Virtual PC is a discontinued x86 emulator for PowerPC Mac hosts and a hypervisor for Microsoft Windows hosts. It was created by Connectix in 1997 and acquired by Microsoft in 2003. The Mac version was discontinued in 2006 following the Mac transition to Intel, while the Windows version was discontinued in 2011 in favour of Hyper-V.

In computing, a service pack comprises a collection of updates, fixes, or enhancements to a software program delivered in the form of a single installable package. Companies often release a service pack when the number of individual patches to a given program reaches a certain (arbitrary) limit, or the software release has shown to be stabilized with a limited number of remaining issues based on users' feedback and bug reports. In large software applications such as office suites, operating systems, database software, or network management, it is not uncommon to have a service pack issued within the first year or two of a product's release. Installing a service pack is easier and less error-prone than installing many individual patches, even more so when updating multiple computers over a network, where service packs are common.
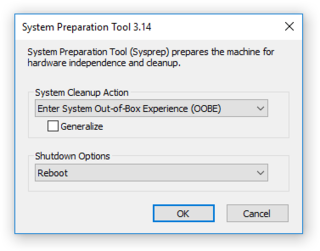
Sysprep is Microsoft's System Preparation Tool for Microsoft Windows operating system deployment.

Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.

Windows Server 2008, codenamed "Longhorn Server", is the eighth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2. It removed support for processors without ACPI, and is the first version that includes Hyper-V.

Windows Preinstallation Environment is a lightweight version of Windows used for the deployment of PCs, workstations, and servers, or troubleshooting an operating system while it is offline. It is intended to replace MS-DOS boot disks and can be booted via USB flash drive, PXE, iPXE, CD, DVD, or hard disk. Traditionally used by large corporations and OEMs, it is now widely available free of charge via Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (WADK).
Microsoft Windows SDK, and its predecessors Platform SDK, and .NET Framework SDK, are software development kits (SDKs) from Microsoft that contain documentation, header files, libraries, samples and tools required to develop applications for Microsoft Windows and .NET Framework. Platform SDK specializes in developing applications for Windows 2000, XP and Windows Server 2003. .NET Framework SDK is dedicated to developing applications for .NET Framework 1.1 and .NET Framework 2.0. Windows SDK is the successor of the two and supports developing applications for Windows XP and later, as well as .NET Framework 3.0 and later.
Microsoft Virtual Server was a virtualization solution that facilitated the creation of virtual machines on the Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2003 operating systems. Originally developed by Connectix, it was acquired by Microsoft prior to release. Virtual PC is Microsoft's related desktop virtualization software package.
The Windows Imaging Format (WIM) is a file-based disk image format. It was developed by Microsoft to help deploy Windows Vista and subsequent versions of the Windows operating system family, as well as Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.

Microsoft Management Console (MMC) is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides system administrators and advanced users an interface for configuring and monitoring the system. It was first introduced in 1998 with the Option Pack for Windows NT 4.0 and later came pre-bundled with Windows 2000 and its successors.
Resource Kit is a term used by Microsoft for a set of software resources and documentation released for their software products, but which is not part of that product. Resource kits offer supplementary resources such as technical guidance, compatibility and troubleshooting information, management, support, maintenance and deployment guides and multipurpose useful administrative utilities, which are available separately.

Software remastering is software development that recreates system software and applications while incorporating customizations, with the intent that it is copied and run elsewhere for "off-label" usage. The term comes from remastering in media production, where it is similarly distinguished from mere copying.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
Windows Deployment Services (WDS) is a deprecated component of the Windows Server operating system that enables centralized, network-based deployment of operating systems to bare-metal computers. It is the successor to Remote Installation Services (RIS). WDS officially supports remote deployment of Windows Vista and later, as well as Windows Server 2008 and later. However, because WDS uses disk imaging, in particular the Windows Imaging Format (WIM), it could deploy virtually any operating system. This is in contrast with its predecessor, RIS, which was a method of automating the installation process.
Windows XP, which is the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000 and the successor to the consumer-oriented Windows Me, has been released in several editions since its original release in 2001.
Microsoft Deployment Toolkit is a free software package from Microsoft for automating the deployment of Windows 10, Server 2019 and older Windows Server and desktop operating systems.
Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995.
The User State Migration Tool (USMT) is a command line utility program developed by Microsoft that allows users comfortable with scripting languages to transfer files and settings between Windows PCs. This task is also performed by Windows Easy Transfer, which was designed for general users but then discontinued with the release of Windows 10, where they instead partnered with Laplink. Starting with Windows 8, many settings and data are now being synchronized in cloud services via a Microsoft Account and OneDrive. USMT allows a high-volume, automated deployment of files and settings, and is also useful in migrating user settings and files during OS upgrades. Because USMT has high complexity and a command line interface, there have been several attempts to provide access to its useful functionality by creating GUI wrappers for it. 32-bit to 64-bit migrations are supported, but 64-bit to 32-bit are not.
Side-by-side assembly technology is a standard for executable files in Windows 98 Second Edition, Windows 2000, and later versions of Windows that attempts to alleviate problems that arise from the use of dynamic-link libraries (DLLs) in Microsoft Windows. Such problems include version conflicts, missing DLLs, duplicate DLLs, and incorrect or missing registration. In side-by-side, Windows stores multiple versions of a DLL in the %systemroot%\WinSxS directory, and loads them on demand. This reduces dependency problems for applications that include a side-by-side manifest.

Microsoft started development on the .NET Framework in the late 1990s originally under the name of Next Generation Windows Services (NGWS). By late 2001 the first beta versions of .NET Framework 1.0 were released. The first version of .NET Framework was released on 13 February 2002, bringing managed code to Windows NT 4.0, 98, 2000, ME and XP.







