around 1119 at a leper hospital in Jerusalem, Kingdom of Jerusalem, whose care became its original purpose, named after its patron saint, Lazarus. It was recognised by King Fulk in 1142 and canonically recognised as a hospitaller and military order of chivalry under the rule of Saint Augustine in the Papal bull Cum a Nobis Petitur of Pope Alexander IV in 1255. Although they were centred on their charism of caring for those afflicted with leprosy, the knights of the Order of Saint Lazarus notably fought in the siege of acre in 1191, arsuf and in 1192 the battle of jaffa. Battle of La Forbie in 1244 and in the Defense of Acre in 1291. The titular seat was successively situated at Jerusalem, then Acre. After the fall of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the order split into two main branches – in Italy and in France.
The Grand Masters of the Knights Templar during the later 12th and the 13th century used a double-sided seal which showed a representation of The Dome of the Rock on one side, and the Order's symbol of two knights on one horse on the other side. This design is first attested as in use by Bertrand de Blanquefort, the order's sixth Grand Master, in 1158, forty years after its foundation, and it remained in use until the dissolution of the order in 1312.
The Regula Magistri or Rule of the Master is an anonymous sixth-century collection of monastic precepts. The text of the Rule of the Master is found in the Concordia Regularum of Benedict of Aniane, who gave it its name.

The Chinon Parchment is a historical document discovered in September 2001 by Barbara Frale, an Italian paleographer at the Vatican Apostolic Archive. On the basis of this document she has claimed that, in 1308, Pope Clement V absolved the last Grand Master, Jacques de Molay, and the rest of the leadership of the Knights Templar from charges brought against them by the Medieval Inquisition.
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and the Temple of Jerusalem, or Templars, was a military order founded in c. 1120.

The Knights Templar, full name The United Religious, Military and Masonic Orders of the Temple and of St John of Jerusalem, Palestine, Rhodes and Malta, is a fraternal order affiliated with Freemasonry. Unlike the initial degrees conferred in a regular Masonic Lodge, which only require a belief in a Supreme Being regardless of religious affiliation, the Knights Templar is one of several additional Masonic Orders in which membership is open only to Freemasons who profess a belief in Christianity. One of the obligations entrants to the order are required to declare is to protect and defend the Christian faith. The word "United" in its full title indicates that more than one historical tradition and more than one actual order are jointly controlled within this system. The individual orders 'united' within this system are principally the Knights of the Temple, the Knights of Malta, the Knights of St Paul, and only within the York Rite, the Knights of the Red Cross.

In 1307, members of the Knights Templar in the Kingdom of France were suddenly charged with heresy and arrested after their leader, Master Jacques de Molay, had recently come to France for meetings with Pope Clement V. Many, including their leader, were burned at the stake while others were sentenced to perpetual imprisonment. The events in France led to a series of trials in other locations, not all of which had the same outcome.

The Larmenius Charter or Carta Transmissionis is a coded Latin manuscript purportedly created by Johannes Marcus Larmenius in February 1324, detailing the transfer of leadership of the Knights Templar to Larmenius after the death of Jacques de Molay. It also has appended to it a list of 22 successive Grand Masters of the Knights Templar after de Molay, ending in 1804, the name of Bernard-Raymond Fabré-Palaprat appearing last on the list. The document is written in a supposed devised ancient Knights Templar Codex. Actually in Freemason custody, the document is kept at the Mark Masons Hall in London. Some researchers have concluded that it is a forgery, while others assert its authenticity.
The Council of Troyes was convened by Bernard of Clairvaux on 13 January 1129 in the city of Troyes. The council, largely attended by French clerics, was assembled to hear a petition by Hugues de Payens, head of the Knights Templar. Pope Honorius II did not attend the council, sending the papal legate, Matthew, cardinal-bishop of Albano. The council addressed issues concerning the Templar Order and a dispute between the bishop of Paris and king of France.

The history of the Knights Hospitaller in the Levant is concerned with the early years of the Order of the Hospital of St. John of Jerusalem, the Knights Hospitaller, through 1309. The Order was formed in the later part of the eleventh century and played a major role in the Kingdom of Jerusalem, in particular, the Crusades. This lasted until the West was expelled from the Holy Land, with the Order conquering Rhodes in the early fourteenth century. Among the most important internal events of the early years of the kingdom were the foundation of the Military Orders, which included the Hospitallers, the Knights Templar and the Teutonic Order. Unlike the Hospitallers' beginnings as a benevolent organization, the Templars and Teutonic knights began with a military mission. These three major Orders would play a major role in the military activities of the kingdom, sometimes cooperatively, sometimes not. On the battlefield they frequently shared among them the most important tactical roles, the vanguard and rear-guard.














