Nord-du-Québec is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.

The Kativik Regional Government is the representative regional authority for most of the Nunavik region of Quebec. Nunavik is the northern half of the Nord-du-Québec administrative region and includes all the territory north of the 55th parallel. The administrative capital is Kuujjuaq, on the Koksoak River, about 50 kilometres inland from the southern end of the Ungava Bay.

Indigenous peoples in Quebec total eleven distinct ethnic groups. The one Inuit community and ten First Nations communities number 141,915 people and account for approximately two per cent of the population of Quebec, Canada.

Kuujjuaq, formerly known as Suoivauqaj (ᓲᐃᕙᐅᖃᔾ) and by other names, is a former Hudson's Bay Company outpost at the mouth of the Koksoak River on Ungava Bay that has become the largest northern village in the Nunavik region of Quebec, Canada. It is the administrative capital of the Kativik Regional Government. Its population was 2,668 as of the 2021 census.
Charlie Watt is a former Canadian Senator from Nunavik, Quebec.

The Koksoak River is a river in northern Quebec, Canada, the largest river in the Nunavik region. The Inuit village and region's administrative centre Kuujjuaq lies on the shores of the Koksoak, about 50 kilometres (31 mi) south from its mouth.
Abitibi—Baie-James—Nunavik—Eeyou is a federal riding in the province of Quebec, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1968. Since the 2019 federal election, its Member of Parliament (MP) has been Sylvie Bérubé of the Bloc Québécois (BQ).

The James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement is an Aboriginal land claim settlement, approved in 1975 by the Cree and Inuit of northern Quebec, and later slightly modified in 1978 by the Northeastern Quebec Agreement, through which Quebec's Naskapi First Nation joined the agreement. The agreement covers economic development and property issues in northern Quebec, as well as establishing a number of cultural, social and governmental institutions for Indigenous people who are members of the communities involved in the agreement.
Makivvik is the legal representative of Quebec's Inuit, established in 1978 under the terms of the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement, the agreement that established the institutions of Nunavik. As such, it is the heir of the Northern Quebec Inuit Association, which signed the agreement with the governments of Quebec and of Canada.

Kuujjuarapik is the southernmost northern village at the mouth of the Great Whale River on the coast of Hudson Bay in Nunavik, Quebec, Canada. Almost 1,000 people, mostly Cree, live in the adjacent village of Whapmagoostui. The community is only accessible by air, Kuujjuarapik Airport and, in late summer, by boat. The nearest Inuit village is Umiujaq, about 160 km (99 mi) north-northeast of Kuujjuarapik. The police services in Kuujjuaraapik are provided by the Nunavik Police Service, formerly the Kativik Regional Police Force. Like most other northern villages in Quebec, there is an Inuit reserved land of the same name, Kuujjuarapik. However, unlike most other Inuit reserved lands, the Inuit reserved land of Kuujjuarapik is not adjacent to its eponymous northern village; rather, it is located considerably farther north and in fact borders on the Inuit reserved land of Umiujaq.

Ivujivik is a northern village in Nunavik, Quebec, and the northernmost settlement in any Canadian province, although there are settlements further north in the territories. Its population in the 2021 Canadian census was 412.

Umiujaq is a northern village near the eastern shore of Hudson Bay in Nunavik in northern Quebec, Canada. The village was established in 1986 by Inuit from Kuujjuarapik, 160 km to the south, who decided to relocate away from the area affected by the James Bay Hydro-electric Project. The population in the Canada 2021 Census was 541.

Akulivik is an Inuit village in Nunavik, in northern Quebec, Canada. It is located on a peninsula that juts southwesterly into Hudson Bay across from Smith Island, Nunavut (Qikirtajuaq). Akulivik lies 1,850 km north of Montreal.

Tasiujaq is a northern village in Nunavik, in northern Quebec, Canada. Its population in the Canada 2021 Census was 420.
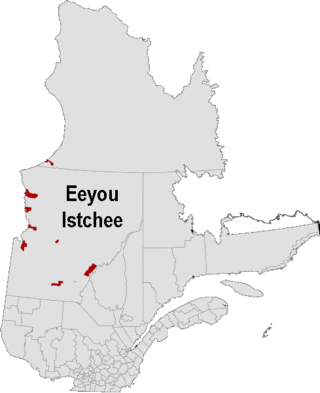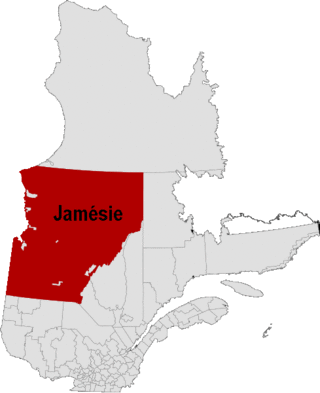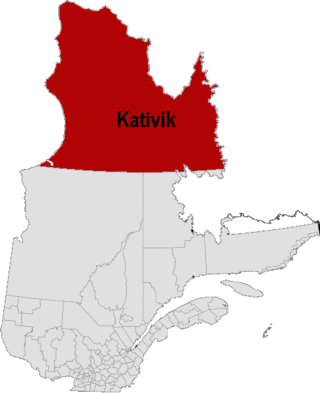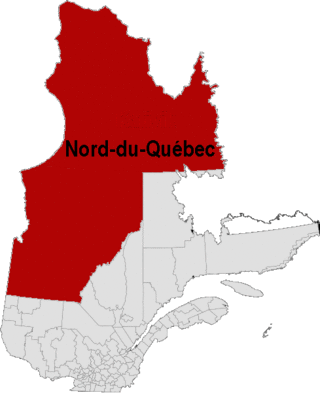
Kativik (ᑲᑎᕕᒃ) is a territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (TE) of Quebec, with geographical code 992. Its land area is 443,372.20 km2, and its population was 12,090 at the 2011 Census of Canada.

Kangiqsujuaq is a northern village in Nunavik, Nord-du-Québec, Quebec, Canada. It had a population of 837 in the Canada 2021 Census. The community has also been known as Wakeham Bay. The name "Kangiqsujuaq" means "the large bay" in Inuktitut.

George River, formerly the East or George's River, is a river in northeastern Quebec, Canada, that flows from Lake Jannière mainly north to Ungava Bay.

Kangirsuk is an Inuit village in northern Nunavik, Quebec, Canada. It is 230 kilometres (140 mi) north of Kuujjuaq, between Aupaluk and Quaqtaq. The community is only accessible by air and, in late summer, by boat. The village used to be known also as Payne Bay and Bellin.

Killiniq is a former Inuit settlement, weather station, trading post, missionary post, fishing station, and Royal Canadian Mounted Police post on Killiniq Island. Previously within Labrador, and then the Northwest Territories, it is now situated within the borders of Nunavut. The community closed in 1978.

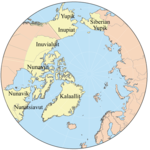
Inuit Nunangat, formerly Inuit Nunaat, refers to the land, water, and ice of the homeland of Inuit in Canada. This Arctic homeland consists of four northern Canadian regions called the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, the territory Nunavut (ᓄᓇᕗᑦ), Nunavik (ᓄᓇᕕᒃ) in northern Quebec, and Nunatsiavut of Newfoundland and Labrador.