Related Research Articles

The 1832 United States presidential election was the 12th quadrennial presidential election, held from Friday, November 2 to Wednesday, December 5, 1832. Incumbent president Andrew Jackson, candidate of the Democratic Party, defeated Henry Clay, candidate of the National Republican Party.

The 1848 United States presidential election was the 16th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1848. In the aftermath of the Mexican–American War, General Zachary Taylor of the Whig Party defeated Senator Lewis Cass of the Democratic Party.

The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott. A third party candidate from the Free Soil party, John P. Hale, also ran and came in third place, but got no electoral votes.
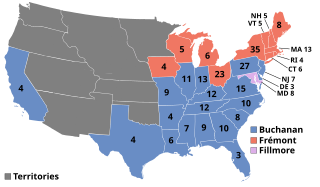
The 1856 United States presidential election was the 18th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1856. In a three-way election, Democrat James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and Know Nothing nominee Millard Fillmore. The main issue was the expansion of slavery as facilitated by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. Buchanan defeated President Franklin Pierce at the 1856 Democratic National Convention for the nomination. Pierce had become widely unpopular in the North because of his support for the pro-slavery faction in the ongoing civil war in territorial Kansas, and Buchanan, a former Secretary of State, had avoided the divisive debates over the Kansas–Nebraska Act by being in Europe as the Ambassador to the United Kingdom.

The 1872 United States presidential election was the 22nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1872. Despite a split in the Republican Party, incumbent President Ulysses S. Grant defeated Democratic-endorsed Liberal Republican nominee Horace Greeley.

The Free Soil Party was a short-lived coalition political party in the United States active from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party. The party was largely focused on the single issue of opposing the expansion of slavery into the western territories of the United States.

The 1856 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from June 17 to June 19, 1856 at Musical Fund Hall at 808 Locust Street in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was the first national nominating convention of the Republican Party, founded two years earlier in 1854. It was held to nominate the party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1856 election. The convention selected former John C. Frémont, a United States Senator from California, for president, and former Senator William L. Dayton of New Jersey for vice president. The convention also appointed members of the newly established Republican National Committee.

The 1856 Whig National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held from September 17 to September 18, in Baltimore, Maryland. Attended by a rump group of Whigs who had not yet left the declining party, the 1856 convention was the last presidential nominating convention held by the Whig Party. The convention nominated a ticket consisting of former President Millard Fillmore and former Ambassador Andrew J. Donelson; both had previously been nominated by the 1856 American National Convention. The Whig ticket finished third in the 1856 presidential election behind the winning Democratic ticket of James Buchanan and John C. Breckinridge, the runner-up Republican ticket of John C. Fremont and William L. Dayton.

The Vermont Republican Party is the affiliate of the Republican Party in Vermont and has been active since its foundation in the 1860s. The party is the second largest in the state behind the Vermont Democratic Party, but ahead of the Vermont Progressive Party. The party historically dominated Vermont politics until the mid-20th century, but was replaced by the Vermont Democratic Party. The party currently has very weak electoral power in the state, controlling none of Vermont's federal elected offices. The only statewide office that the party currently controls is the governorship, held by Phil Scott.
The 1840 Democratic National Convention was held in Baltimore, Maryland, from May 5 to May 6. The Democratic Party re-nominated President Martin Van Buren by acclamation, but failed to select a nominee for vice president. Van Buren is the only major party presidential nominee since the ratification of the 12th Amendment to seek election without a running mate. Dragged down by the unpopularity of the Panic of 1837, Van Buren was defeated by the Whig Party's ticket in the 1840 presidential election.

The 1831 National Republican National Convention was held to determine the presidential ticket of the National Republican Party in the 1832 United States presidential election. The convention was held in Baltimore, Maryland in December 1831. The party nominated Senator Henry Clay of Kentucky for president and former Representative John Sergeant of Pennsylvania for vice president.
References
- Cluskey, Michael W. (ed.). The Political Textbook. J.B. Smith & co., Philadelphia: 1860. Google Books digitized version