
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods.

The family Argulidae, whose members are commonly known as carp lice or fish lice, are parasitic crustaceans in the class Ichthyostraca. It is the only family in the monotypic subclass Branchiura and the order Arguloida, although a second family, Dipteropeltidae, has been proposed. Although they are thought to be primitive forms, they have no fossil record.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.

The salmon louse is a species of copepod in the genus Lepeophtheirus. It is a sea louse, a parasite living mostly on salmon, particularly on Pacific and Atlantic salmon and sea trout, but is also sometimes found on the three-spined stickleback. It feeds on the mucus, skin and blood of the fish. Once detached, they can be blown by wind across the surface of the sea, like plankton. When they encounter a suitable marine fish host, they adhere themselves to the skin, fins, or gills of the fish, and feed on the mucus or skin. Sea lice only affect fish and are not harmful to humans.

Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.

Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form. Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow. The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will grow into what adults. This is especially true of crustaceans which live as benthic adults, more-so than where the larvae are planktonic, and thereby easily caught.

Pennellidae is a family of parasitic copepods. When anchored on a host, they have a portion of the body on the outside of the host, whereas the remaining anterior part of the parasite is hidden inside tissues of the host.

Lernaeocera branchialis, sometimes called cod worm, is a parasite of marine fish, found mainly in the North Atlantic. It is a marine copepod which starts life as a small pelagic crustacean larva. It is among the largest of copepods, ranging in size from 2 to 3 millimetres when it matures as a copepodid larva to more than 40 mm as a sessile adult.

Lernaeopodidae is a family of parasitic copepods. The females are typically large and fleshy, and attach to the host permanently using a plug made of chitin called the bulla. The males cling on to the females using their antennae. They parasitize both marine and freshwater fish. Some lernaeopodids, including Clavella and Salmincola, can have negative impacts on fish in aquaculture.
Pennella is a genus of large copepods which are common parasites of large pelagic fishes. They begin their life cycle as a series of free-swimming planktonic larvae. The females metamorphose into a parasitic stage when they attach to a host and enter into its skin. The males are free swimming. Due to their large size and mesoparasitic life history there have been a number of studies of Pennella, the members of which are among the largest of the parasitic Copepoda. All species are found as adults buried into the flesh of marine bony fish, except for a single species, Pennella balaenopterae which can be found in the muscles and blubber of cetaceans and occasionally other marine mammals, and is the largest species of copepod.
Pennella balaenopterae is a large ectoparasitic copepod specialising in parasitising marine mammals. It is the largest member of the genus Pennella, the other species of which are parasites of larger marine fish.

Lepeophtheirus is a genus of sea louse. The best-known species is L. salmonis, the salmon louse. Other species include L. pectoralis, which uses flatfish as its host, particularly the European flounder, and is also the type species of the genus Lepeophtheirus.

Myoxocephalus brandtii, the snowy sculpin, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This species is found in the northwest Pacific, with a range extending from the Sea of Okhotsk to Hokkaido and the Sea of Japan.

Lepeophtheirus pectoralis is a species of parasitic copepod from the northeast Atlantic Ocean, and the type species of the genus Lepeophtheirus. It is a parasite of flatfish, with the European flounder, the plaice, and the dab as the most frequent hosts. It feeds on the mucus, skin, and blood of the fish, with egg-producing females infecting the pectoral and pelvic fins of the host, while immature individuals and males are found on the rest of the body.

Sebastes schlegelii, also known as the Korean rockfish, Northern black seaperch, and Black rockfish, is a predatory species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae It is found in the Northwest Pacific Ocean.
Peniculisa is a genus of marine parasitic copepods in the family Pennellidae.

Peniculus is a genus of marine copepods in the family Pennellidae. They occur worldwide and typically parasitize coastal or epipelagic fish, with the exception of Peniculus hokutoae that was found parasitizing a mesopelagic myctophid, Symbolophorus evermanni.
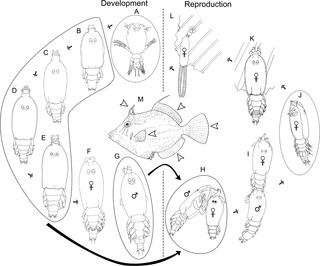
Peniculus minuticaudae is a species of parasitic pennellid copepod. It is known from the northeast Pacific Ocean. It was originally described in 1956, redescribed in 2012, and its complete life cycle has been elucidated on the cultured threadsail filefish, Stephanolepis cirrhifer in 2013.

Peniculus hokutoae is a species of parasitic pennellid copepod. It was described in 2018 from a single female. The type-host is the myctophid fish Symbolophorus evermanni and the type-locality is off Japan. The Japanese name of this species is hokuto-kozutsu-hijikimushi.
















