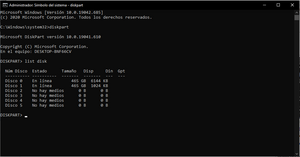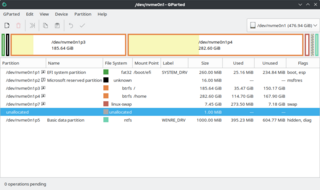
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk after a partitioning scheme is chosen for the new disk before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
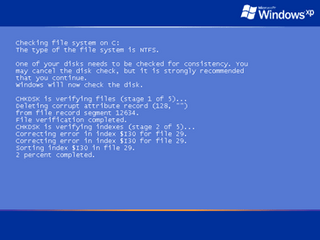
In computing, CHKDSK is a system tool and command in DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and related operating systems. It verifies the file system integrity of a volume and attempts to fix logical file system errors. It is similar to the fsck command in Unix and similar to Microsoft ScanDisk, which co-existed with CHKDSK in Windows 9x and MS-DOS 6.x.

System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows the user to revert their computer's state to that of a previous point in time, which can be used to recover from system malfunctions or other problems. First included in Windows Me, it has been included in all following desktop versions of Windows released since, excluding Windows Server. In Windows 10, System Restore is turned off by default and must be enabled by users in order to function. This does not affect personal files such as documents, music, pictures, and videos.
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition.
In computing, SUBST is a command on the DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems used for substituting paths on physical and logical drives as virtual drives.
The Logical Disk Manager (LDM) is an implementation of a logical volume manager for Microsoft Windows NT, developed by Microsoft and Veritas Software. It was introduced with the Windows 2000 operating system, and is supported in Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 and Windows 11. The MMC-based Disk Management snap-in hosts the Logical Disk Manager. On Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, Microsoft deprecated LDM in favor of Storage Spaces.

TestDisk is a free and open-source data recovery utility that helps users recover lost partitions or repair corrupted filesystems. TestDisk can collect detailed information about a corrupted drive, which can then be sent to a technician for further analysis. TestDisk supports DOS, Microsoft Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, SunOS, and MacOS. TestDisk handles non-partitioned and partitioned media. In particular, it recognizes the GUID Partition Table (GPT), Apple partition map, PC/Intel BIOS partition tables, Sun Solaris slice and Xbox fixed partitioning scheme. TestDisk uses a command line user interface. TestDisk can recover deleted files with 97% accuracy.
In Windows NT operating systems, a Windows service is a computer program that operates in the background. It is similar in concept to a Unix daemon. A Windows service must conform to the interface rules and protocols of the Service Control Manager, the component responsible for managing Windows services. It is the Services and Controller app, services.exe, that launches all the services and manages their actions, such as start, end, etc.

The Recovery Console is a feature of the Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 operating systems. It provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command-line interface.

Microsoft Drive Optimizer is a utility in Microsoft Windows designed to increase data access speed by rearranging files stored on a disk to occupy contiguous storage locations, a technique called defragmentation. Microsoft Drive Optimizer was first officially shipped with Windows XP.
The NTFS file system defines various ways to redirect files and folders, e.g., to make a file point to another file or its contents without making a copy of it. The object being pointed to is called the target. Such file is called a hard or symbolic link depending on a way it's stored on the filesystem.
NTBackup is the first built-in backup utility of the Windows NT family. It was introduced with Windows NT 3.51. NTBackup comprises a GUI (wizard-style) and a command-line utility to create, customize, and manage backups. It takes advantage of Shadow Copy and Task Scheduler. NTBackup stores backups in the BKF file format on external sources, e.g., floppy disks, hard drives, tape drives, and Zip drives. When used with tape drives, NTBackup uses the Microsoft Tape Format (MTF), which is also used by BackupAssist, Backup Exec, and Veeam Backup & Replication and is compatible with BKF.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
In computing, label is a command included with some operating systems. It is used to create, change, or delete a volume label on a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk. Used without parameters, label changes the current volume label or deletes the existing label.
In some operating systems, vol is a command within the command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe. It is used to display the volume label and volume serial number of a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk, if they exist.
In computing, WBAdmin is a command-line utility built into Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 10 and Windows 11 operating systems. The command is used to perform backups and restores of operating systems, drive volumes, computer files, folders, and applications from a command-line interface.
Ranish Partition Manager is a freeware hard disk partition editor, disk cloning utility, and boot manager, that gives a high level of control for creating multi-boot systems. It is available on the freeware live CD SystemRescueCD and the Ultimate Boot CD. It runs under MS-DOS, PC DOS, DR-DOS, or FreeDOS.
In computing, systeminfo, is a command-line utility included in Microsoft Windows versions from Windows XP onwards and in ReactOS.
Hetman Partition Recovery is a shareware program for recovery of deleted data from hard drive partitions and other storage media. The utility supports both functioning disks and damaged logical partitions and recovers data from both reformatted disks and disks which have had their file system changed from FAT to NTFS or vice versa. In addition to working on existing partitions the tool can also find deleted logical drives, displaying them to the user for further search and recovery of deleted files as well as correcting errors in logical partition design. Hetman Partition Recovery supports reading of regular, zipped, and encrypted files, from disks formatted under NTFS and/or FAT file systems.