The cd command, also known as chdir, is a command-line shell command used to change the current working directory in various operating systems. It can be used in shell scripts and batch files.

The mkdir command in the Unix, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems is used to make a new directory. It is also available in the EFI shell and in the PHP scripting language. In DOS, OS/2, Windows and ReactOS, the command is often abbreviated to md.
In computing, rmdir is a command which will remove an empty directory on various operating systems.
In computing, CLS is a command used by the command-line interpreters COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe on DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems to clear the screen or console window of commands and any output generated by them. It does not clear the user's history of commands, however. The command is also available in the DEC RT-11 operating system, in the open-source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox and in the EFI shell. In other environments, such as Linux and Unix, the same functionality is provided by the clear command.
In computing, echo is a command that outputs the strings that are passed to it as arguments. It is a command available in various operating system shells and typically used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a computer file, or as a source part of a pipeline.

Command Prompt, also known as cmd.exe or cmd, is the default command-line interpreter for the OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems. On Windows CE .NET 4.2, Windows CE 5.0 and Windows Embedded CE 6.0 it is referred to as the Command Processor Shell. Its implementations differ between operating systems, but the behavior and basic set of commands are consistent. cmd.exe is the counterpart of COMMAND.COM in DOS and Windows 9x systems, and analogous to the Unix shells used on Unix-like systems. The initial version of cmd.exe for Windows NT was developed by Therese Stowell. Windows CE 2.11 was the first embedded Windows release to support a console and a Windows CE version of cmd.exe. The ReactOS implementation of cmd.exe is derived from FreeCOM, the FreeDOS command line interpreter.

In computing, exit is a command used in many operating system command-line shells and scripting languages.

In computing, more is a command to view the contents of a text file one screen at a time. It is available on Unix and Unix-like systems, DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS. Programs of this sort are called pagers. more is a very basic pager, originally allowing only forward navigation through a file, though newer implementations do allow for limited backward movement.

In computing, move is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS/4NT, and PowerShell. It is used to move one or more files or directories from one place to another. The original file is deleted, and the new file may have the same or a different name. The command is analogous to the Unix mv command and to the OpenVOS move_file and move_dircommands.

In computing, ren is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, 4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to rename computer files and in some implementations also directories. It is analogous to the Unix mv command. However, unlike mv, ren cannot be used to move files, as a new directory for the destination file may not be used. Alternatively, move may be used if available. On versions of MS-DOS that do not support the move command, the user would simply copy the file to a new destination, and then delete the original file. A notable exception to this rule is DOSBox, in which ren may be used to move a file, since move is not supported.

In computing, type is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS/4NT and Windows PowerShell used to display the contents of specified files on the computer terminal. The analogous Unix command is cat.

In computing, del is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, NDOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to delete one or more files or directories from a file system.

In computing, the print command provides single-user print spooling capability in a number of operating systems. It is roughly similar to that provided by the UNIX System V lp and BSD lpr print spooler systems.

In computing, find is a command in the command-line interpreters (shells) of a number of operating systems. It is used to search for a specific text string in a file or files. The command sends the specified lines to the standard output device.
In some operating systems, vol is a command within the command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe. It is used to display the volume label and volume serial number of a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk, if they exist.

In computing, help is a command in various command line shells such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, Bash, qshell, 4DOS/4NT, Windows PowerShell, Singularity shell, Python, MATLAB and GNU Octave. It provides online information about available commands and the shell environment.

In computing, TIME is a command in DEC RT-11, DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and a number of other operating systems that is used to display and set the current system time. It is included in command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.

In computing, net is a command in IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, ReactOS and Greentea OS used to manage and configure the operating system from the command-line. It is also part of the IBM PC Network Program for DOS.
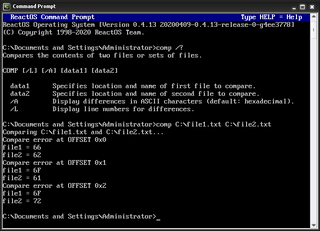
In computing, comp is a command used on DEC OS/8, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and related computer operating systems such as ReactOS. It is used to perform comparisons of multiple computer files to show the differences between them.