
The politics of Cameroon takes place in a framework of a unitary presidential republic, whereby the President of Cameroon is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly of Cameroon.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislature of Serbia. The assembly is composed of 250 proportionally elected deputies by secret ballot, on 4 years term. The assembly elects a president (speaker) who presides over the sessions. The current president of the national assembly is Maja Gojković since 23 April 2014.
The Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA), previously known as the Empire Parliamentary Association, is an organisation which works to support good governance, democracy and human rights.
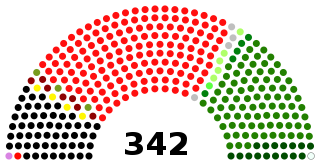
The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral Majlis-e-Shura, which also comprises the Senate of Pakistan. The National Assembly and the Senate both convene at Parliament House in Islamabad. The National Assembly is a democratically elected body consisting of a total of 336 members, before 25th amendment they used to be 342' who are referred to as Members of the National Assembly (MNAs), of which 272 are directly elected members and 70 reserved seats for women and religious minorities. A political party must secure 137 seats to obtain and preserve a majority.

The Parliament of Pakistan is the federal and supreme legislative body of Pakistan. It is a bicameral federal legislature that consists of the Senate as the upper house and the National Assembly, as the lower house. According to the constitution of Islamic Republic of Pakistan, the President of Pakistan is also a component of the Parliament. The National Assembly is elected for a five-year term on the basis of adult franchise and one-man one-vote. The tenure of a Member of the National Assembly is for the duration of the house, or sooner, in case the Member dies or resigns. The tenure of the National Assembly also comes to an end if dissolved on the advice of the Prime Minister or by the president in his discretion under the Constitution.

The Parliament of Ghana is the legislative body of the Government of Ghana.

The Speaker of the National Assembly ; informally as Speaker National Assembly, is the presiding official of the National Assembly of Pakistan– a lower house of the Parliament of Pakistan.

The National Assembly is the lower house of the Parliament of Cameroon. It has 180 members, elected for five-year terms in 49 single and multi-seat constituencies.

The National Assembly is one of the two components of the Parliament of Guyana. Under Article 51 of the Constitution of Guyana, the Parliament of Guyana consists of the President and the National Assembly. The National Assembly has 65 members elected using the system of proportional representation. Twenty five are elected from the ten geographical constituencies and forty are awarded at the national level on the basis of block votes secured, using the LR-Hare Formula as prescribed by the elections Laws (Amendment) Act 15 of 2000.

The National Assembly is Mauritius's unicameral legislature, which was called the Legislative Assembly until 1992, when the country became a republic. The Constitution of Mauritius provides for the parliament of Mauritius to consist of the President and the National Assembly. The parliament of Mauritius is modelled after the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy, where members of parliament are voted in at regular general elections, on the basis of a first past the post system.

The Punjab Legislative Assembly or the Punjab Vidhan Sabha is the unicameral legislature of the state of Punjab in India. At present, it consists of 117 members, directly elected from 117 single-seat constituencies. The tenure of the Legislative Assembly is five years unless dissolved sooner. The current Speaker of the Assembly is Rana K. P. Singh. The meeting place of the Legislative Assembly since 6 March 1961 is the Vidhan Bhavan in Chandigarh.

The Constitution of Cameroon is the supreme law of the Republic of Cameroon. Adopted in 1972, it is Cameroon's third constitution. The document consists of a preamble and 13 Parts, each divided into Articles. The Constitution outlines the rights guaranteed to Cameroonian citizens, the symbols and official institutions of the country, the structure and functions of government, the procedure by which the Constitution may be amended, and the process by which the provisions of the Constitution are to be implemented.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Cameroon:
Cavayé Yéguié Djibril is a Cameroonian politician who has been the President of the National Assembly of Cameroon since 1992. He is a leading member of the Cameroon People's Democratic Movement (CPDM).
Jean-Bernard Ndongo Essomba is a Cameroonian politician. He was President of the Parliamentary Group of the Cameroon People's Democratic Movement (RDPC) in the National Assembly of Cameroon from 1992 to 1997 and he has held that post again since 2002.










