An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label such as 192.0.2.1 that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: network interface identification and location addressing.
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating success or failure when communicating with another IP address, for example, an error is indicated when a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached. ICMP differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications.

Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. IPv4 was the first version deployed for production on SATNET in 1982 and on the ARPANET in January 1983. It is still used to route most Internet traffic today, even with the ongoing deployment of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), its successor.

Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and is intended to replace IPv4. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, which subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on labels rather than network addresses. Whereas network addresses identify endpoints the labels identify established paths between endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the multiprotocol component of the name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.

ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available for virtually all operating systems that have networking capability, including most embedded network administration software.
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone network (PSTN), and computer networks, such as the Internet.
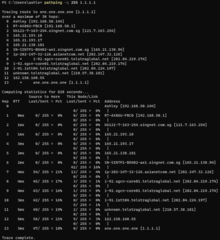
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point.

In computer networking, IP over Avian Carriers (IPoAC) is a joke proposal to carry Internet Protocol (IP) traffic by birds such as homing pigeons. IP over Avian Carriers was initially described in RFC 1149 issued by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), written by D. Waitzman, and released on April 1, 1990. It is one of several April Fools' Day Request for Comments.
In computer networking, a routing table, or routing information base (RIB), is a data table stored in a router or a network host that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics (distances) associated with those routes. The routing table contains information about the topology of the network immediately around it.

Nmap is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses.
A default gateway is the node in a computer network using the Internet protocol suite that serves as the forwarding host (router) to other networks when no other route specification matches the destination IP address of a packet.
anoNet is a decentralized friend-to-friend network built using VPNs and software BGP routers. anoNet works by making it difficult to learn the identities of others on the network allowing them to anonymously host IPv4 and IPv6 services.
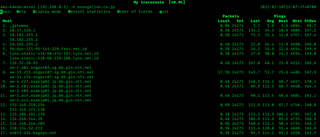
My traceroute, originally named Matt's traceroute (MTR), is a computer program which combines the functions of the traceroute and ping programs in one network diagnostic tool.
Sockstress is a method that is used to attack servers on the Internet and other networks utilizing TCP, including Windows, Mac, Linux, BSD and any router or other internet appliance that accepts TCP connections. The method does this by attempting to use up local resources in order to crash a service or the entire machine, essentially a denial of service attack.
In wired computer networking, including the Internet, a hop occurs when a packet is passed from one network segment to the next. Data packets pass through routers as they travel between source and destination. The hop count refers to the number of network devices through which data passes from source to destination.

In computing, route is a command used to view and manipulate the IP routing table in Unix-like and Microsoft Windows operating systems and also in IBM OS/2 and ReactOS. Manual manipulation of the routing table is characteristic of static routing.
IP routing is the application of routing methodologies to IP networks. This involves not only protocols and technologies but includes the policies of the worldwide organization and configuration of Internet infrastructure. In each IP network node, IP routing involves the determination of a suitable path for a network packet from a source to its destination in an IP network. The process uses static configuration rules or dynamically obtained from routing protocols to select specific packet forwarding methods to direct traffic to the next available intermediate network node one hop closer to the desired final destination, a total path potentially spanning multiple computer networks.
Bufferbloat is a cause of high latency and jitter in packet-switched networks caused by excess buffering of packets. Bufferbloat can also cause packet delay variation, as well as reduce the overall network throughput. When a router or switch is configured to use excessively large buffers, even very high-speed networks can become practically unusable for many interactive applications like voice over IP (VoIP), audio streaming, online gaming, and even ordinary web browsing.
A network extrusion is a kind of VPN tunnel where a subnet is moved to another location, without any router advertisement changes. Such a subnet is routed to normally, but then send via a VPN tunnel to appear anywhere else on the internet. This type of VPN connection is often used for: