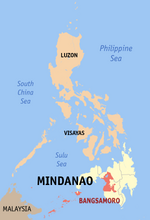
Maguindanao is a province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM). Since 2014 the provincial capital is Buluan but the legislative branch of the provincial government, the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, convenes in the old provincial capitol in the town of Sultan Kudarat. It borders Lanao del Sur to the north, Cotabato to the east, Sultan Kudarat to the south, and the Illana Bay to the west.

Parang, officially the Municipality of Parang, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 71,495 people.

Pigcawayan, officially the Municipality of Pigcawayan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 52,744 people.

Ampatuan, officially the Municipality of Ampatuan, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 28,941 people.

Datu Abdullah Sangki, officially the Municipality of Datu Abdullah Sangki, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 30,117 people.

Datu Odin Sinsuat, officially the Municipality of Datu Odin Sinsuat, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 116,768 people.

General Salipada K. Pendatun, officially the Municipality of General Salipada K. Pendatun, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 31,263 people.

Kabuntalan, officially the Municipality of Kabuntalan, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,439 people.

Paglat, officially the Municipality of Paglat, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 18,727 people.

Shariff Aguak, officially the Municipality of Shariff Aguak, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,982 people.

Sultan Kudarat, officially the Municipality of Sultan Kudarat, is a 1st class municipality and legislative capital of the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 105,121 people.

Sultan sa Barongis, officially the Municipality of Sultan sa Barongis, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 24,476 people.

Sultan Sumagka, officially the Municipality of Sultan Sumagka, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,463 people.

Upi, officially the Municipality of Upi, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,004 people.

Matanog, officially the Municipality of Matanog, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 36,034 people.

Pagalungan, officially the Municipality of Pagalungan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Bangsamoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 46,277 people.

Rajah Buayan, officially the Municipality of Rajah Buayan, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 27,832 people.

Datu Blah T. Sinsuat, officially the Municipality of Datu Blah T. Sinsuat, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 28,243 people.
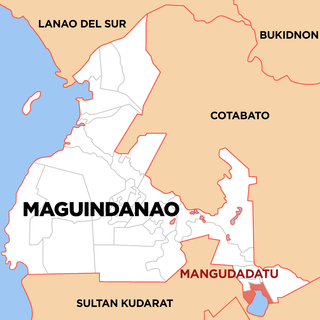
Mangudadatu, officially the Municipality of Mangudadatu, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 26,203 people.

Datu Anggal Midtimbang, officially the Municipality of Datu Anggal Midtimbang, is a municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 28,224 people.