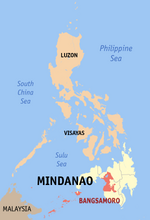
Maguindanao was a province of the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM). From 2014 to 2022, its provincial capital was Buluan, but the legislative branch of government, the Maguindanao Provincial Board, convened at the old provincial capitol in Sultan Kudarat. It bordered Lanao del Sur to the north, Cotabato to the east, Sultan Kudarat to the south, and Illana Bay to the west.

Cotabato or North Cotabato, officially the Province of Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan. Some of its barangays are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

Soccsksargen, formerly known as Central Mindanao, is an administrative region of the Philippines, designated as Region XII. Located in south-central Mindanao, its name is an acronym that stands for the region's four provinces and one highly urbanized city. The regional center is in Koronadal, located in the province of South Cotabato, and the center of commerce and industry is General Santos, which is the most populous city in the region.

The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao was an autonomous region of the Philippines, located in the Mindanao island group of the Philippines, that consisted of five predominantly Muslim provinces: Basilan, Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi. It was the only region that had its own government. The region's de facto seat of government was Cotabato City, although this self-governing city was outside its jurisdiction.

Cotabato City, officially the City of Cotabato, is a third class independent component city in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 325,079 people, making it as the most populated city under the independent component city status.

Pikit, officially the Municipality of Pikit is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 67,024 people.

Aleosan, officially the Municipality of Aleosan, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 36,892 people.

Carmen, officially the Municipality of Carmen, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 79,140 people.

Kabacan officially the Municipality of Kabacan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 77,164 people.

Midsayap, officially the Municipality of Midsayap, is a 1st class municipality in the Province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 117,365 people.

Pigcawayan, officially the Municipality of Pigcawayan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 52,744 people.

Pagalungan, officially the Municipality of Pagalungan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Maguindanao del Sur, Bangsamoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 46,277 people.

Bangsamoro, officially the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, is an autonomous region in the Philippines, located in the southwestern portion of the island of Mindanao.

An autonomous region of the Philippines is a first-level administrative division that has the authority to control a region's culture and economy. The Constitution of the Philippines allows for two autonomous regions: in the Cordilleras and in Muslim Mindanao. Currently, Bangsamoro, which largely consists of the Muslim-majority areas of Mindanao, is the only autonomous region in the country.

The 2019 Bangsamoro autonomy plebiscite was a two-part plebiscite held in Mindanao, Philippines, that ratified the Bangsamoro Organic Law (BOL) and replaced the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) with the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), as well as the scope of the said region.

The Police Regional Office Bangsamoro Autonomous Region, also known as the Bangsamoro Police, is the regional office of the Philippine National Police meant to cover the whole Bangsamoro autonomous region.

The transition period of the now-defunct Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) into the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) began when the Bangsamoro Organic Law was ratified in a two-part plebiscite held in January and February 2019. It is set to end after the first set of regular officials are elected in 2025.

Fort Pikit is a historic fortification in Pikit, Cotabato, Philippines.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Bangsamoro is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao on March 11, 2020, when the first case of the disease was confirmed in Lanao del Sur. Cases has been confirmed in Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, and the independent city of Cotabato.
Frances Cynthia Guiani-Sayadi is a Filipino politician who was mayor of Cotabato City from 2019 to 2022.