
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 60 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—2 in North America, 9 in Central and South America, and 3 in Australia.
Genus /ˈdʒiː.nəs/ is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name.

The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek lagos + morphē. There are 110 recent species of lagomorph of which 109 are extant, including 34 species of pika, 42 species of rabbit, and 33 species of hare.

Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae, Anseranatidae, and Anatidae, the largest family, which includes over 170 species of waterfowl, among them the ducks, geese, and swans. Most modern species in the order are highly adapted for an aquatic existence at the water surface. With the exception of screamers, males have penises, a trait that has been lost in the Neoaves. Due to their aquatic nature, most species are web-footed.

Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The name "Sturnidae" comes from the Latin word for starling, sturnus. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas as well as North America, Hawaii and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common.

Lindos is an archaeological site, a fishing village and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 178.9 km2. It lies on the east coast of the island. It is about 40 km south of the town of Rhodes and its fine beaches make it a popular tourist and holiday destination. Lindos is situated in a large bay and faces the fishing village and small resort of Charaki.
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon.

In zoological nomenclature, a type species is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus.
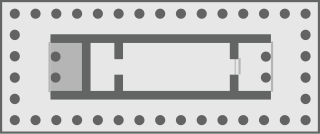
An opisthodomos can refer to either the rear room of an ancient Greek temple or to the inner shrine, also called the adyton. The confusion arises from the lack of agreement in ancient inscriptions. In modern scholarship, it usually refers to the rear porch of a temple. On the Athenian Acropolis especially, the opisthodomos came to be a treasury, where the revenues and precious dedications of the temple were kept. Its use in antiquity was not standardised. In part because of the ritual secrecy of such inner spaces, it is not known exactly what took place within opisthodomoi; it can safely be assumed that practice varied widely by place, date and particular temple.

Caligula is a genus of moths of the family Saturniidae. It is primarily an Oriental genus, found in India, China and Southeast Asia. The genus is often treated as a synonym of Rinaca. It is named after Roman emperor Caligula.

In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms in a taxonomic hierarchy. Examples of taxonomic ranks are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain, etc.

Ratt is an American glam metal band formed in San Diego in 1976, that had significant commercial success in the 1980s, with their albums having been certified as gold, platinum, and multi-platinum by the RIAA. The group is best known for their hit singles "Round and Round" and "Lay It Down," both of which charted in the top 40 of the Billboard Hot 100. Other songs such as "Wanted Man," "You're in Love," "Dance," and "Way Cool Jr." also charted on the Hot 100.
The Lindos Chronicle is an inscription from Lindos, Rhodes, dated to 99 BC. It records dedications made in the temple to Athena at Lindos prior to the destruction of the original temple in 392–1. The chronicle is one of the longest surviving Hellenistic inscriptions. It was excavated early in the 20th century by a Danish expedition, which found it used as paving block of the Byzantine church of Saint Stephen, near the theatre of Lindos. It contains decrees of Lindians, as well report on previous dedications of rulers and generals to Athena Lindia.

Caligula lindia is a moth of the family Saturniidae. It was described by Frederic Moore in 1865. It is found in south-eastern Afghanistan north to the Salang Pass, and Kashmir. It is also found in the Himalayan foothills of northern India, from Kashmir to Bhutan and southern Tibet, China and Nepal. It is found up to heights of 2,400 meters.

Rinaca is a genus of moths in the family Saturniidae erected by Frederic Moore in 1862. It is often treated as a subgenus of Saturnia.

S.O.S. Sahara is a 1938 German drama film directed by Jacques de Baroncelli and starring Charles Vanel, Jean-Pierre Aumont and Marta Labarr. The film was made in the French language, produced by the French subsidiary of the German studio UFA. It was shot on location in Algeria. The screenplay was based on a play Men Without a Past by Jean Martet. Martet's credit was removed from the film during the Nazi occupation of France, and he later brought a court case against UFA establishing his rights to the film.
The Temple of Athena is the Parthenon on the Athenian Acropolis in Greece.

The Temple of Athena Lindia was a sanctuary in Lindos in Rhodes, dedicated to the goddess Athena. It was a significant Pan-Hellenic shrine of Athena and arguably the regional center of her cult.
Lindiidae is a family of rotifers belonging to the order Ploima.














