Related Research Articles

Lesotho's geographic location makes it extremely vulnerable to political and economic developments in South Africa. Its capital is the small city of Maseru. It is a member of many regional economic organizations including the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the Southern African Customs Union (SACU). Lesotho also is active in the United Nations, the Organisation of African Unity, now the African Union, the Non-Aligned Movement, and many other international organizations. In addition to the Republic of Korea, the United States, South Africa, Ireland, People's Republic of China, Libya, and the European Union all currently retain resident diplomatic missions in Lesotho. Foreign relations of Lesotho are administered by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Relations.
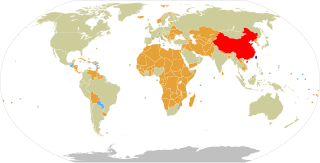
Taiwan, formally known as the Republic of China (ROC), currently has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State, as of 17 February 2024. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories, and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates under the One-China Principle. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.

Since its founding in 1949, the People's Republic of China (PRC) has had a diplomatic tug-of-war with its rival in Taiwan, the Republic of China (ROC). Throughout the Cold War, both governments claimed to be the sole legitimate government of all China and allowed countries to recognize either one or the other. Until the 1970s, most Western countries in the Western Bloc recognized the ROC while the Eastern Bloc and Third World countries generally recognized the PRC. This gradually shifted and today only 11 UN member states recognize the ROC while the PRC is recognized by the United Nations, as well as 181 UN member states. Both the ROC and the PRC maintain the requirement of recognizing its view of the One China policy to establish or maintain diplomatic relations.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China is the first-ranked executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, responsible for the country's foreign relations. It is led by the minister of foreign affairs, currently Wang Yi, who serves as the nation's principal representative abroad. The ministry is headquartered in Chaoyang District, Beijing, the country's primary diplomatic quarter.
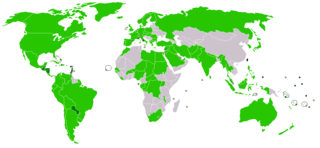
Numerous states have ceased their diplomatic recognition of the Republic of China during the last 70 years, since the founding of the People's Republic of China. Under the One China policy, the ROC is recognized by 11 UN member states and Holy See with 59 UN member states and Somaliland maintaining unofficial cultural and economic relations.

The Republic of Kiribati and the People's Republic of China (PRC) established diplomatic relations on June 25, 1980, and resumed on September 27, 2019. Between 2003 and 2019, The government of Kiribati recognized the Republic of China, and, in accordance with the "One China" policy, the People's Republic of China did not have diplomatic relations to the country.
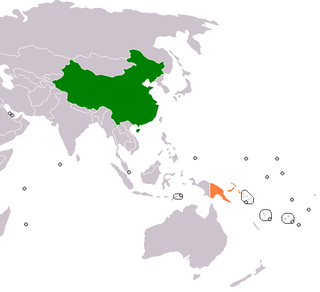
The Independent State of Papua New Guinea and China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations in 1976, soon after Papua New Guinea became independent. The two countries currently maintain diplomatic, economic and, to a lesser degree, military relations. Relations are cordial; China is a significant provider of both investments and development aid to Papua New Guinea.

Samoa and China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations in 1976. The two countries currently maintain cordial relations; China provides economic aid to Samoa.
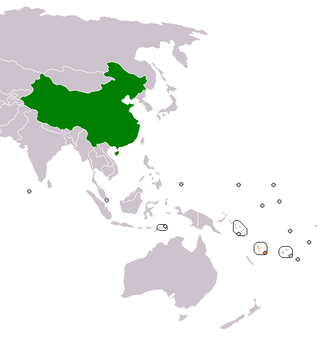
The Republic of Vanuatu and the People's Republic of China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations on March 26, 1982. China established an embassy in Vanuatu in 1989, while Vanuatu established an honorary consulate in China in 1999; it officially became an embassy in 2005. The current Ambassador of China in Vanuatu is Liu Quan. The current Ambassador of Vanuatu in China is former Minister of Finance Willie Jimmy.

The People's Republic of China and Lesotho maintain historical, political, economic, trade, aid, healthcare and migration connections.

Diplomatic relations between China and the Federated States of Micronesia were established on September 11, 1989. The Chinese government first established an embassy in the capital of Palikir in 1990, and dispatched its first ambassador in 1991. In April 2023, the Chinese government allegedly threatened to assassinate the Micronesian president, David Panuelo, and so, Micronesia severed official relations between the two countries. It said it decided to increase relations with Taiwan and it accused China of bribing officials and trying to control the United States’ influence in the region. Initially, the Micronesian ambassador to Tokyo, Japan also served as Micronesia's ambassador to China, before Micronesia established an embassy in Beijing in 2007. President John Haglelgam was the first senior government agent from Micronesia to visit China, doing so in 1990. The current Chinese ambassador to Micronesia is Zhang Weidong, while the Micronesian ambassador to Beijing is Akillino H. Susaia.

Diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and Grenada were established on 1 October 1985. Prime Minister Herbert Blaize established diplomatic relations with the Republic of China in 1989, prompting Beijing to sever diplomatic ties to Grenada. This position was later reversed under Prime Minister Keith Mitchell.

This article contains several lists of ambassadors from China. The incumbents change from time to time; sometimes a post starts or stops being temporarily headed by a lower ranking diplomat. Occasionally, a post is created or abolished.

Lesotho–Russia relations are the bilateral relations between Russia and Lesotho.

Canada and Taiwan have maintained unofficial bilateral relations since 1970. First contacts between Canada and Taiwan began in 1871 with the arrival of George Leslie Mackay.

Solomon Islands and China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations in 2019. Prior to this, Solomon Islands had diplomatic relations with Taiwan.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China, does not have official diplomatic relations with Lithuania, since Lithuania does not officially recognize the Republic of China and maintains a One-China Policy whereby it views the People's Republic of China as the sole legitimate government representing China, including Taiwan. Despite this, relations between Lithuania and Taiwan have grown closer in recent years. In 2021, Taiwan opened the "Taiwanese Representative Office in Lithuania". Meanwhile, Lithuania intends to open a representative office in Taiwan. The recent strengthening of relations between Lithuania and Taiwan in 2021 has been heavily opposed by the People's Republic of China (PRC), which doesn't recognize Taiwan. Notably, the PRC has downgraded its embassy in Lithuania to the status of a "chargé d'affaires" in protest. The PRC and Lithuania had previously maintained full diplomatic relations with one another since 1991.
References
- ↑ Tian Changsong
- ↑ Previous Ambassador, , 驻莱索托历任大使,