The foreign relations of Afghanistan are in a transitional phase since the 2021 fall of Kabul to the Taliban and the collapse of the internationally-recognized Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. No country has recognised the new regime, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. Although some countries have engaged in informal diplomatic contact with the Islamic Emirate, formal relations remain limited to representatives of the Islamic Republic.

The foreign relations of Sudan are generally in line with the Muslim Arab world, but are also based on Sudan's economic ties with the People's Republic of China and Russia.

Ensuring national security, increasing influence among its Arab neighbours and securing the return of the Golan Heights, have been the primary goals of the Syrian Arab Republic's foreign policy. At many points in its history, Syria has seen tension with its neighbours, such as Turkey, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, and Lebanon. Syria enjoyed an improvement in relations with several of the states in its region in the 21st century, prior to the Arab Spring and the Syrian Civil War.

Foreign relations of Australia are influenced by its position as a leading trading nation and as a significant donor of humanitarian aid. Australia's foreign policy is guided by a commitment to multilateralism and regionalism, as well as to build strong bilateral relations with its allies. Key concerns include free trade, terrorism, refugees, economic co-operation with Asia and stability in the Indo-Pacific. Australia is active in the United Nations and the Commonwealth of Nations. Given its history of starting and supporting important regional and global initiatives, it has been described as a regional middle power par excellence.

Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by states or institutions against states, groups, or individuals. Economic sanctions are a form of coercion that attempts to get an actor to change its behavior through disruption in economic exchange. Sanctions can be intended to compel or deterrence.

United States sanctions are financial and trade restrictions imposed against individuals, entities, and jurisdictions whose actions contradict U.S. foreign policy or national security goals. Financial sanctions are primarily administered by the U.S. Department of the Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), while export controls are primarily administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).

Foreign relations date back to 1807, when the Russian warship Neva arrived in Sydney as part of its circumnavigation of the globe. Consular relations between Australia and the Russian Empire were established in 1857. Diplomatic relations between Australia and the Soviet Union were established in 1942, and the first Australian embassy opened in 1943. Due to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, relations became very tense after Australia imposed sanctions against Russia. Russia placed Australia on a list of "unfriendly countries", along with Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, the United States, European Union members, NATO members, Canada, New Zealand, Switzerland, Micronesia and Ukraine.

Diplomatic relations between Australia and Ukraine were established in 1992. Ukraine has had an embassy in Canberra since March 2003 and the Australian Embassy in Kyiv was established in December 2014, however, Australia closed its embassy in Kyiv in February 2022 due to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.

The Republic of South Sudan established relations with sovereign states and international organizations following independence on 9 July 2011. South Sudan's former ruling country of Sudan was the first state in the world to recognize South Sudan.

Australia–North Korea relations refers to the existing bilateral relationship between Australia and North Korea. Relations were officially established on 31 July 1974 when Australia extended diplomatic recognition to North Korea under the Whitlam government. Overall, relations have been stressed and at times, tense, due to Australia's historical involvement in the Korean War and military alliance with the United States, and contemporary disputes such as North Korea's nuclear weapons program and accusations of human rights abuses by both sides.
International sanctions have been imposed against Russia and Crimea during the Russo-Ukrainian War by a large number of countries, including the United States, Canada, the European Union, and international organisations following the Russian annexation of Crimea, which began in late February 2014. Belarus has also been sanctioned for its cooperation with and assistance to Russian armed forces. The sanctions were imposed against individuals, businesses, and officials from Russia and Ukraine. Russia responded with sanctions against several countries, including a total ban on food imports from Australia, Canada, Norway, Japan, the United States, the EU and the United Kingdom.
A number of countries and international bodies have imposed international sanctions against North Korea. Currently, many sanctions are concerned with North Korea's nuclear weapons program and were imposed after its first nuclear test in 2006.
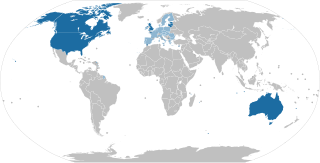
Magnitsky legislation refers to laws providing for governmental sanctions against foreign individuals who have committed human rights abuses or been involved in significant corruption. They originated with the United States which passed the first Magnitsky legislation in 2012, following the torture and death of Sergei Magnitsky in Russia in 2009. Since then, a number of countries have passed similar legislation such as Canada, the United Kingdom and the European Union.









