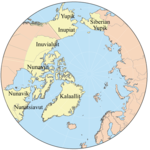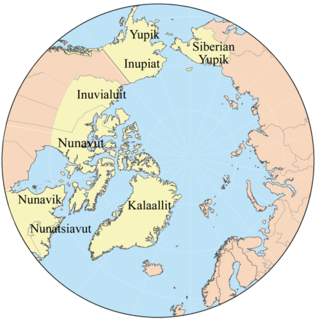
Eskimo is an exonym used to refer to two closely related Indigenous peoples: the Inuit and the Yupik of eastern Siberia and Alaska. A related third group, the Aleut, which inhabit the Aleutian Islands, are generally excluded from the definition of Eskimo. The three groups share a relatively recent common ancestor, and speak related languages belonging to the Eskimo–Aleut language family.

The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and adjacent subarctic, reaching farthest south in Labrador. The related Yupik languages are the two main branches of Eskaleut, a primary language family. The Inuit live primarily in three countries: Greenland, Canada, and the United States.

Inuit religion is the shared spiritual beliefs and practices of the Inuit, an indigenous people from Alaska, Canada, parts of Siberia and Greenland. Their religion shares many similarities with some Alaska Native religions. Traditional Inuit religious practices include animism and shamanism, in which spiritual healers mediate with spirits. Today many Inuit follow Christianity, but traditional Inuit spirituality continues as part of a living, oral tradition and part of contemporary Inuit society. Inuit who balance indigenous and Christian theology practice religious syncretism.

Nunavik comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of 443,684.71 km2 (171,307.62 sq mi) north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the Inuit of Quebec and part of the wider Inuit Nunangat. Almost all of the 13,181 inhabitants of the region, of whom 90% are Inuit, live in fourteen northern villages on the coast of Nunavik and in the Cree reserved land (TC) of Whapmagoostui, near the northern village of Kuujjuarapik.
In Canada, indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although Indian is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors Indian and Eskimo have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. Aboriginal peoples as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the Constitution Act, 1982, though in most Indigenous circles Aboriginal has also fallen into disfavour.

The Inuit Circumpolar Council (ICC), formerly Inuit Circumpolar Conference, is a multinational non-governmental organization (NGO) and Indigenous Peoples' Organization (IPO) representing the 180,000 Inuit, Yupik, and Chukchi peoples people living in Alaska, Canada, Greenland, and Chukotka (Russia). ICC was ECOSOC-accredited and was granted special consultative status at the UN in 1983.

Inuktitut, also Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the tree line, including parts of the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, to some extent in northeastern Manitoba as well as the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. It is one of the aboriginal languages written with Canadian Aboriginal syllabics.

Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for Canada's northern lands and territories, and one of two departments with responsibility for policies relating to Indigenous peoples in Canada.

Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada, is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit across Inuit Nunangat and the rest of Canada. Their mission is to "serve as a national voice protecting and advancing the rights and interests of Inuit in Canada."

Kinngait, formerly known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
Native Americans or Native American may refer to:
In Canada, an Indian band or band, sometimes referred to as a First Nation band or simply a First Nation, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the Indian Act. Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all status Indians are members of a band.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Inuit art, also known as Eskimo art, refers to artwork produced by the Inuit, that is, the people of the Arctic previously known as Eskimos, a term that is now often considered offensive. Historically, their preferred medium was walrus ivory, but since the establishment of southern markets for Inuit art in 1945, prints and figurative works carved in relatively soft stone such as soapstone, serpentinite, or argillite have also become popular.

Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland (Denmark), Canada, and Alaska. The Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.

Mary Jeannie May Simon is a Canadian civil servant, diplomat, and former broadcaster who has served as the 30th governor general of Canada since July 26, 2021. Simon is Inuk, making her the first Indigenous person to hold the office.
Over the course of centuries, many Indigenous Canadians have played a critical role in shaping the history of Canada. From art and music, to law and government, to sports and war; Indigenous customs and culture have had a strong influences on defining Canadian culture. The Indspire Awards are the annual awards presented by Indspire, formerly the National Aboriginal Achievement Foundation. The awards were first established in 1993 in conjunction with the United Nations declaring the 1990s "International Decade of the World's Indigenous peoples". June 21 is Canada's National Aboriginal Day, in recognition of the cultural contributions made by Canada's indigenous population. The day was first celebrated in 1996 following Governor General of Canada Roméo LeBlanc's proclamation.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to Indigenous peoples in Canada, comprising the First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples.

Greenlanders are people identified with Greenland or the indigenous people, the Greenlandic Inuit. This connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Greenlanders, many of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being Greenlandic. However, the term can in different contexts be delimited more precisely in different ways: as the inhabitants of Greenland, as nationals of Greenland or more broadly as persons who feel a cultural affiliation in a broad sense to Greenland. More controversial is a more recent use of the word in the sense persons of Greenlandic origin, i.e. persons whose parents were born in Greenland.
First Nations or first peoples may refer to: