
Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and designed for businesses as the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0. It was released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, officially released to retail on February 17, 2000, and released on September 26, 2000, for Windows 2000 Datacenter Server. It was Microsoft's business operating system until the introduction of Windows XP Professional in 2001.
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system from 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1 up until Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. From Windows Vista onwards it was replaced by the BOOTMGR bootloader. NTLDR is typically run from the primary storage device, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk. NTLDR can also load a non NT-based operating system given the appropriate boot sector in a file.
The Security Account Manager (SAM) is a database file in Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, 8.1, 10 and 11 that stores users' passwords. It can be used to authenticate local and remote users. Beginning with Windows 2000 SP4, Active Directory authenticates remote users. SAM uses cryptographic measures to prevent unauthenticated users accessing the system.
The Encrypting File System (EFS) on Microsoft Windows is a feature introduced in version 3.0 of NTFS that provides filesystem-level encryption. The technology enables files to be transparently encrypted to protect confidential data from attackers with physical access to the computer.
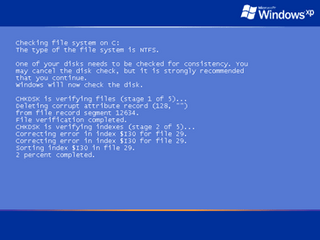
In computing, CHKDSK is a system tool and command in DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and related operating systems. It verifies the file system integrity of a volume and attempts to fix logical file system errors. It is similar to the fsck command in Unix and similar to Microsoft ScanDisk, which co-existed with CHKDSK in Windows 9x and MS-DOS 6.x.

System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows the user to revert their computer's state to that of a previous point in time, which can be used to recover from system malfunctions or other problems. First included in Windows Me, it has been included in all following desktop versions of Windows released since, excluding Windows Server. In Windows 10, System Restore is turned off by default and must be enabled by users in order to function. This does not affect personal files such as documents, music, pictures, and videos.
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).

BartPE is a discontinued tool that customizes Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 into a lightweight environment, similar to Windows Preinstallation Environment, which could be run from a Live CD or Live USB drive. A BartPE system image is created using PE Builder, a freeware program created by Bart Lagerweij.
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition.

Windows Preinstallation Environment is a lightweight version of Windows used for the deployment of PCs, workstations, and servers, or troubleshooting an operating system while it is offline. It is intended to replace MS-DOS boot disks and can be booted via USB flash drive, PXE, iPXE, CD, DVD, or hard disk. Traditionally used by large corporations and OEMs, it is now widely available free of charge via Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (WADK).
As the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000, as well as the successor to Windows Me, Windows XP introduced many new features but it also removed some others.
In computing, bootcfg is a command on Microsoft Windows NT-based operating systems which acts as a wrapper for editing the boot.ini file.

In computing, ATTRIB is a command in Intel ISIS-II, DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS that allows the user to change various characteristics, or "attributes" of a computer file or directory. The command is also available in the EFI shell.
NTBackup is the first built-in backup utility of the Windows NT family. It was introduced with Windows NT 3.51. NTBackup comprises a GUI (wizard-style) and a command-line utility to create, customize, and manage backups. It takes advantage of Shadow Copy and Task Scheduler. NTBackup stores backups in the BKF file format on external sources, e.g., floppy disks, hard drives, tape drives, and Zip drives. When used with tape drives, NTBackup uses the Microsoft Tape Format (MTF), which is also used by BackupAssist, Backup Exec, and Veeam Backup & Replication and is compatible with BKF.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
A Microsoft Windows Emergency Repair Disk (ERD) is a specially formatted diskette that creates backups of important system files and settings and is used to troubleshoot and repair problems in Microsoft Windows NT and Windows 2000 systems. An ERD is used in conjunction with the Windows repair option. The Emergency Repair Disk provides only the ability to restore the system to a bootable state. It is not a replacement for system and file backups. Note: The emergency repair disk is not to be confused with a standard boot diskette as it cannot be used alone.
A System Deployment Image is a file format used primarily with Microsoft products to contain an arbitrary disk image, including boot sector information.

In computing, diskpart is a command-line disk partitioning utility included in Windows 2000 and later Microsoft operating systems, replacing its predecessor, fdisk. The command is also available in ReactOS.
In computing, WBAdmin is a command-line utility built into Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 10 and Windows 11 operating systems. The command is used to perform backups and restores of operating systems, drive volumes, computer files, folders, and applications from a command-line interface.







