
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It is named after the city of Ramsar in Iran, where the convention was signed in 1971.

A transboundary protected area (TBPA) is an ecological protected area that spans boundaries of more than one country or sub-national entity. Such areas are also known as transfrontier conservation areas (TFCAs) or peace parks.

Mai Po Marshes (Chinese: 米埔濕地; Hong Kong Hakka: Mi3bu4 Sip5ti4) is a nature reserve located in San Tin near Yuen Long in Hong Kong. it is within Yuen Long District.

.

The Bhoj Wetland consists of two lakes located in the city of Bhopal, the capital of the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. The two lakes are the Bhojtal & the Lower Lake, which lie to the west of the city center. The Bhojtal has an area of 31 km², and drains a catchment or watershed of 361 km². The watershed of the Bhojtal is mostly rural, with some urbanized areas around its eastern end. The lower lake has an area of 1.29 km². Its catchment is 9.6 km² and is mostly urbanized; the Lower Lake also receives subsurface seepage from the Bhojtal.
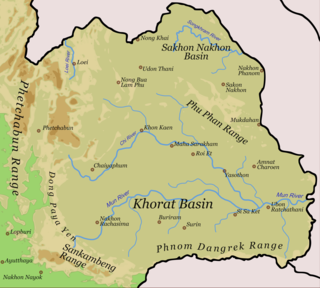
The Songkhram River is a tributary of the Mekong River. It originates in the hills between Nong Han District, Udon Thani Province and Sawang Daen Din District, Sakon Nakhon Province. It flows through Seka District, Wanon Niwat, and Si Songkhram District and empties into the Mekong River in tambon Chai Buri, Tha Uthen District, Nakhon Phanom Province. It is 420 kilometres (260 mi) long.

World Wetlands Day is an environmentally related celebration which dates back to the year 1971 when several environmentalists gathered to reaffirm protection and love for wetlands, which are water ecosystems containing plant life and other organisms that bring ecological health in abundance to not only water bodies but environments as a whole. The World Wetlands Secretary Department is originally from Gland, Switzerland. The adoption of the Ramsar convention in "the Iranian city of Ramsar on the shores of the Caspian Sea" occurred on February 2, 1971.

Sasthamcotta Lake or Sasthamkotta Lake, also categorized as a wetland, is the largest fresh water lake in Kerala, a state of India on the south of the West Coast. The lake is named after the ancient Sastha temple located on its bank. It meets the drinking water needs of half million people of the Quilon district and also provides fishing resources. The purity of the lake water for drinking use is attributed to the presence of large population of larva called cavaborus that consumes bacteria in the lake water. The lake is a designated wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention since November 2002.

Polar Bear Pass, is a 262,400 hectare wetland and mountain pass on Bathurst Island within the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. The pass is on federal Crown land.

Wadi Wurayah is a 12,700-hectare (31,000-acre) wadi between the towns of Masafi, Khor Fakkan, and Bidiyah in the United Arab Emirates. It has been designated as Ramsar Wetland of International Importance.
The Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the List of Ramsar wetlands of international importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution or other human interference. It is a voluntary mechanism to highlight specific wetlands of international importance that are facing immediate challenges. It is maintained as part of the List of Ramsar wetlands of international importance.

The Moist Pacific Coast mangroves ecoregion covers a series of disconnected mangrove sites along the Pacific Ocean coast of Costa Rica and Panama. These sites occur mostly on coastal flatlands around lagoons, particularly where rivers from the inland mountains reach the sea, bringing fresh water to the coastal forests. The area is in a transition zone from the drier coastline to the north; rainfall in this ecoregions is over 2,000 mm/year, and reaches over 3,600 mm/year at the southern end.

The Tehuantepec-El Manchon mangroves ecoregion covers a series of mangrove woodlands along the Pacific Ocean coast of the state of Chiapas, Mexico. The ecoregion is relatively large and continuous, with trees up to 25 meters in height. The region supports stands of a type of yellow mangrove that normally only grown further south. The coast of Mexico here is wet - over 2,500 mm/year of rain. Four RAMSAR wetlands of international important are found in the zone, and a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Of particular importance are the wide variety of permanent and migratory birds in the area.

The Alvarado mangroves ecoregion covers a series of mangrove forest areas along the Gulf of Mexico coast of the states of Tamaulipas and Veracruz in Mexico. they are the most northerly mangroves in the western Gulf. The largest tracts of mangrove swamps occur at the mouths of rivers, and nearby coastal lagoon.

Gab Mejia is a Filipino conservation photographer based in Manila, Philippines.



















