Overtime is the amount of time someone works beyond normal working hours. The term is also used for the pay received for this time. Normal hours may be determined in several ways:
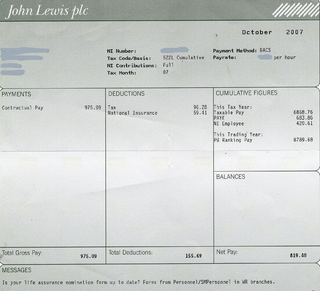
A payroll is a list of employees of a company who are entitled to receive compensation as well as other work benefits, as well as the amounts that each should obtain. Along with the amounts that each employee should receive for time worked or tasks performed, payroll can also refer to a company's records of payments that were previously made to employees, including salaries and wages, bonuses, and withheld taxes, or the company's department that deals with compensation. A company may handle all aspects of the payroll process in-house or can outsource aspects to a payroll processing company.
The 35-hour workweek is a labour reform policy adopted in France in February 2000, under Prime Minister Lionel Jospin's Plural Left government. Promoted by Minister of Labour Martine Aubry, it was adopted in two phases: the Aubry 1 law in June 1998 and the Aubry 2 law in January 2000. The previous legal working week was 39 hours, established by President François Mitterrand, also a member of the Socialist Party. The 35-hour working week had been on the Socialist Party's 1981 electoral program, titled 110 Propositions for France, but was not pursued because of the poor state of the economy.

Working (laboring) time is the period of time that a person spends at paid labor. Unpaid labor such as personal housework or caring for children or pets is not considered part of the working week.

The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is a United States federal payroll tax payable by both employees and employers to fund Social Security and Medicare—federal programs that provide benefits for retirees, people with disabilities, and children of deceased workers.

The Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993 (FMLA) is a United States labor law requiring covered employers to provide employees with job-protected, unpaid leave for qualified medical and family reasons. The FMLA was a major part of President Bill Clinton's first-term domestic agenda, and he signed it into law on February 5, 1993. The FMLA is administered by the Wage and Hour Division of the United States Department of Labor.
Garnishment is a legal process for collecting a monetary judgment on behalf of a plaintiff from a defendant. Garnishment allows the plaintiff to take the money or property of the debtor from the person or institution that holds that property. A similar legal mechanism called execution allows the seizure of money or property held directly by the debtor.
Under the Constitution of Canada, the responsibility for enacting and enforcing labour laws, including the minimum wage, rests primarily with the ten Provinces of Canada. The three Territories of Canada have a similar power, delegated to them by federal legislation. Some provinces allow lower wages to be paid to liquor servers and other gratuity earners or to inexperienced employees.
A full-time job is employment in which workers work a minimum number of hours defined as such by their employer.

Southdale Center is a shopping mall located in Edina, Minnesota, a suburb of the Twin Cities. It opened in 1956 and is both the first and the oldest fully enclosed, climate-controlled shopping mall in the United States. Southdale Center has 1,297,608 square feet of leasable retail space, and contains 106 retail tenants. The mall is owned by Simon Property Group and the anchor stores are Macy's, Dave & Buster's, AMC Theatres, Hennepin Service Center, and Life Time Athletic.

The National Restaurant Association is a restaurant industry business association in the United States, representing more than 380,000 restaurant locations. It also operates the National Restaurant Association Educational Foundation. The association was founded in 1919 and is headquartered in Washington, D.C.
Overtime rate is a calculation of hours worked by a worker that exceed those hours defined for a standard workweek. This rate can have different meanings in different countries and jurisdictions, depending on how that jurisdiction's labor law defines overtime. In many jurisdictions, additional pay is mandated for certain classes of workers when this set number of hours is exceeded. In others, there is no concept of a standard workweek or analogous time period, and no additional pay for exceeding a set number of hours within that week.

The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 29 U.S.C. § 203 (FLSA) is a United States labor law that creates the right to a minimum wage, and "time-and-a-half" overtime pay when people work over forty hours a week. It also prohibits employment of minors in "oppressive child labor". It applies to employees engaged in interstate commerce or employed by an enterprise engaged in commerce or in the production of goods for commerce, unless the employer can claim an exemption from coverage. The Act was enacted by the 75th Congress and signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1938.

The California Labor Code, more formally known as "the Labor Code", is a collection of civil law statutes for the State of California. The code is made up of statutes which govern the general obligations and rights of persons within the jurisdiction of the State of California. The stated goal of the Department of Industrial Relations is to promote and develop the welfare of the wage earners of California, to improve their working conditions and to advance their opportunities for profitable employment."

Crunch Fitness is a U.S.-based brand of over 400 franchised and corporate owned fitness clubs located in the United States, Puerto Rico, Canada, Spain, Portugal, Costa Rica, and Australia. Founded by Doug Levine in 1989, its current Worldwide CEO is Jim Rowley.
Work–life balance in the United States is having enough time for work and enough time to have a personal life in the United States. Related, though broader, terms include lifestyle balance and life balance. The most important thing in work and life is the personal ability to demonstrate and meet the needs of work and personal life in order to achieve goals. People should learn to deal with role engagement management, role conflict management and managing life needs to achieve balance. Balance is about how to properly achieve the desired work and life satisfaction and needs in a conflict situation.

Anytime Fitness Franchisor, LLC, doing business as Anytime Fitness, is an American franchise of 24 hour health and fitness clubs that is based in Woodbury, Minnesota, United States. The company operates over 5,000 franchised locations in 50 countries. In 2014, Anytime Fitness was named the top franchise of 2014 by Entrepreneur magazine.

Wage theft is the failing to pay wages or provide employee benefits owed to an employee by contract or law. It can be conducted by employers in various ways, among them failing to pay overtime; violating minimum-wage laws; the misclassification of employees as independent contractors; illegal deductions in pay; forcing employees to work "off the clock", not paying annual leave or holiday entitlements, or simply not paying an employee at all.

Employer compensation in the United States refers to the cash compensation and benefits that an employee receives in exchange for the service they perform for their employer. Approximately 93% of the working population in the United States are employees earning a salary or wage.
Fluctuating workweek overtime, sometimes also called Chinese overtime, is the practice of calculating overtime wages based on a salaried employee's average hourly wage.













