| Leucopsacidae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Porifera |
| Class: | Hexactinellida |
| Order: | Lyssacinosida |
| Family: | Leucopsacidae Ijima, 1903 [1] |
| Genera | |
Leucopsacidae is a family of glass sponges belonging to the order Lyssacinosa.
| Leucopsacidae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Porifera |
| Class: | Hexactinellida |
| Order: | Lyssacinosida |
| Family: | Leucopsacidae Ijima, 1903 [1] |
| Genera | |
Leucopsacidae is a family of glass sponges belonging to the order Lyssacinosa.

The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael, is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001.
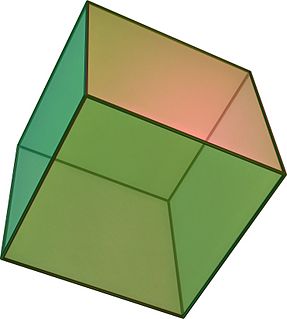
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex.

In economics, the Gini coefficient, sometimes called the Gini index or Gini ratio, is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to represent the income inequality or wealth inequality within a nation or any other group of people. It was developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper Variability and Mutability.

Poseidon was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses. In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a chief deity at Pylos and Thebes.. He had also the cult title "earth shaker". In the myths of isolated Arcadia he is related with Demeter and Persephone and he was venerated as a horse, however it seems that he was originally a god of the waters. He is often regarded as the tamer or father of horses, and with a strike of his trident, he created springs which are related with the word horse. His Roman equivalent is Neptune.

In mathematics, especially order theory, a partially ordered set formalizes and generalizes the intuitive concept of an ordering, sequencing, or arrangement of the elements of a set. A poset consists of a set together with a binary relation indicating that, for certain pairs of elements in the set, one of the elements precedes the other in the ordering. The relation itself is called a "partial order." The word partial in the names "partial order" and "partially ordered set" is used as an indication that not every pair of elements needs to be comparable. That is, there may be pairs of elements for which neither element precedes the other in the poset. Partial orders thus generalize total orders, in which every pair is comparable.
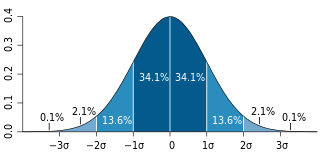
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range.
Semantics is the study of meaning. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines including linguistics, philosophy, and computer science.

U or u is the 21st and sixth-to-last letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet and the fifth vowel letter of the modern English alphabet. Its name in English is u, plural ues.

Kin selection is the evolutionary strategy that favours the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction. Kin altruism can look like altruistic behaviour whose evolution is driven by kin selection. Kin selection is an instance of inclusive fitness, which combines the number of offspring produced with the number an individual can ensure the production of by supporting others, such as siblings.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.

Haplorhini is a suborder of primates containing the tarsiers and the simians, as sister of the Strepsirrhini ("moist-nosed"). The name is sometimes spelled Haplorrhini. The simians include catarrhines, and the platyrrhines.

Sphaerites is a genus of beetles, the only genus in the family Sphaeritidae, sometimes called the false clown beetles. It is closely related to the clown beetles but with distinct characteristics. There are five known species, widespread in temperate area but not commonly seen.

In psychological trait theory, the Big Five personality traits, also known as the five-factor model (FFM) and the OCEAN model, is a suggested taxonomy, or grouping, for personality traits, developed from the 1980s onwards. When factor analysis is applied to personality survey data, it reveals semantic associations: some words used to describe aspects of personality are often applied to the same person. For example, someone described as conscientious is more likely to be described as "always prepared" rather than "messy". These associations suggest five broad dimensions used in common language to describe the human personality and psyche.
Commonly "cousin" refers to a "first cousin", a relative whose most recent common ancestor with the subject is a grandparent. More generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor.

The Future Purana is one of the eighteen major works in the Purana genre of Hinduism, written in Sanskrit. The title Bhavishya means "future" and implies it is a work that contains prophecies regarding the future, however, the "prophecy" parts of the extant manuscripts are a modern era addition and hence not an integral part of the Bhavishya Purana. Those sections of the surviving manuscripts that are dated to be older, are partly borrowed from other Indian texts such as Brihat Samhita and Shamba Purana. The veracity and authenticity of much of the Bhavishya Purana has been questioned by modern scholars and historians, and the text is considered an example of "constant revisions and living nature" of Puranic genre of Hindu literature.

A film series or movie series is a collection of related films in succession that share the same fictional universe, or are marketed as a series.

Isopogon is a genus of 35 species of mainly low-growing and prostrate perennial shrubs in the family Proteaceae endemic to Australia. They are found throughout Australia, though Western Australia has the greatest variety with 27 of the 35 species found there. They are popularly known as drumsticks due to the shape of their inflorescences.
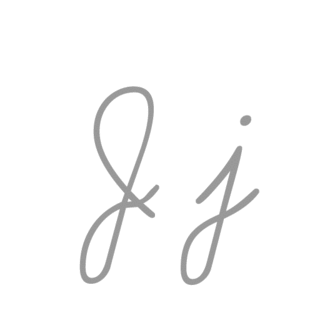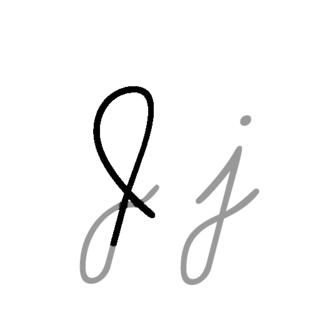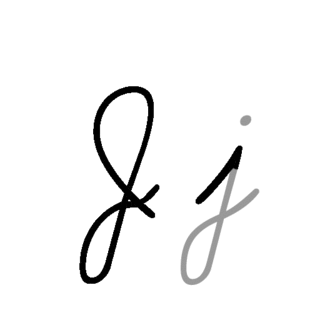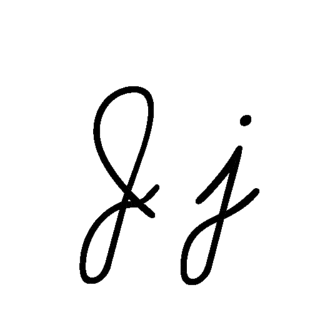
J or j is the tenth letter in the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its usual name in English is jay, with a now-uncommon variant jy. When used in the International Phonetic Alphabet for the y sound, it may be called yod.
I or i is the ninth letter and the third vowel letter of the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is i, plural ies.
A billion is a number with two distinct definitions:
| This poriferan- (or sponge-) related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |