| Regions of Cameroon Régions du Cameroun (French) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Cameroon |
| Number | 10 |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
 |
|---|
The Republic of Cameroon is divided into ten regions.
| Regions of Cameroon Régions du Cameroun (French) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Cameroon |
| Number | 10 |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
 |
|---|
The Republic of Cameroon is divided into ten regions.
Between 1961 and 1972, Cameroon was a federal republic made up of two federated states, East Cameroon and West Cameroon.
A unitary system came into being in 1972. The country was then divided into provinces. In 1983, Centre-South Province was divided into Centre and South and at the same time, Adamawa and Far North Provinces were split from North Province. See summary of administrative history in Zeitlyn 2018. [1]
In 2008, the President of the Republic of Cameroon, President Paul Biya signed decrees abolishing "provinces" and replacing them with "regions". Hence, all of the country's ten provinces are now known as regions.
The Northwest region and Southwest region were granted special status in December 2019, giving them additional powers.
|

Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area Rio dos Camarões, which became Cameroon in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in the north in the 19th century, and various ethnic groups of the west and northwest established powerful chiefdoms and fondoms.
An arrondissement is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
Korea has had administrative districts that can be considered provinces since the 7th century. These divisions were initially called ju in Unified Silla and Later Baekje, and there were nine in total. After Goryeo conquered these states in the 10th century, twelve divisions called mok were established, although they were reorganized into ten do in the 11th century.

In the Philippines, regions are administrative divisions that primarily serve to coordinate planning and organize national government services across multiple local government units (LGUs). Most national government offices provide services through their regional branches instead of having direct provincial or city offices. Regional offices are usually but not necessarily located in the city designated as the regional center.

Chile is divided into 16 regions, which are the country's first-level administrative division. Each region is headed by directly elected regional governor and a regional board.

Below is a list of the 18 states of the Sudan. Prior to 9 July 2011, the Republic of the Sudan was composed of 25 states. The ten southern states now form part of the independent country of South Sudan. Two additional states were created in 2012 within the Darfur region, and one in 2013 in Kordofan, bringing the total to 18.

The provinces of Bulgaria are the first-level administrative subdivisions of the country.

The Northwest Region, or North-West Region is a region with special status in Cameroon. Its capital is Bamenda. The Northwest Region was part of the Southern Cameroons, found in the western highlands of Cameroon. It is bordered to the southwest by the Southwest Region, to the south by the West Region, to the east by the Adamawa Region, and to the north by Nigeria. Various Ambazonian nationalist and separatist factions regard the region as being distinct as a polity from Cameroon.

The administrative divisions of North Korea are organized into three hierarchical levels. These divisions were created in 2002. Many of the units have equivalents in the system of South Korea. At the highest level are nine provinces and four special municipalities. The second-level divisions are cities, counties, and districts. These are further subdivided into third-level entities: towns, dongs (neighborhoods), ris (villages), and workers' districts.

The South Region is located in the southwestern and south-central portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the East Region, to the north by the Centre Region, to the northwest by the Littoral Region, to the west by the Gulf of Guinea, and to the south by the countries of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Congo. The South occupies 47,720 km2 of territory, making it the fourth largest region in the nation. The major ethnic groups are the various Beti-Pahuin peoples, such as the Ewondo, Fang, and Bulu.
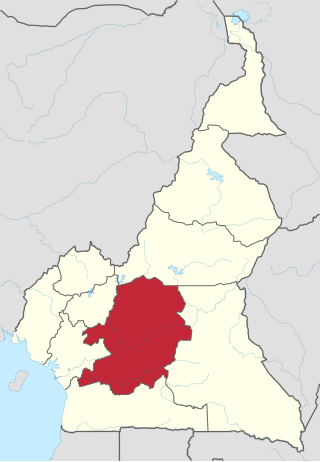
The Centre Region occupies 69,000 km2 of the central plains of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the north by the Adamawa Region, to the south by the South Region, to the east by the East Region, and to the West by the Littoral and West Regions. It is the second largest of Cameroon's regions in land area. Major ethnic groups include the Bassa, Ewondo, and Vute.
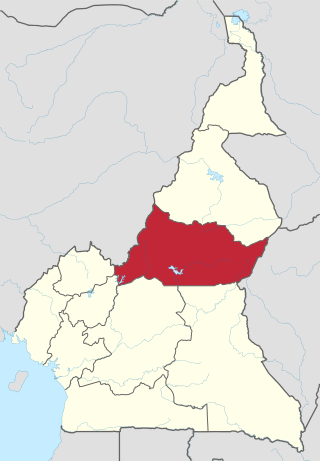
The Adamawa Region is a constituent region of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Centre and East regions to the south, the Northwest and West regions to the southwest, Nigeria to the west, the Central African Republic (CAR) to the east, and the North Region to the north.
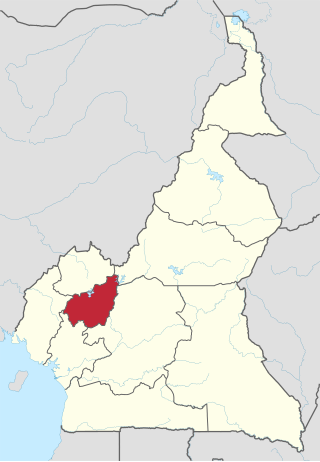
The West Region is 14,000 km2 of territory located in the central-western portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Northwest Region to the northwest, the Adamawa Region to the northeast, the Centre Region to the southeast, the Littoral Region to the southwest, and the Southwest Region to the west. The West Region is the smallest of Cameroon's ten regions in area, yet it has the highest population density.

The North Region makes up 66,090 km2 of the northern half of The Republic of Cameroon. Neighbouring territories include the Far North Region to the north, the Adamawa Region to the south, Nigeria to the west, Chad to the east, and Central African Republic to the southeast. The city of Garoua is both the political and industrial capital. Garoua is Cameroon's third largest port, despite the fact that the Bénoué River upon which it relies is only navigable for short periods of the year.
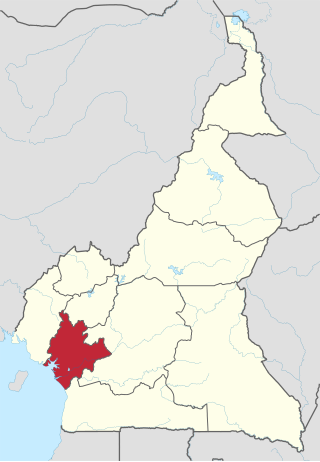
The Littoral Region is a region of Cameroon. Its capital is Douala. As of 2004, its population was 3,174,437. Its name is due to the region being largely littoral, and associated with the sea coast.

The regions of Cameroon are divided into 58 divisions or departments. The divisions are further subdivided into subdivisions (arrondissements) and districts. The divisions are listed below, by Macro-Region and region.

The constitution divides Cameroon into 10 semi-autonomous regions, each under the administration of an elected Regional Council. A presidential decree of 12 November 2008 officially instigated the change from provinces to regions. Each region is headed by a presidentially appointed governor. These leaders are charged with implementing the will of the president, reporting on the general mood and conditions of the regions, administering the civil service, keeping the peace, and overseeing the heads of the smaller administrative units. Governors have broad powers: they may order propaganda in their area and call in the army, gendarmes, and police. All local government officials are employees of the central government's Ministry of Territorial Administration, from which local governments also get most of their budgets.
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman provincia, which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term province has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city".

The Republic of Cameroon is a decentralized unitary state.