
Pseudevernia is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. The type species of the genus, Pseudevernia furfuracea, has substantial commercial value in the perfume industry.

Punctelia is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. The genus, which contains about 50 species, was segregated from genus Parmelia in 1982. Characteristics that define Punctelia include the presence of hook-like to thread-like conidia, simple rhizines, and point-like pseudocyphellae. It is this last feature that is alluded to in the vernacular names speckled shield lichens or speckleback lichens.

Punctelia rudecta, commonly known as the rough speckled shield or the speckleback lichen, is a North American species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. This species can be readily identified by the light color of the thallus underside, the relatively large lobes at the edges of the thallus, and the tiny white pores present on the top of the thallus that are characteristic of the genus Punctelia. The lichen is quite abundant and widespread in the eastern and southeastern United States, although it also occurs in Canada and northern Mexico, but is less common in these regions. The lichen usually grows on bark, and less commonly on shaded rocks. There are several lookalike Punctelia species; these can often be distinguished from P. rudecta by differences in distribution or in the nature of the reproductive structures present on the thallus.
Punctelia roseola is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in Brazil, it was described as a new species in 2009 by lichenologists Patrícia Jungbluth, Marcello Marcelli, and John Alan Elix. The specific epithet refers to the pale rose colour of the medulla. The holotype was collected from Jurumirim municipality in São Paulo State, close to the Tietê River. There it was found growing on an isolated tree in a dry pasture, without direct sunlight. It has a grey thallus measuring 10–20 cm (4–8 in) wide; the lower thallus surface is pale, becoming darker near the centre. The lichen contains atranorin, lecanoric acid, and several butlerins as minor compounds, butlerlin D as a somewhat major compound, and gyrophoric acid as the major secondary metabolite in the medulla.
Punctelia subalbicans is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is found in Australia and New Zealand, where it grows on the bark of various tree species.
Punctelia tomentosula is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in Peru, it was described as a new species in 1999 by Japanese lichenologist Syo Kurokawa.

Atranorin is a chemical substance produced by some species of lichen. It is a secondary metabolite belonging to a group of compounds known as depsides. Atranorin has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, cytotoxic, antioxidant, antiviral, and immunomodulatory properties. In rare cases, people can react allergic to atranorin.

Constipatic acid is a fatty acid found in several lichen species. It was isolated, identified, and named by Douglas Chester and John Alan Elix in a 1979 publication. The compound was extracted from the Australian leafy lichen called Xanthoparmelia constipata, which was collected on schist boulders west of Springton, South Australia. The related compounds protoconstipatic acid and dehydroconstipatic acid were also reported concurrently. Syo Kurokawa and Rex Filson had previously detected the compounds using thin-layer chromatography when they formally described the lichen as a new species in 1975, but had not characterised them chemically.

Punctelia punctilla is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is found in Africa, South America, and North America, where it grows on bark and on rocks. The main characteristics that distinguish Punctelia punctilla from other species of Punctelia are the presence of isidia on the thallus surface, a pale brown thallus undersurface, and the presence of lecanoric acid in the medulla.

Punctelia hypoleucites, commonly known as the southwestern speckled shield lichen, is a species of foliose (leafy) lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. First formally described by Finnish botanist William Nylander as a species of Parmelia, it was transferred to the genus Punctelia in 1982. The lichen is found in Africa, North America, and South America, where it grows on the bark of both hardwood and coniferous trees. Its greenish-grey thallus is covered with tiny white pseudocyphellae – minute holes in the thallus surface that facilitate gas exchange. Some macroscopic features that help distinguish this species from other related members of the genus include the presence and the structure of the apothecia, the absence of asexual surface propagules, and the light brown color of the thallus undersurface. Chemically, the presence of lecanoric acid in the medulla and atranorin in the cortex help distinguish it from lookalikes.

Punctelia perreticulata is a widely distributed species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It occurs in Mediterranean Europe and Russia, North America, South America, Australia, and New Zealand, where it grows on rocks, bark, or wood. Its main distinguishing features are its thallus surface, marked with many shallow depressions, grooves, or pits, and sorediate pseudocyphellae. The lower side of the thallus is ivory to tan towards the centre and the major secondary metabolite in the medulla is lecanoric acid. A lookalike species with which it has been historically confused is Punctelia subrudecta; this lichen can be distinguished from Punctelia perreticulata by the texture of the thallus surface, or, more reliably, by the length of its conidia.
Punctelia diffractaica is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is found in Peru.
Punctelia subflava is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae that occurs in Australia.

Punctelia borreri is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is a common and widely distributed species, occurring in tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions of Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, Oceania, and South America. The lichen typically grows on bark of deciduous trees, and less commonly on rock. Some European countries have reported increases in the geographic range or regional frequency of the lichen in recent decades, attributed alternatively to a reduction of atmospheric sulphur dioxide levels or an increase in temperatures resulting from climate change.

Salazinic acid is a depsidone with a lactone ring. It is found in some lichens, and is especially prevalent in Parmotrema and Bulbothrix, where its presence or absence is often used to help classify species in those genera.
Parmotrema hypoleucinum is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. A study of Parmotrema hypoleucinum in Tunisia revealed that it contains atranorin and (+)-iso-usnic acid, chemical compounds of interest for their anti-inflammatory activity. The species was originally scientifically described by Austrian lichenologist Julius Steiner in 1918 as a member of genus Parmelia. Mason Hale transferred it to Parmotrema in 1974.
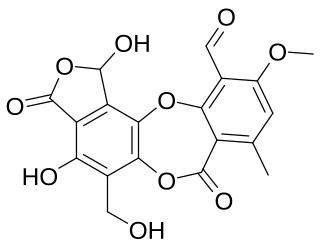
Constictic acid is a chemical compound of the depsidone class. It was first isolated in 1968 from lichen of the genus Usnea. It has since been found in many other lichen genera including Menegazzia, Crespoa, and Xanthoparmelia.

Xanthoparmelia joranadia is a lichen which belongs to the Xanthoparmelia genus. The lichen is rare and is listed as imperiled by the Nature Conservatory. It is noted for being similar to Xanthoparmelia arida and Xanthoparmelia lecanorica.
Xanthoparmelia arida is a lichen which belongs to the Xanthoparmelia genus. The lichen is an arid shield lichen and is uncommon it is listed as apparently secure by the Nature Conservatory. It is noted for being similar to Xanthoparmelia joranadia.
Xanthoparmelia lecanorica is a lichen which belongs to the Xanthoparmelia genus. It is noted for being similar in appearance and has often been misidentified as Xanthoparmelia arida.











