
Extreme poverty is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, including food, safe drinking water, sanitation facilities, health, shelter, education and information. It depends not only on income but also on access to services". Historically, other definitions have been proposed within the United Nations.

The economy of Cambodia currently follows an open market system and has seen rapid economic progress in the last decade. Cambodia had a gross domestic product (GDP) of $28.54 billion in 2022. Per capita income, although rapidly increasing, is low compared with most neighboring countries. Cambodia's two largest industries are textiles and tourism, while agricultural activities remain the main source of income for many Cambodians living in rural areas. The service sector is heavily concentrated on trading activities and catering-related services. Recently, Cambodia has reported that oil and natural gas reserves have been found off-shore.

The economy of Colombia is the fourth largest in Latin America as measured by gross domestic product and the third-largest economy in South America. Colombia has experienced a historic economic boom over the last decade. Throughout most of the 20th century, Colombia was Latin America's 4th and 3rd largest economy when measured by nominal GDP, real GDP, GDP (PPP), and real GDP at chained PPPs. Between 2012 and 2014, it became the third largest in Latin America by nominal GDP. As of 2024, the GDP (PPP) per capita has increased to over US$19,000, and real gross domestic product at chained PPPs increased from US$250 billion in 1990 to nearly US$800 billion. Poverty levels were as high as 65% in 1990, but decreased to under 30% by 2014, and 27% by 2018. They decreased by an average of 1.35% per year since 1990.

The economy of Guatemala is a considered a developing economy, highly dependent on agriculture, particularly on traditional crops such as coffee, sugar, and bananas. Guatemala's GDP per capita is roughly one-third of Brazil's. The Guatemalan economy is the largest in Central America. It grew 3.3 percent on average from 2015 to 2018. However, Guatemala remains one of the poorest countries in Latin America and the Caribbean, having highly unequal incomes and chronically malnourished children. The country is beset by political insecurity, and lacks skilled workers and infrastructure. It depends on remittances for nearly one-tenth of the GDP.

Haiti has a free market economy with low labor costs. A republic, it was a French colony before gaining independence in an uprising by its enslaved people. It faced embargoes and isolation after its independence as well as political crises punctuated by foreign interventions and devastating natural disasters. Haiti's estimated population in 2018 was 11,439,646. The Economist reported in 2010: "Long known as the poorest country in the Western hemisphere, Haiti has stumbled from one crisis to another since the Duvalier years."

The economy of Jordan is classified as a lower middle income economy. Jordan's GDP per capita rose by 351% in the 1970s, declined 30% in the 1980s, and rose 36% in the 1990s. After King Abdullah II's accession to the throne in 1999, liberal economic policies were introduced. Jordan's economy had been growing at an annual rate of 8% between 1999 and 2008. However, growth has slowed to 2% after the Arab Spring in 2011. The substantial increase of the population, coupled with slowed economic growth and rising public debt led to a worsening of poverty and unemployment in the country. As of 2023, Jordan has a GDP of US$50.85 billion, ranking it 89th worldwide.

The economy of Malawi is $7.522 billion by gross domestic product as of 2019, and is predominantly agricultural, with about 80% of the population living in rural areas. The landlocked country in south central Africa ranks among the world's least developed countries and poorest countries. Approximately 50% of the population lives below the national poverty line, with 25% living in extreme poverty.

The economy of Nicaragua is focused primarily on the agricultural sector. Nicaragua itself is the least developed country in Central America, and the second least developed in the Americas by nominal GDP, behind only Haiti. In recent years, under the administrations of Daniel Ortega, the Nicaraguan economy has expanded somewhat, following the Great Recession, when the country's economy actually contracted by 1.5%, due to decreased export demand in the American and Central American markets, lower commodity prices for key agricultural exports, and low remittance growth. The economy saw 4.5% growth in 2010 thanks to a recovery in export demand and growth in its tourism industry. Nicaragua's economy continues to post growth, with preliminary indicators showing the Nicaraguan economy growing an additional 5% in 2011. Consumer Price inflation have also curtailed since 2008, when Nicaragua's inflation rate hovered at 19.82%. In 2009 and 2010, the country posted lower inflation rates, 3.68% and 5.45%, respectively. Remittances are a major source of income, equivalent to 15% of the country's GDP, which originate primarily from Costa Rica, the United States, and European Union member states. Approximately one million Nicaraguans contribute to the remittance sector of the economy.

The gross domestic product (GDP) of Niger was $16.617 billion US dollars in 2023, according to official data from the World Bank. This data is based largely on internal markets, subsistence agriculture, and the export of raw commodities: foodstuffs to neighbors and raw minerals to world markets. Niger, a landlocked West African nation that straddles the Sahel, has consistently been ranked on the bottom of the Human Development Index, at 0.394 as of 2019. It has a very low per capita income, and ranks among the least developed and most heavily indebted countries in the world, despite having large raw commodities and a relatively stable government and society not currently affected by civil war or terrorism. Economic activity centers on subsistence agriculture, animal husbandry, re-export trade, and export of uranium.

Somalia is classified by the United Nations as a least developed country, with the majority of its population being dependent on agriculture and livestock for their livelihood. The economy of Somalia is $4.918 billion by gross domestic product as of 2020. For 1994, the CIA estimated it at purchasing power parity to be approximately $3.3 billion. In 2001, it was estimated to be $4.1 billion. By 2009, the CIA estimated that it had grown to $5.731 billion, with a projected real growth rate of 2.6%. In 2014, the International Monetary Fund estimated economic activity to have expanded by 3.7% primarily. This expansion was driven by growth in the primary sector and the secondary sector. According to a 2007 British Chambers of Commerce report, the private sector has experienced growth, particularly in the service sector. Unlike the pre-civil war period, when most services and the industrial sector were government-run, there has been substantial, albeit unmeasured, private investment in commercial activities. The investment has been largely financed by the Somali diaspora, and includes trade and marketing, money transfer services, transportation, communications, fishery equipment, airlines, telecommunications, education, health, construction and hotels.

The United States is a highly developed mixed economy. It is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP; it is also the second largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), behind China. It has the world's sixth highest per capita GDP (nominal) and the eighth highest per capita GDP (PPP) as of 2024. The U.S. accounted for 26% of the global economy in 2023 in nominal terms, and about 15.5% in PPP terms. The U.S. dollar is the currency of record most used in international transactions and is the world's reserve currency, backed by a large U.S. treasuries market, its role as the reference standard for the petrodollar system, and its linked eurodollar. Several countries use it as their official currency and in others it is the de facto currency. Since the end of World War II, the economy has achieved relatively steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid advances in technology.

The economy of Venezuela is based primarily on petroleum, as the country holds the largest crude oil supply in the world. Venezuela was historically among the wealthiest economies in South America, particularly from the 1950s to 1980s. During the 21st century, under the leadership of socialist populist Hugo Chávez and his successor Nicolás Maduro, the Venezuelan economy has collapsed, prompting millions of citizens to flee Venezuela. GDP has fallen by 80 percent in less than a decade. The economy is characterized by corruption, good shortages, unemployment, mismanagement of the oil sector, and since 2014, hyperinflation.

The economy of France is a highly developed social market economy with notable state participation in strategic sectors. It is the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and the ninth-largest economy by PPP, constituting around 4% of world GDP. Due to a volatile currency exchange rate, France's GDP as measured in dollars fluctuates sharply, being smaller in 2024 than in 2008. France has a diversified economy, that is dominated by the service sector, whilst the industrial sector accounted for 19.5% of its GDP and the primary sector accounted for the remaining 1.7%. In 2020, France was the largest Foreign Direct Investment recipient in Europe, and Europe's second largest spender in research and development. It was ranked among the 10 most innovative countries in the world by the 2020 Bloomberg Innovation Index, as well as the 15th most competitive nation globally according to the 2019 Global Competitiveness Report. It was the fifth-largest trading nation in the world. France is also the most visited destination in the world, as well as the European Union's leading agricultural power.

The economy of Bolivia is the 95th-largest in the world in nominal terms and the 87th-largest in purchasing power parity. Bolivia is classified by the World Bank to be a lower middle income country. With a Human Development Index of 0.703, it is ranked 114th. Driven largely by its natural resources, Bolivia has become a region leader in measures of economic growth, fiscal stability and foreign reserves, although it remains a historically poor country. The Bolivian economy has had a historic single-commodity focus. From silver to tin to coca, Bolivia has enjoyed only occasional periods of economic diversification. Political instability and difficult topography have constrained efforts to modernize the agricultural sector. Similarly, relatively low population growth coupled with low life expectancy has kept the labor supply in flux and prevented industries from flourishing. Rampant inflation and corruption previously created development challenges, but in the early twenty-first century the fundamentals of its economy showed unexpected improvement, leading Moody's Investors Service to upgrade Bolivia's economic rating in 2010 from B2 to B1. The mining industry, especially the extraction of natural gas and zinc, currently dominates Bolivia's export economy.

The economy of Africa consists of the trade, industry, agriculture, and human resources of the continent. As of 2019, approximately 1.3 billion people were living in 53 countries in Africa. Africa is a resource-rich continent. Recent growth has been due to growth in sales, commodities, services, and manufacturing. West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa and Southern Africa in particular, are expected to reach a combined GDP of $29 trillion by 2050.
The economic development in India followed socialist-inspired politicians for most of its independent history, including state-ownership of many sectors; India's per capita income increased at only around 1% annualised rate in the three decades after its independence. Since the mid-1980s, India has slowly opened up its markets through economic liberalisation. After more fundamental reforms since 1991 and their renewal in the 2000s, India has progressed towards a free market economy. The Indian economy is still performing well, with foreign investment and looser regulations driving significant growth in the country.

The causes of poverty may vary with respect to nation, region, and in comparison with other countries at the global level. Yet, there is a commonality amongst these causes. Philosophical perspectives and especially historical perspectives, including some factors at a micro and macro level can be considered in understanding these causes.

Poverty in Haiti is a long lasting issue that affects the residents on a daily basis playing a significant role in their everyday lives. Issues including housing, nutrition, education, healthcare, infant mortality rates, and environmental factors are very common amongst the poorest communities in the nation. Haiti has long struggled with poor living conditions in the more rural areas of the country causing many Haitians to migrate towards the capital city of Port-au-Prince. Poverty in Haiti is regarded as among the most severe in the Western hemisphere.
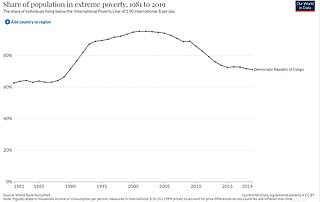
Poverty is widespread and unchecked across the 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Despite being the second-largest country in Africa, with an approximate area of 2.3 million square kilometres (890,000 sq mi), and being endowed with rich natural resources, the DRC is the second-poorest country in the world. The average annual income is only $449 US dollars. In 2019, the United Nations (UN) Human Development Index (HDI) ranked the DRC as the 175th least-developed country out of 189 countries with an HDI of 0.480. In 2023, almost 75% of Congolese people live on less than $2.15 a day, defined as the threshold for extreme poverty.




















