Related Research Articles

U.S. Route 160 (US 160) is a 1,465 mile (2,358 km) long east–west United States highway in the Midwestern and Western United States. The western terminus of the route is at US 89 five miles (8 km) west of Tuba City, Arizona. The eastern terminus is at US 67 and Missouri 158 southwest of Poplar Bluff, Missouri. Its route, if not its number, was made famous in song in 1975, as the road from Wolf Creek Pass to Pagosa Springs, Colorado in C.W. McCall's country music song Wolf Creek Pass.

William Scoresby, was an English whaler, Arctic explorer, scientist and clergyman.

Operation Tabarin was the code name for a secret British expedition to the Antarctic during World War Two, operational 1943–46. Conducted by the Admiralty on behalf of the Colonial Office, its primary objective was to strengthen British claims to sovereignty of the British territory of the Falkland Islands Dependencies (FID), to which Argentina and Chile had made counter claims since the outbreak of war. This was done by establishing permanently occupied bases, carrying out administrative activities such as postal services and undertaking scientific research. The meteorological observations made aided Allied shipping in the South Atlantic Ocean.
The Mawson Coast is that portion of the coast of Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica, lying between William Scoresby Bay, at 59°34′E, and Murray Monolith, at 66°54′E. The coast was sighted during the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE), 1929–30, under Sir Douglas Mawson. Further exploration and landings at Cape Bruce and Scullin Monolith were made during BANZARE, 1930–31. Mawson Coast was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia after Mawson in recognition of his great contribution to Antarctic exploration.
Kemp Coast is that portion of the coast of Antarctica that lies between the head of Edward VIII Bay, at 56°25′E, and William Scoresby Bay, at 59°34′E. It is named for a British sealing captain, Peter Kemp, who discovered land in this vicinity in 1833.
The Edward VIII Plateau is a dome-shaped, ice-covered peninsula between Magnet Bay and Edward VIII Bay in Antarctica. It was probably seen by personnel on the RSS William Scoresby in 1936, and mapped from aerial photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936-37, and named Gulfplataet. It was renamed "King Edward Plateau" by ANCA, but the form Edward VIII Plateau has been approved by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) to be consistent with the names of nearby Edward VIII Bay and Ice Shelf.
Stefansson Bay is a bay indenting the coast for 16 kilometres (10 mi) between Law Promontory and Fold Island. Mawson of the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) applied the name to a sweep of the coast west of Cape Wilkins which he observed on about February 18, 1931. Exploration by DI personnel on the William Scoresby, 1936, and the Lars Christensen expedition 1936–37, defined this section of the coast more accurately. It was named for Vilhjalmur Stefansson, Arctic explorer.
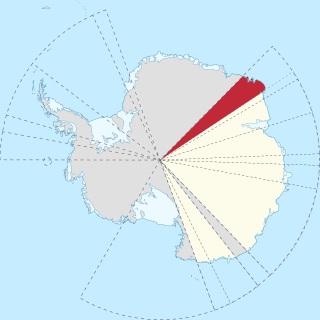
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
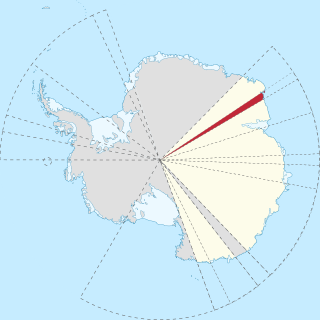
Kemp Land is a thin sliver of Antarctica including, and lying inland from, the Kemp Coast. Part of the Australian Antarctic claim it is defined as lying between 56° 25' E and 59° 34' E, and, as with other sectors of the Antarctic, is deemed being limited by the 60° S parallel. It is bounded in the east by Mac. Robertson Land and in the west by Enderby Land. Kemp Land includes one major group of islands, the Øygarden Group.
Ives Tongue is a narrow tongue of land projecting from an island between Fold Island and the coast of Kemp Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and named in February 1936 by a Discovery Investigations expedition on the RRS William Scoresby.
William Scoresby Bay is a coastal embayment at the western side of William Scoresby Archipelago, Antarctica. It is 8 kilometres (5 mi) long and 5.6 kilometres (3.5 mi) wide, with shores marked by steep rock headlands and snow-free hills rising to 210 m. The practical limits of the bay are extended 6.4 kilometres (4 mi) northward, from the coast by island groups located along its east and west margin. Discovered in February 1936 by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel on the RSS William Scoresby, for which the bay was named. The bay separates the Kemp Coast to the east from the Mawson Coast to the west. The Hobbs Islands sit 19 kilometres northeast.
Stillwell Hills is a group of largely snow-free rocky hills composed of banded gneisses and including Kemp Peak and Lealand Bluff, extending along the southwest side of William Scoresby Bay. This area was explored by Discovery Investigations personnel on the RSS William Scoresby in February 1936, and by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37, the latter group taking air photos used to map these hills for the first time. Geologic investigation of the area was made by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) in 1961. Named by ANCA for Dr. Frank Leslie Stillwell, geologist with Australasian Antarctic Expedition (AAE), 1911–14, who derived a theory of metamorphic differentiation from banded gneisses of the same type on George V Coast.
William Scoresby Archipelago is a group of islands which extends northward from the coast just east of William Scoresby Bay, Antarctica. The more important islands in the group are Bertha, Islay, Couling, and the Sheehan Islands. Most of the islands and features in this archipelago were discovered in February 1936 by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel on the RSS William Scoresby. They named the group after their ship.
Beacon Valley is an ice-free valley between Pyramid Mountain and Beacon Heights, in Victoria Land. It was mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, and named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) after Beacon Heights.
Blackrock Head is a conspicuous coastal rock outcrop on the eastern part of Law Promontory, 3 nautical miles (6 km) northwest of Tryne Point in Antarctica. It was discovered in February 1936 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the William Scoresby and so named by them for its black, rocky appearance.

Borradaile Island is one of the Balleny Islands. It was the site of the first landing south of the Antarctic Circle, and features the "remarkable pinnacle" called Beale Pinnacle, near Cape Beale on its south-eastern coast, and Cape Scoresby on its north-western coast.
Warnock Islands is a group of small offshore islands lying 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) south and southwest of Dales Island at the north end of William Scoresby Archipelago. Discovered and named in February 1936 by DI personnel on the William Scoresby.
Tillett Booby Islands is a group of small, somewhat dispersed islands, the largest rising 70 m above the sea, lying 5 nautical miles (9 km) northeast of Cape Wilkins. Discovered and named in February 1936 by DI personnel on the William Scoresby.
Tilley Nunatak is a bold, rocky outcrop 5 nautical miles (9 km) south of Hobbs Islands, projecting from the coastal ice cliffs eastward of William Scoresby Bay. Discovered in February 1936 by DI personnel on the William Scoresby and named by them for Professor C.E. Tilley, who studied the rock specimens brought back by the expedition.
References
- ↑ "Lealand Bluff". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey . Retrieved 2010-08-06.
Coordinates: 67°27′S59°33′E / 67.450°S 59.550°E