
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system on the North American continent, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for 2,340 miles (3,770 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The longest river in Africa, it has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer. The Nile is amongst the smallest of the major world rivers by measure of cubic metres flowing annually. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. Additionally, the Nile is an important economic river, supporting agriculture and fishing.

The Bridge on the River Kwai is a 1957 epic war film directed by David Lean and based on the 1952 novel written by Pierre Boulle. Although the film uses the historical setting of the construction of the Burma Railway in 1942–1943, the plot and characters of Boulle's novel and the screenplay are almost entirely fictional. The cast includes Alec Guinness, William Holden, Jack Hawkins, and Sessue Hayakawa.

The Brooklyn Bridge is a hybrid cable-stayed/suspension bridge in New York City, spanning the East River between the boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn. Opened on May 24, 1883, the Brooklyn Bridge was the first fixed crossing of the East River. It was also the longest suspension bridge in the world at the time of its opening, with a main span of 1,595.5 feet (486.3 m) and a deck 127 ft (38.7 m) above mean high water. The span was originally called the New York and Brooklyn Bridge or the East River Bridge but was officially renamed the Brooklyn Bridge in 1915.

The Krishna River is the fourth-largest river in terms of water inflows and river basin area in India, after the Ganges, Godavari and Brahmaputra. The river, also called Krishnaveni, is almost 1,288 kilometres (800 mi) long. It is a major source of irrigation in the Indian states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.

The Hudson River is a 315-mile (507 km) river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York in the United States. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the Upper New York Bay between New York City and Jersey City, eventually draining into the Atlantic Ocean at New York Harbor. The river serves as a political boundary between the states of New Jersey and New York at its southern end. Farther north, it marks local boundaries between several New York counties. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet which formed during the most recent period of North American glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Even as far north as the city of Troy, the flow of the river changes direction with the tides.

The Godavari is India's second longest river after the Ganga and third largest in India, drains about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra. It flows east for 1,465 kilometres (910 mi), draining the states of Maharashtra (48.6%), Telangana (18.8%), Andhra Pradesh (4.5%), Chhattisgarh (10.9%) and Odisha (5.7%). The river ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal through an extensive network of tributaries. Measuring up to 312,812 km2 (120,777 sq mi), it forms one of the largest river basins in the Indian subcontinent, with only the Ganga and Indus rivers having a larger drainage basin. In terms of length, catchment area and discharge, the Godavari is the largest in peninsular India, and had been dubbed as the Dakshina Ganga.
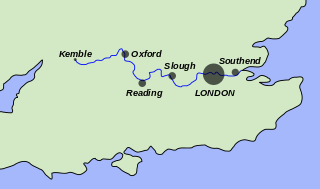
The River Thames, known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England, including London. At 215 mi (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.

The River Severn, at 220 miles (354 km) long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of 107 m3/s (3,800 cu ft/s) at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in the Cambrian Mountains in mid Wales, at an altitude of 2,001 feet (610 m), on the Plynlimon massif, which lies close to the Ceredigion/Powys border near Llanidloes. The river then flows through Shropshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire. The county towns of Shrewsbury, Gloucester and the City of Worcester lie on its course.

Tower Bridge is a Grade I listed combined bascule and suspension bridge in London, built between 1886 and 1894, designed by Horace Jones and engineered by John Wolfe Barry with the help of Henry Marc Brunel. It crosses the River Thames close to the Tower of London and is one of five London bridges owned and maintained by the Bridge House Estates, a charitable trust founded in 1282. The bridge was constructed to give better access to the East End of London, which had expanded its commercial potential in the 19th century. The bridge was opened by Edward, Prince of Wales and Alexandra, Princess of Wales in 1894.

Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It replaced a 19th-century stone-arched bridge, which in turn superseded a 600-year-old stone-built medieval structure. This was preceded by a succession of timber bridges, the first of which was built by the Roman founders of London.

The River Liffey is a river in eastern Ireland that ultimately flows through the centre of Dublin to its mouth within Dublin Bay. Its major tributaries include the River Dodder, the River Poddle and the River Camac. The river supplies much of Dublin's water and supports a range of recreational activities.

The Brahmaputra, also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachal Pradesh, and Luit in Assamese, is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, China, India, and Bangladesh. As such, it is known by various names in the region: Assamese: লুইত luit[luɪt], ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ নদ {{lang|as-Latn|Brohmoputro nod}, ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ নদ Brohmoputro[bɹɔɦmɔputɹɔ]; Sanskrit: ब्रह्मपुत्र, IAST: Brahmaputra; Tibetan: ཡར་ཀླུངས་གཙང་པོ་, Wylie: yar klung gtsang po Yarlung Tsangpo; simplified Chinese: 布拉马普特拉河; traditional Chinese: 布拉馬普特拉河; pinyin: Bùlāmǎpǔtèlā Hé. It is also called Tsangpo-Brahmaputra and red river of India. It is the 9th largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest.

The George Washington Bridge is a double-decked suspension bridge spanning the Hudson River, connecting the New York City borough of Manhattan with the New Jersey borough of Fort Lee. The bridge is named after George Washington, the first president of the United States. The George Washington Bridge is the world's busiest motor vehicle bridge, carrying over 103 million vehicles in 2016. It is owned by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, a bi-state government agency that operates infrastructure in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The George Washington Bridge is also informally known as the GW Bridge, the GWB, the GW, or the George, and was known as the Fort Lee Bridge or Hudson River Bridge during construction. The George Washington Bridge measures 4,760 feet (1,450 m) long and has a main span of 3,500 feet (1,100 m). It was the longest main bridge span in the world from its opening until the Golden Gate Bridge opened in 1937.

The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows 348 miles (560 km) to Chesapeake Bay. The river length extends to 444 miles (715 km) if one includes the Jackson River, the longer of its two source tributaries. It is the longest river in Virginia. Jamestown and Williamsburg, Virginia's first colonial capitals, and Richmond, Virginia's current capital, lie on the James River.

The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the Canton River, is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-all for the watersheds of the Xi ("West"), Bei ("North"), and Dong ("East") rivers of Guangdong. These rivers are all considered tributaries of the Pearl River because they share a common delta, the Pearl River Delta. Measured from the farthest reaches of the Xi River, the 2,400-kilometer (1,500 mi)-long Pearl River system is China's third-longest river, after the Yangtze River and the Yellow River, and second largest by volume, after the Yangtze. The 453,700 km2 (175,200 sq mi) Pearl River Basin (珠江流域) drains the majority of Liangguang, as well as parts of Yunnan, Guizhou, Hunan and Jiangxi in China; it also drains northern parts of Vietnam's Northeast Cao Bằng and Lạng Sơn provinces.

A swing bridge is a movable bridge that has as its primary structural support a vertical locating pin and support ring, usually at or near to its center of gravity, about which the turning span can then pivot horizontally as shown in the animated illustration to the right. Small swing bridges as found over canals may be pivoted only at one end, opening as would a gate, but require substantial underground structure to support the pivot.

The Hooghly River or the Bhāgirathi-Hooghly, called the 'Ganga' or the 'Kati-Ganga' in mythological texts, is the eastern distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, India, rising close to Giria in Murshidabad. It is referred to as an arm of the Ganges in the Encyclopedia Britannica and was previously the major flow of the waters of the Ganga It is because of this reason, people believe the holy waters of the Ganga still flow through the Bhagirathi-Hoogly and hence it is still worshipped today. The other distributary of Ganga then flows into Bangladesh as the Padma. Today there is a man-made canal called the Farakka Feeder Canal connecting the Ganges to the Bhagirathi.





























































