This is a list of Royal Navy seaplane carriers.
This is a list of Royal Navy seaplane carriers.
| Main guns | The number and type of the main battery guns |
| Displacement | Ship displacement at full combat load |
| Propulsion | Number of shafts, type of propulsion system, and top speed generated |
| Service | The dates work began and finished on the ship and its ultimate fate |
| Laid down | The date the keel began to be assembled |
| Commissioned | The date the ship was commissioned |

| Ship | Aircraft | Displacement | Propulsion | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||
| HMS Ark Royal | 9 | 7,450 long tons (7,570 t) | 2 shafts Brown-Curtis geared turbines 6 boilers | 7 November 1913 | December 1914 | Sold December 1946 for conversion to a merchant ship. |
| HMS Empress | 3 | 2,540 long tons (2,581 t) | 3 shafts Parsons turbines | 1906 | 25 August 1914 | Returned to owners November 1919 |
| HMS Engadine | 4 | 1,676 long tons (1,703 t) | 2 shafts Steam turbine | 1910 | 13 August 1914 | Sold back to original owners 1919. |
| HMS Riviera | 4 | 1,850 long tons (1,880 t) | 3 shafts Parsons turbines 6 boilers | 1910 | 11 August 1914 | Returned to owners 1919 |
| HMS Campania | 10 | 18,000 long tons (18,289 t) | 2 shafts Steam engines | 1892 | 17 April 1915 | Sank during a gale, 5 November 1918 |
| HMS Anne | 2 | 4,083 long tons (4,149 t) | 1 shaft | 1911 | 4 August 1915 | Returned to owners 1922 |
| HMS Raven II | 2 | 4,678 long tons (4,753 t) | 1 shaft | 1911 | 12 June 1915 | Sold for mercantile service 1923 |
| HMS Ben-my-Chree | 6 | 3,880 long tons (3,942 t) | 3 shafts Steam turbines 3 boilers | 1907 | 3 March 1915 | Sunk on 11 January 1917 by shore-based Turkish artillery fire. |
| HMS Vindex | 7 | 2,950 long tons (2,997 t) | 3 shafts Steam turbines 4 boilers | 1916 | 1 October 1918 | Scrapped 1948 |
| HMS Manxman | 8 | 2,540 long tons (2,581 t) | 2 shafts Brown-Curtis geared turbines | 1903 | 17 April 1916 | Sold for Scrap 9 August 1949 |
| HMS Nairana | 7 | 3,547 long tons (3,604 t) | 2 shafts Parsons geared turbines | 1914 | 25 August 1917 | Sold 1920 |
| HMS Pegasus | 9 | 2,540 long tons (2,581 t) | 2 shafts Brown-Curtis geared turbines | 1914 | 28 August 1917 | |
| HMS Albatross | 9 | 6,350 long tons (6,452 t) | 2 shafts Steam turbines 4 boilers | 5 May 1926 | 19 April 1938 | |
| HMS Vindictive | 12 | 11,500 long tons (11,700 t) | 4 shafts Parsons turbines 12 boilers | 29 June 1916 | 1 October 1918 | Sold for scrap February 1946 |
An airport is an aerodrome with facilities for flights to take off and land. Airports often have facilities to store and maintain aircraft, and a control tower. An airport consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals.

A reconnaissance aircraft is a military aircraft designed or adapted to perform aerial reconnaissance with roles including collection of imagery intelligence, signals intelligence, as well as measurement and signature intelligence. Modern technology has also enabled some aircraft and UAVs to carry out real-time surveillance in addition to general intelligence gathering.

A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of taking off and landing (alighting) on water. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their technological characteristics: floatplanes and flying boats; the latter are generally far larger and can carry far more. Seaplanes that can also take off and land on airfields are in a subclass called amphibious aircraft, or amphibians. Seaplanes were sometimes called hydroplanes, but currently this term applies instead to motor-powered watercraft that use the technique of hydrodynamic lift to skim the surface of water when running at speed.

A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are regarded by some as the first aircraft carriers and appeared just before the First World War.

A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, making the vehicle an amphibious aircraft. British usage is to call floatplanes "seaplanes" rather than use the term "seaplane" to refer to both floatplanes and flying boats.

Lake Hood Seaplane Base is a state-owned seaplane base located three nautical miles (6 km) southwest of the central business district of Anchorage in the U.S. state of Alaska. The Lake Hood Strip is a gravel runway located adjacent to the seaplane base. The gravel strip airport's previous code of has been decommissioned and combined with as another landing surface.
Elfin Cove Seaplane Base is a state-owned public-use seaplane base located in Elfin Cove, on Chichagof Island in the Hoonah-Angoon Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Scheduled airline service is subsidized by the Essential Air Service program.
Pelican Seaplane Base is a public-use seaplane base located in and owned by the City of Pelican, on Chichagof Island in the Hoonah-Angoon Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Scheduled airline service is subsidized by the Essential Air Service program.

The Raid on Cuxhaven was a British ship-based air-raid on the Imperial German Navy at Cuxhaven mounted on Christmas Day, 1914.

Ketchikan Harbor Seaplane Base is a privately owned, public use seaplane base located at the harbor of Ketchikan, a city in the Ketchikan Gateway Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located near the Ketchikan International Airport, which also has its own seaplane landing area. Prior to the opening of the Ketchikan International Airport in 1973, scheduled passenger seaplane service was operated with amphibian aircraft between the seaplane base and the Annette Island Airport located approximately 20 miles south, as this land plane airfield previously served as the primary airport for Ketchikan, with scheduled airline flights being operated by Pan American World Airways, Pacific Northern Airlines and Western Airlines into Annette Island over the years.

Angoon Seaplane Base is a state-owned public-use seaplane base located one nautical mile (2 km) southeast of the central business district of Angoon, a city on Admiralty Island in the Hoonah-Angoon Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Scheduled airline service is subsidized by the Essential Air Service program.

Tenakee Seaplane Base is a state-owned public-use seaplane base located in Tenakee Springs, a city on Chichagof Island in the Hoonah-Angoon Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Scheduled airline service is subsidized by the Essential Air Service program.
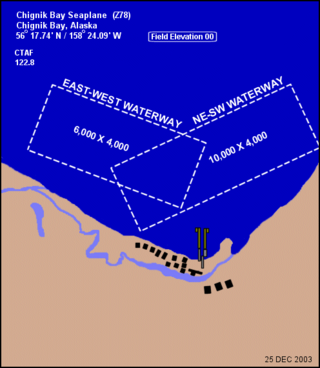
Chignik Bay Seaplane Base is a public-use seaplane base serving Chignik, a city in the Lake and Peninsula Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska.
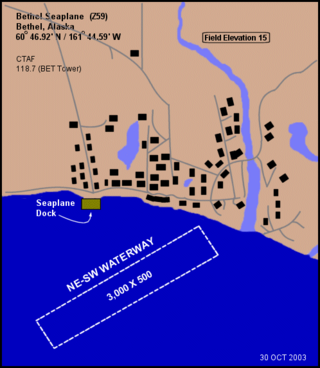
Bethel Seaplane Base is a public use seaplane base located on the Kuskokwim River in Bethel, a city in the Bethel Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska.
The Yokosuka E5Y was a single-engine Japanese seaplane used for reconnaissance. The E5Y was also built by Kawanishi as the E5K
Kerala Seaplane was a commercial seaplane service promoted by Kerala Tourism Infrastructure Limited in the Indian state of Kerala. It was launched on 2 June 2013 at Kollam with the inaugural flight being operated by Kairali Aviation. However, commercial operations could not start due to opposition from the local fishing community. The Kerala Government was keen on restarting regular operations of the project in 2014. The service was to be the first such service in mainland India, and the second in India after Jal Hans, which operates seaplanes in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Work on the Kerala seaplane project began at the end of July, 2012 and has been praised for being one of the fastest projects to be completed in Kerala.

Tailwind Air LLC is a commuter scheduled air carrier and charter airline based in Westchester Airport and Sikorsky Memorial Airport. Its main seaplane base is New York Skyports Seaplane Base (NYS) and it also owns its own Boston Harbor seaplane base (MA17), near Logan International Airport in Boston. The airline has a sister company named Tailwind Air, LLC, which charters and manages a fleet of land planes.

Tropic Ocean Airways is a seaplane charter and scheduled service airline based in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Tropic Ocean Airways operates several Cessna airframes on floats.