Related Research Articles
Cormac mac Art Ó Melaghlain, was King of Mide from around 1209/10 to 1239. He managed to win several notable victories over the Anglo-Normans and as a result was one of the more prominent and successful later Kings of Mide. Whatever gains Cormac made were not to prove long lasting however, even in his own reign, and the successor lords of Clann Cholmain were largely insignificant to the politics of later medieval Ireland.

Cathal Crobhdearg Ua Conchobair (1153–1224), was a king of Connacht. He was the youngest son of the High King of Ireland Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair and brother to the last fully recognized High King Ruadri Ua Conchobair. His own sons Aedh Ua Conchobair and Feidhlimidh Ua Conchobair were kings of Connacht after him.
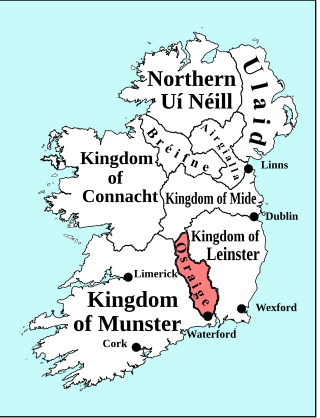
Osraige or Osraighe, Osraí, anglicized as Ossory, was a medieval Irish kingdom comprising what is now County Kilkenny and western County Laois, corresponding to the Diocese of Ossory. The home of the Osraige people, it existed from around the first century until the Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. It was ruled by the Dál Birn dynasty, whose medieval descendants assumed the surname Mac Giolla Phádraig.

The Synod of Kells took place in 1152, under the presidency of Giovanni Cardinal Paparoni, and continued the process begun at the Synod of Ráth Breasail (1111) of reforming the Irish church. The sessions were divided between the abbeys of Kells and Mellifont, and in later times the synod has been called the Synod of Kells-Mellifont and the Synod of Mellifont-Kells.
Events from the year 1331 in Ireland.

Mac Amhlaoibh and Mac Amhalghaidh are two different Gaelic patronymic names with different origins and meanings, but which share the same or similar Anglicisations. These Gaelic names are borne by at least three unrelated native Irish clans or septs.
Gilla Pátraic, also known as Patricius, was the second Bishop of Dublin. Gilla Pátraic was elevated to the see of Dublin following bishop Dúnán's death in 1074. He was consecrated by Lanfranc, Archbishop of Canterbury. Whether Gilla Pátraic or Dúnán was the first Irish bishop to be consecrated in Canterbury is disputed.
The White Rod, White Wand, Rod of Inauguration, or Wand of Sovereignty, in the Irish language variously called the slat na ríghe and slat tighearnais, was the primary symbol of a Gaelic king or lord's legitimate authority and the principal prop used in his inauguration ceremony. First documented in the 12th century Life of Máedóc of Ferns, but assumed to have been used long before then, it is last documented in Ireland in the early 17th century. In Scotland the rod was used into the 13th century for the inauguration of its last Gaelic-speaking kings, and for the Norse-Gaelic Lords of the Isles into the 15th.

Innes McCartney is a British nautical archaeologist and historian. He is a Visiting Fellow at Bournemouth University in the UK.

Kilbennen or Kilbannon is a medieval ecclesiastical site and National Monument located in County Galway, Ireland.

Stradbally is a barony in County Laois, Ireland.

Cider, an alcoholic drink made from apples, is widely available in Ireland at pubs, off licences, and supermarkets. It has been made in regions of the island for hundreds of years.
In Gaelic Ireland, a bruiden was a building offering shelter, drink and food, often translated as "hostel", "banqueting hall" or "inn."

Loughtee Upper, or Upper Loughtee, is a barony in County Cavan, Ireland. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898.

Saul Monastery is a former Christian monastery located in County Down, Northern Ireland. It is traditionally associated with the 5th-century Saint Patrick, who is said to have founded it shortly after arriving in Ireland, and having died there at the end of his missionary work.

Killashee Round Tower is an Irish round tower that forms part of the monastic remnants of Killashee, County Kildare, Ireland. On the Record of Monuments and Places its number is KD024-003.
References
- ↑ "Part 58 of Annals of Inisfallen". celt.ucc.ie.
- ↑ "Annales Hiberniae". celt.ucc.ie.
- ↑ "Patrick of Dublin – Elizabeth Boyle".
- ↑ society, Irish archaeological and Celtic (September 14, 1842). "Publications". Society. – via Google Books.
- ↑ "The Writings of Bishop Patrick, 1074-1084". Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies. September 14, 1955 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Lettens, Jan. "Smalls wreck [+1100]". Wrecksite. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ↑ "French archaeologist discover 12th century shipwreck". Antara News. 24 February 2012. Retrieved 7 June 2015.