
The cd command, also known as chdir, is a command-line shell command used to change the current working directory in various operating systems. It can be used in shell scripts and batch files.

In computing, dir (directory) is a command in various computer operating systems used for computer file and directory listing. It is one of the basic commands to help navigate the file system. The command is usually implemented as an internal command in the command-line interpreter (shell). On some systems, a more graphical representation of the directory structure can be displayed using the tree command.

The mkdir command in the Unix, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems is used to make a new directory. It is also available in the EFI shell and in the PHP scripting language. In DOS, OS/2, Windows and ReactOS, the command is often abbreviated to md.

fdisk is a command-line utility for disk partitioning. It has been part of DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and early versions of Microsoft Windows, as well as certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. Windows 2000 and its successors have replaced fdisk with a more advanced tool called diskpart.
In computing, CLS is a command used by the command-line interpreters COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe on DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems to clear the screen or console window of commands and any output generated by them. It does not clear the user's history of commands, however. The command is also available in the DEC RT-11 operating system, in the open-source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox and in the EFI shell. In other environments, such as Linux and Unix, the same functionality is provided by the clear command.

In computing, XCOPY is a command used on IBM PC DOS, MS-DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, FreeDOS, ReactOS, and related operating systems for copying multiple files or entire directory trees from one directory to another and for copying files across a network.
File attributes are a type of meta-data that describe and may modify how files and/or directories in a filesystem behave. Typical file attributes may, for example, indicate or specify whether a file is visible, modifiable, compressed, or encrypted. The availability of most file attributes depends on support by the underlying filesystem where attribute data must be stored along with other control structures. Each attribute can have one of two states: set and cleared. Attributes are considered distinct from other metadata, such as dates and times, filename extensions or file system permissions. In addition to files, folders, volumes and other file system objects may have attributes.

In computing, tree is a recursive directory listing command or program that produces a depth-indented listing of files. Originating in PC- and MS-DOS, it is found in Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, PTS-DOS, FreeDOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS. A version for Unix and Unix-like systems is also available.
In computing, DELTREE is a command line command in some Microsoft operating systems, SpartaDOS X and FreeDOS that recursively deletes an entire subdirectory of files.

In computing, del is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, NDOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to delete one or more files or directories from a file system.
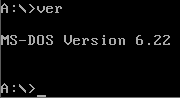
In computing, ver is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe and 4DOS/4NT. It prints the name and version of the operating system, the command shell, or in some implementations the version of other commands. It is roughly equivalent to the Unix command uname.

In computing, find is a command in the command-line interpreters (shells) of a number of operating systems. It is used to search for a specific text string in a file or files. The command sends the specified lines to the standard output device.
In some operating systems, vol is a command within the command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe. It is used to display the volume label and volume serial number of a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk, if they exist.

In computing, help is a command in various command line shells such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, Bash, qshell, 4DOS/4NT, Windows PowerShell, Singularity shell, Python, MATLAB and GNU Octave. It provides online information about available commands and the shell environment.

In computing, copy is a command in various operating systems. The command copies computer files from one directory to another.

In computing, TIME is a command in DEC RT-11, DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and a number of other operating systems that is used to display and set the current system time. It is included in command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT.

In computing, format, a command-line utility that carries out disk formatting. It is a component of various operating systems, including 86-DOS, MS-DOS, IBM PC DOS and OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS.
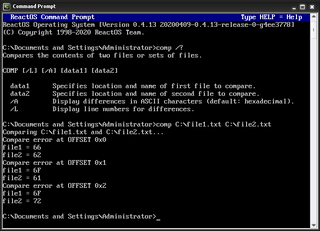
In computing, comp is a command used on DEC OS/8, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and related computer operating systems such as ReactOS. It is used to perform comparisons of multiple computer files to show the differences between them.
In computing, diskcomp is a command used for comparing the complete contents of a floppy disk to another one.














