Related Research Articles
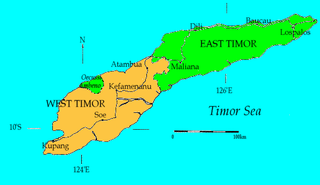
West Timor is an area covering the western part of the island of Timor, except for the district of Oecussi-Ambeno. Administratively, West Timor is part of East Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesia. The capital as well as its main port is Kupang. During the colonial period, the area was named Dutch Timor and was a centre of Dutch loyalists during the Indonesian National Revolution (1945–1949). From 1949 to 1975 it was named Indonesian Timor.

Portuguese Timor was a colonial possession of Portugal that existed between 1702 and 1975. During most of this period, Portugal shared the island of Timor with the Dutch East Indies.

East Timor, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. The country comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor and the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco. The first inhabitants are thought to be descendant of Australoid and Melanesian peoples. The Portuguese began to trade with Timor by the early 16th century and colonised it throughout the mid-century. Skirmishing with the Dutch in the region eventually resulted in an 1859 treaty for which Portugal ceded the western half of the island. Imperial Japan occupied East Timor during World War II, but Portugal resumed colonial authority after the Japanese surrender.

The political system in East Timor is a unitary semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of East Timor is the head of government and the President of East Timor functions as head of state. East Timor has a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the president and the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Parliament. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The East Timorese constitution was modelled on that of Portugal, with lesser power given to the president. The country is still in the process of building its administration and governmental institutions. The Economist Intelligence Unit rated East Timor a "flawed democracy" in 2022.
The culture of Timor-Leste reflects numerous cultural influences, including Portuguese, Roman Catholic, and Malay, on the indigenous Austronesian cultures in Timor-Leste.

The national flag of Timor-Leste consists of a red field with the black isosceles triangle based on the hoist-side bearing a white five-pointed star in the center superimposed on the larger yellow triangle, also based on the hoist-side, that extends to the center of the flag.

The languages of Timor-Leste include both Austronesian and Papuan languages. The lingua franca and national language of Timor-Leste is Tetum, an Austronesian language influenced by Portuguese, with which it has equal status as an official language. The language of the Oecusse exclave is Uab Meto (Dawan). Fataluku is a Papuan language widely used in the eastern part of the country. A dialect of Malay-based creole called Dili Malay is spoken by a number of residents in the capital Dili, it borrowed words mostly from Portuguese and Tetum. Both Portuguese and Tetum have official recognition under the Constitution of Timor-Leste, as do other indigenous languages, including: Bekais, Bunak, Galoli, Habun, Idalaka, Kawaimina, Kemak, Lovaia, Makalero, Makasae, Mambai, Tokodede and Wetarese.

Francisco Xavier do Amaral was an East Timorese politician. A founder of the Frente Revolucionária de Timor Leste Independente (Fretilin), Amaral was sworn in as the first President of East Timor when the country, then a Portuguese colony, made a unilateral declaration of independence on 28 November 1975. He was a member of the National Parliament for the Timorese Social Democratic Association from 2001 until his death in 2012. Amaral was also known as "Abo (Grandfather) Xavier", a term of endearment, by East Timorese.

The Timor Gap Treaty was formally known as the Treaty between Australia and the Republic of Indonesia on the zone of cooperation in an area between the Indonesian province of East Timor and Northern Australia. It was a bilateral treaty between the governments of Australia and Indonesia, which provided for the joint exploitation of petroleum and hydrocarbon resources in a part of the Timor Sea Seabed. The treaty was signed on 11 December 1989 and came into force on 9 February 1991. The signatories to the treaty were then Australian Foreign Affairs Minister Gareth Evans and then Indonesian Foreign Minister Ali Alatas.

The Indonesian invasion of East Timor, known in Indonesia as Operation Lotus, began on 7 December 1975 when the Indonesian military (ABRI/TNI) invaded East Timor under the pretext of anti-colonialism and anti-communism to overthrow the Fretilin regime that had emerged in 1974. The overthrow of the popular and short-lived Fretilin-led government sparked a violent quarter-century occupation in which approximately 100,000–180,000 soldiers and civilians are estimated to have been killed or starved to death. The Commission for Reception, Truth and Reconciliation in East Timor documented a minimum estimate of 102,000 conflict-related deaths in East Timor throughout the entire period from 1974 to 1999, including 18,600 violent killings and 84,200 deaths from disease and starvation; Indonesian forces and their auxiliaries combined were responsible for 70% of the killings.

An independence referendum was held in East Timor on 30 August 1999, organised by United Nations Mission in East Timor. The referendum's origins lay with the request made by the President of Indonesia, B. J. Habibie, to the United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan on 27 January 1999, for the United Nations to hold a referendum, whereby East Timor would be given choice of either greater autonomy within Indonesia or independence.

The Indonesian occupation of East Timor began in December 1975 and lasted until October 1999. After centuries of Portuguese colonial rule in East Timor, the 1974 Carnation Revolution in Portugal led to the decolonisation of its former colonies, creating instability in East Timor and leaving its future uncertain. After a small-scale civil war, the pro-independence Fretilin declared victory in the capital city of Dili and declared an independent East Timor on 28 November 1975.

The National Council of Maubere Resistance was an umbrella organisation of East Timorese individuals and organisations dedicated to resisting the Indonesian occupation of 1975–1999.

Timor-Leste, also known as East Timor, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-western half, and the minor islands of Atauro and Jaco. The western half of the island of Timor is administered by Indonesia. Australia is the country's southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea. The country's size is 14,950 square kilometres (5,770 sq mi). Dili, on the north coast of Timor, is its capital and largest city.

East Timor and Indonesia established diplomatic relations in 2002. Both share the island of Timor. Indonesia invaded the former Portuguese colony in 1975 and annexed East Timor in 1976, maintaining East Timor as its 27th province until a United Nations-sponsored referendum in 1999, in which the people of East Timor chose independence. Following a United Nations interim administration, East Timor gained independence in 2002. Indonesia already had a consulate in Dili during the Portuguese colonial period, though Indonesia formalized their relations by establishing an embassy in Dili. Since October 2002, East Timor has an embassy in Jakarta and consulates in Denpasar and Kupang. Relations between the two countries are generally considered highly positive, despite various problems. Numerous agreements regulate cooperation in different areas. East Timorese are visa-free in Indonesia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1272 was adopted unanimously on 25 October 1999, after recalling previous resolutions on East Timor, particularly resolutions 384 (1975), 389 (1976), 1236 (1999), 1246 (1999), 1262 (1999) and 1264 (1999). The council established the United Nations Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET) that was responsible for the administration of the territory until its independence in 2002.

The Moral Economy of the Peasant: Rebellion and Subsistence in Southeast Asia is a 1976 book by James C. Scott on the nature of subsistence ethics in peasant cultures. He asserted that the highest priority for most peasants is ensuring that their incomes will not fall below minimal subsistence level. They desire higher income levels, and will pursue them aggressively under some circumstances, but if their only path toward higher incomes is a gamble that might drop them below subsistence level if it did not work out, they will almost always reject that gamble.
East Timorese nationality law is regulated by the 2002 Constitution, the Nationality Act of the same year, the regulation of the Nationality Act Decree-Law No. 1 of 2004, as well as various international agreements to which East Timor has been a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of East Timor. The legal means to acquire nationality and formal membership in a nation differ from the relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. East Timorese nationality is typically obtained either on the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in East Timor; or under the rules of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth abroad to at least one parent with East Timorese nationality. It can also be granted to a permanent resident who has lived in East Timor for a given period of time through naturalization.

United Nations Administered East Timor refers to the period between 25 October 1999 and 20 May 2002 when East Timor was administered by the United Nations Transitional Administration in East Timor as a United Nations protectorate.
References
- ↑ Almeida, Bernardo (2017). "The Main Characteristics of the Timorese Legal System – a Practical Guide". Verfassung und Recht in Übersee / Law and Politics in Africa, Asia and Latin America. 50 (2): 175–187. doi:10.5771/0506-7286-2017-2-175. hdl: 1887/70068 . ISSN 0506-7286. JSTOR 26429316. S2CID 145045925.
- ↑ SIMÕES, FERNANDO DIAS (2015). "Law and Language in Timor-Leste: Bridging the Divide". Contemporary Southeast Asia. 37 (3): 381–405. doi:10.1355/cs37-3c. ISSN 0129-797X. JSTOR 24916610.