
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be command languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipulation, program execution, and printing text. A script which sets up the environment, runs the program, and does any necessary cleanup or logging, is called a wrapper.

A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to control the execution of the system using shell scripts.

The cd command, also known as chdir, is a command-line shell command used to change the current working directory in various operating systems. It can be used in shell scripts and batch files.
In computing, the working directory of a process is a directory of a hierarchical file system, if any, dynamically associated with the process. It is sometimes called the current working directory (CWD), e.g. the BSD getcwd function, or just current directory. When a process refers to a file using a simple file name or relative path (as opposed to a file designated by a full path from a root directory), the reference is interpreted relative to the working directory of the process. So for example a process with working directory /rabbit-shoes that asks to create the file foo.txt will end up creating the file /rabbit-shoes/foo.txt.
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97. The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.

4DOS is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed to replace the default command interpreter COMMAND.COM in Microsoft DOS and Windows. It was written by Rex C. Conn and Tom Rawson and first released in 1989. Compared to the default, it has a large number of enhancements.
In computer programming, glob patterns specify sets of filenames with wildcard characters. For example, the Unix Bash shell command mv *.txttextfiles/ moves all files with names ending in .txt from the current directory to the directory textfiles. Here, * is a wildcard and *.txt is a glob pattern. The wildcard * stands for "any string of any length including empty, but excluding the path separator characters ".
In computing, CLS is a command used by the command-line interpreters COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe on DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems to clear the screen or console window of commands and any output generated by them. It does not clear the user's history of commands, however. The command is also available in the DEC RT-11 operating system, in the open-source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox and in the EFI shell. In other environments, such as Linux and Unix, the same functionality is provided by the clear command.
Command-line completion is a common feature of command-line interpreters, in which the program automatically fills in partially typed commands.

Command Prompt, also known as cmd.exe or cmd, is the default command-line interpreter for the OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems. On Windows CE .NET 4.2, Windows CE 5.0 and Windows Embedded CE 6.0 it is referred to as the Command Processor Shell. Its implementations differ between operating systems, but the behavior and basic set of commands are consistent. cmd.exe is the counterpart of COMMAND.COM in DOS and Windows 9x systems, and analogous to the Unix shells used on Unix-like systems. The initial version of cmd.exe for Windows NT was developed by Therese Stowell. Windows CE 2.11 was the first embedded Windows release to support a console and a Windows CE version of cmd.exe. The ReactOS implementation of cmd.exe is derived from FreeCOM, the FreeDOS command line interpreter.

A command shell is a command-line interface to interact with and manipulate a computer's operating system.
In computing, a shell is a computer program that exposes an operating system's services to a human user or other programs. In general, operating system shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI), depending on a computer's role and particular operation. It is named a shell because it is the outermost layer around the operating system.
Take Command Console (TCC), formerly known as 4DOS for Windows NT (4NT), is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed as a substitute for the default command interpreter in Microsoft Windows, CMD.EXE.
A batch file is a script file in DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows. It consists of a series of commands to be executed by the command-line interpreter, stored in a plain text file. A batch file may contain any command the interpreter accepts interactively and use constructs that enable conditional branching and looping within the batch file, such as IF, FOR, and GOTO labels. The term "batch" is from batch processing, meaning "non-interactive execution", though a batch file might not process a batch of multiple data.
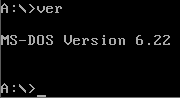
In computing, ver is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe and 4DOS/4NT. It prints the name and version of the operating system, the command shell, or in some implementations the version of other commands. It is roughly equivalent to the Unix command uname.
In computing, pushd and popd are a pair of commands which allow users to quickly switch between the current and previous directory when using the command line. When called, they use a directory stack to sequentially save and retrieve directories visited by the user.

In computing, help is a command in various command line shells such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, Bash, qshell, 4DOS/4NT, Windows PowerShell, Singularity shell, Python, MATLAB and GNU Octave. It provides online information about available commands and the shell environment.

In computing, TIME is a command in DEC RT-11, DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and a number of other operating systems that is used to display and set the current system time. It is included in command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT.

A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with a computer program by inputting lines of text called command-lines. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive interface available with punched cards.








