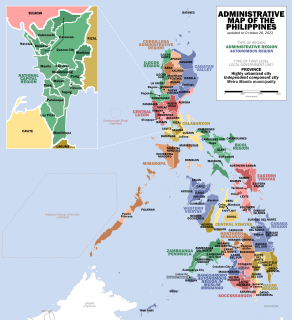
In the Philippines, regions are administrative divisions that primarily serve to coordinate planning and organize national government services across multiple local government units (LGUs). Most national government offices provide services through their regional branches instead of having direct provincial or city offices. Regional offices are usually but not necessarily located in the city designated as the regional center.

Cotabato, officially the Province of Cotabato and formerly but still colloquially known as North Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan. Some of its barangays are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

Cotabato City, officially the City of Cotabato, is a 3rd class independent component city in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 325,079, making it as the most populated city under the independent component city status.

Pikit, officially the Municipality of Pikit is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 164,646 people.

Islam was the first-recorded monotheistic religion in the Philippines. Islam reached the Philippines in the 14th century with the arrival of Muslim traders from the Persian Gulf, southern India, and their followers from several sultanate governments in the Malay Archipelago. The first Muslims to arrive were traders followed by missionaries in the late 14th and early 15th centuries. They facilitated the formation of Sultanates and conquests in Mindanao and Sulu. The people who converted to Islam came to be known as the Moros. The Muslim conquest reached as far as the Tondo which was supplanted by Brunei's vassal-state Maynila.
Elections in the Philippines are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/members of the Sangguniang Bayan, barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan are elected to serve for a three-year term.

Carmen, officially the Municipality of Carmen, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 107,603 people.

The collective term Moro people or Bangsamoro people refers to the 13 Muslim ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro. As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people.

The Spanish colonial fortifications in the Philippines are strongholds constructed by Filipinos and Spanish under the rule of the Spaniards in the Philippines for protection against local and foreign aggressors during the Spanish Colonial Period. The fortifications were also used during the American and Japanese occupation eras. Many of the fortifications have been badly damaged, either due to old age or conflicts in the past. Currently, there has been initiatives to restore all Spanish fortifications throughout the Philippines. The initiative began when the Baluarte Luna of La Union and the Intramuros of Manila were restored in the 2010s. In 2013, a typhoon and earthquake hit Central Visayas and damaged numerous Spanish fortifications. This led to the largest restoration activity for fortifications in Philippine history.
The local government in the Philippines is divided into three levels: provinces and independent cities, component cities and municipalities, and barangays, all of which are collectively known as local government units (LGUs). In one area, above provinces and independent cities, is an autonomous region, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao. Below barangays in some cities and municipalities are sitios and puroks. All of these, with the exception of sitios and puroks, elect their own executives and legislatures. Sitios and puroks are often but not necessarily led by an elected barangay councilor.

These lists contain an overview of the government recognized cultural properties in the Philippines. The lists are based on the official lists provided by the National Commission for Culture and the Arts, National Historical Commission of the Philippines, and the National Museum of the Philippines.

Bangsamoro, officially the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, is an autonomous region located in the southern Philippines.
Operation Darkhorse was an offensive against the Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters (BIFF) launched by the Armed Forces of the Philippines on January 27, 2014.

The Bangsamoro Organic Law, also known as the Bangsamoro Basic Law (BBL), and officially designated as Republic Act No. 11054, is a Philippine law which provided for the establishment of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM).

An autonomous region of the Philippines is a first-level administrative division that has the authority to control a region's culture and economy. The Constitution of the Philippines allows for two autonomous regions: in the Cordilleras and in Muslim Mindanao. Currently, Bangsamoro, which largely consists of the Muslim-majority areas of Mindanao, is the only autonomous region in the country.

The 2019 Bangsamoro autonomy plebiscite was a two-part plebiscite held in Mindanao, Philippines that ratified the Bangsamoro Organic Law (BOL) and replaced the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) with the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), as well as the scope of the said region.

Fort Pikit is a historic fortification in Pikit, Cotabato, Philippines.





















