Related Research Articles

A single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a camera that typically uses a mirror and prism system that permits the photographer to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. With twin lens reflex and rangefinder cameras, the viewed image could be significantly different from the final image. When the shutter button is pressed on most SLRs, the mirror flips out of the light path, allowing light to pass through to the light receptor and the image to be captured.

The Four Thirds System is a standard created by Olympus and Eastman Kodak for digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) design and development. Four Thirds refers to both the size of the image sensor (4/3") as well as the aspect ratio (4:3). The Olympus E-1 was the first Four Thirds DSLR, announced and released in 2003. In 2008, Olympus and Panasonic began publicizing the Micro Four Thirds system, a mirrorless camera system which used the same sensor size; by eliminating the reflex mirror, the Micro Four Thirds cameras were significantly smaller than the Four Thirds cameras. The first Micro Four Thirds cameras were released in 2009 and the final Four Thirds cameras were released in 2010; by that time, approximately 15 Four Thirds camera models had been released by Olympus and Panasonic in total. The Four Thirds system was quietly discontinued in 2017, six years after the final cameras were released.

Macro photography is extreme close-up photography, usually of very small subjects and living organisms like insects, in which the size of the subject in the photograph is greater than life-size . By the original definition, a macro photograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative or image sensor is life-size or greater. In some senses, however, it refers to a finished photograph of a subject that is greater than life-size.

A digital single-lens reflex camera is a digital camera that combines the optics and mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a solid-state image sensor and digitally records the images from the sensor.

Advanced Photo System type-C (APS-C) is an image sensor format approximately equivalent in size to the Advanced Photo System film negative in its C ("Classic") format, of 25.1×16.7 mm, an aspect ratio of 3:2 and Ø 30.15 mm field diameter. It is therefore also equivalent in size to the Super 35 motion picture film format, which has the dimensions of 24.89 mm × 18.66 mm and Ø 31.11 mm field diameter.
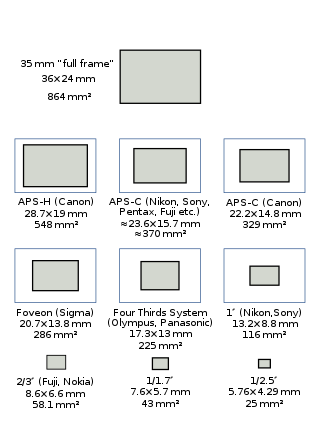
A full-frame DSLR is a digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) with a 35 mm image sensor format. Historically, 35 mm was one of the standard film formats, alongside larger ones, such as medium format and large format. The full-frame DSLR is in contrast to full-frame mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras, and DSLR and mirrorless cameras with smaller sensors, much smaller than a full 35 mm frame. Many digital cameras, both compact and SLR models, use a smaller-than-35 mm frame as it is easier and cheaper to manufacture imaging sensors at a smaller size. Historically, the earliest digital SLR models, such as the Nikon NASA F4 or Kodak DCS 100, also used a smaller sensor.

Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure.

Tilt–shift photography is the use of camera movements that change the orientation or position of the lens with respect to the film or image sensor on cameras.

In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor.

The Micro Four Thirds system is a standard released by Olympus Imaging Corporation and Panasonic in 2008, for the design and development of mirrorless interchangeable lens digital cameras, camcorders and lenses. Camera bodies are available from Blackmagic, DJI, JVC, Kodak, Olympus, OM System, Panasonic, Sharp, Logitech Mevo and Xiaomi. MFT lenses are produced by Cosina Voigtländer, Kowa, Kodak, Mitakon, Olympus, Panasonic, Samyang, Sharp, Sigma, SLR Magic, Tamron, Tokina, TTArtisan, Veydra, Xiaomi, Laowa, Yongnuo, Zonlai, Lensbaby, Venus Optics and 7artisans amongst others.

A mirrorless camera is a digital camera which, in contrast to DSLRs, does not use a mirror in order to ensure that the image presented to the photographer through the viewfinder is identical to that taken by the camera. They have come to replace DSLRs, which have historically dominated interchangeable lens cameras. Other terms include electronic viewfinder interchangeable lens (EVIL) and compact system camera (CSC).

The E-mount is a lens mount designed by Sony for their NEX and ILCE series of camcorders and mirrorless cameras. The E-mount supplements Sony's α mount, allowing the company to develop more compact imaging devices while maintaining compatibility with 35mm sensors. E-mount achieves this by:

The Fujifilm X series is a line of digital cameras produced by Fujifilm. The series encompasses fixed lens and interchangeable lens mirrorless cameras and premium compact point-and-shoot cameras aimed at consumer, enthusiast and professional photographers. The X series is part of the larger FinePix range of digital cameras from Fujifilm.

The Fujifilm X-Pro1 is a mirrorless interchangeable-lens digital camera announced in January 2012 and launched in March 2012. It is part of Fujifilm's X-Series of cameras. In October 2012 Fujifilm released a very similar, yet smaller, camera named the X-E1. In January 2016 Fujifilm announced its successor, the X-Pro2.

The Fujifilm FinePix HS is a series of bridge cameras that started in February 2010 with the HS10 model. The special feature of the HS cameras is the manual zoom that - otherwise common only with system cameras - allows a quick and precise change of the focal length but demands two-handed operation.

The Fujifilm X100 is a series of digital compact cameras with a fixed prime lens. Originally part of the FinePix line, then becoming a member of the X series from Fujifilm, the X100 series includes the FinePix X100, X100S, X100T, X100F, X100V, and X100VI. They each have a large image sensor and a 23 mm lens. All six cameras have received generally positive reviews.

The Fujifilm X-T3 is a mirrorless interchangeable-lens digital camera announced on September 6, 2018. It is weather-resistant, has a backside-illuminated X-Trans CMOS 4 APS-C sensor and an X-Processor 4 quad core processor. It is the successor to 2016's Fujifilm X-T2. It uses the Fujifilm X-mount.

The Leica Q2 is a full-frame fixed-lens camera introduced in 2019. It was succeeded by the Leica Q3 in 2023.
The Leica S-System is a medium format digital single lens reflex camera system introduced by Leica Camera in 1996. Beginning with the Leica S1, a prototype top-end studio digital camera unveiled at Photokina 1996. It went into production at the end of 1997.

The Leica Q3 is a full-frame fixed-lens camera introduced in 2023 as the successor to the Leica Q2.
References
- ↑ "Technical Specs - Leica Q3". Archived from the original on 2024-01-12. Retrieved 2024-01-14.
- ↑ "Leica Q3 43 review". Digital Photography Review. Retrieved 2025-01-11.
- 1 2 "Leica Q3 43".
- ↑ "Leica Q3 43 APO Review". Thorsten Overgaard Photography. Retrieved 2025-01-11.
- ↑ "Leica Q3 announced: 60MP BSI CMOS sensor and Tilting Screen". Archived from the original on 2024-01-14. Retrieved 2024-01-14.
- ↑ "What's the Best Compact Camera? We Reviewed Them and Compared". The Phoblographer. Archived from the original on 2024-01-14. Retrieved 2024-01-14.
