Related Research Articles
The Patuxent Range or macizo Armada Argentina is a major range of the Pensacola Mountains, comprising the Thomas Hills, Anderson Hills, Mackin Table and various nunataks and ridges bounded by the Foundation Ice Stream, Academy Glacier and the Patuxent Ice Stream. Discovered and partially photographed on January 13, 1956 in the course of a transcontinental nonstop plane flight by personnel of U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return.
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.
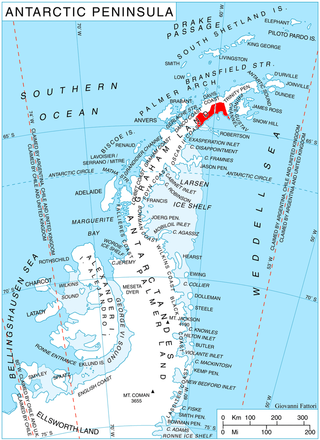
Drygalski Glacier is a broad glacier, 18 nautical miles long and 15 miles (24 km) wide at its head, which flows from Herbert Plateau southeast between Ruth Ridge and Kyustendil Ridge, and enters Solari Bay immediately north of Sentinel Nunatak on Nordenskjöld Coast, the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered in 1902 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, under Otto Nordenskiöld, and named "Drygalski Bay" after Professor Erich von Drygalski. The feature was determined to be a glacier by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1947.
Shelton Nunataks are two isolated nunataks located 10 miles (16 km) southeast of Thomas Mountains, in Palmer Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Willard S. Shelton, electrician at Eights Station in 1964.
The Enceladus Nunataks are a group of about eight nunataks scattered over a wide area at the head of the drainage basin of Saturn Glacier, in southern Alexander Island, Antarctica. They were mapped from trimetrogon air photography taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and from survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1948–50. The group was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee from association with Saturn Glacier, Enceladus being one of the moons of the planet Saturn.
On the continent of Antarctica, the Aramis Range is the third range south in the Prince Charles Mountains, situated 11 miles southeast of the Porthos Range and extending for about 30 miles in a southwest–northeast direction. It was first visited in January 1957 by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party led by W.G. Bewsher, who named it for a character in Alexandre Dumas' novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.
Aphrodite Glacier is a glacier 15 nautical miles (28 km) long flowing north to the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula 3 nautical miles (6 km) west of Victory Nunatak.
Bond Nunatak is a snow-capped nunatak with rock exposures on its west face, rising north of Mount Bouvier on Adelaide Island. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963 for Flight Lieutenant Peter R. Bond, RAF, pilot with the British Antarctic Survey Aviation Unit based at Adelaide station in 1962–63.
The Cameron Nunataks are a small cluster of nunataks rising above the west margin of Evans Neve, at the southern end of the Freyberg Mountains. The cluster was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–64, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Roy E. Cameron, biologist at McMurdo Station, summers 1966–67 and 1967–68.
Wyers Nunataks is a group of nunataks at the base of Sakellari Peninsula, just west of Wyers Ice Shelf in Enderby Land. Plotted from air photos taken from ANARE aircraft in 1956 and 1957. Named by Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA) for R.W.L. Wyers, glaciologist at Mawson Station in 1961.

Janke Nunatak is an isolated nunatak, 4 nautical miles (7 km) northeast of Carlson Peak in the western Hauberg Mountains, in Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for John W. Janke, a radioman with the Eights Station winter party in 1964.
Knott Nunatak is a nunatak 1 nautical mile (2 km) northwest of the northern extremity of the LeMay Range, in the west-central portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1960. The nunatak was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1977 for Christopher E. Knott, British Antarctic Survey general assistant at Stonington Island, 1974–75, and Adelaide Island, 1975–76, who participated in a plane table survey of this area.

Dewar Nunatak is a mainly snow-covered nunatak rising to 520 metres (1,700 ft) in the middle of Shambles Glacier, on the east coast of Adelaide Island. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963 for Graham J.A. Dewar, a British Antarctic Survey geologist at Adelaide station, 1961–63.
Mount Ditte is a mountain, 1,400 metres (4,600 ft) high, surmounting Cape Alexandra in the southeast extremity of Adelaide Island. It was discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, and named by Jean-Baptiste Charcot for Alfred Ditte, a noted French chemist.

Long Glacier is a glacier about 8 nautical miles long in the southeastern part of Thurston Island, Antarctica. It flows south to the Abbot Ice Shelf, 14 nautical miles (26 km) west of Harrison Nunatak. The glacier was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–66, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Fred A. Long, Jr., an aviation machinist of U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6, who wintered at Little America V in 1957 and was in Antarctica in the 1960–61 and 1962–63 seasons.
The Haslam Heights are a line of peaks trending north-northeast–south-southwest, rising to about 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) to the west of Vallot Glacier and Nye Glacier in Arrowsmith Peninsula, Graham Land, Antarctica. They were probably first seen by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10 under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, which roughly charted the area in 1909. They were roughly mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1948, and named in 1985 by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Rear Admiral Sir David W. Haslam, Hydrographer of the Navy, 1975–85.
The Mathis Nunataks are an isolated cluster of nunataks near the head of Arthur Glacier, 8 nautical miles (15 km) east-southeast of Mount Warner, in the Ford Ranges of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. They were mapped by the United States Antarctic Service (1939–41) and by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos (1959–65). The group was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Terry R. Mathis, a traverse engineer with the Byrd Station glaciological strain network, summer season (1967–68), and station engineer with the Byrd Station winter party (1968).
Titan Nunatak is a broad, rather flat-topped nunatak, rising to about 460 m, standing between Coal Nunatak and Tethys Nunataks in the southeast corner of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The nunatak was first sighted and photographed from the air by Lincoln Ellsworth on November 23, 1935, and mapped from photos obtained on that flight by W.L.G. Joerg. Observed from the northwest, only the summit protrudes above the coastal ice, and it was uncertain whether this was a Peak on Alexander Island or an island in George VI Sound. Its true nature was determined by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey who surveyed this nunatak in 1949. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee for its association with nearby Saturn Glacier, Titan being one of the satellites of the planet Saturn, the sixth planet of the Solar System.
Kay Nunatak is a dark rocky nunatak rising to 500 metres (1,600 ft), situated at the south side of Mobiloil Inlet and forming the northernmost outlier of the Hitchcock Heights, on the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The nunatak was photographed from the air by Sir Hubert Wilkins on December 20, 1928, and by Lincoln Ellsworth in 1935. It was named in 1952 by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for John D. Kay of the American Geographical Society, who by utilizing these photographs assisted in constructing the first reconnaissance map of this area.
References
- ↑ "Lincoln Nunatak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 17 June 2013.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Lincoln Nunatak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Lincoln Nunatak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.