
Iqaluit is the capital of the Canadian territory of Nunavut, its largest community, and its only city. It was known as Frobisher Bay from 1942 to 1987, after the large bay on the coast on which the city is situated. The northernmost city in Canada, its traditional Inuktitut name was restored in 1987.

Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of 1,230,000 km2 (470,000 sq mi). It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. It is an inland marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It drains a very large area, about 3,861,400 km2 (1,490,900 sq mi), that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay.

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km²; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.

Rankin Inlet is an Inuit hamlet on the Kudlulik Peninsula in Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest hamlet and second-largest settlement in Nunavut, after the territorial capital, Iqaluit. On the northwestern Hudson Bay, between Chesterfield Inlet and Arviat, it is the regional centre for the Kivalliq Region.

Alert, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada, is the northernmost continuously inhabited place in the world, on Ellesmere Island at latitude 82°30'05" north, 817 km (508 mi) from the North Pole. It takes its name from HMS Alert, which wintered 10 km (6.2 mi) east of the present station, off what is now Cape Sheridan, in 1875–1876.

Eureka is a small research base on Fosheim Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is located on the north side of Slidre Fiord, which enters Eureka Sound farther west. It is the third-northernmost permanent research community in the world. The only two farther north are Alert, which is also on Ellesmere Island, and Nord, in Greenland. Eureka has the lowest average annual temperature and the lowest amount of precipitation of any weather station in Canada.

Arctic Bay is an Inuit hamlet located in the northern part of the Borden Peninsula on Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Arctic Bay is located in the Eastern Time Zone although it is quite close to the time zone boundary. The predominant languages are Inuktitut and English. Arctic Bay is notable for being the birthplace of the former Premier of Nunavut and, as of 2021, the Commissioner of Nunavut, Eva Aariak. It is the northernmost public community in Canada not formed from forced relocation.
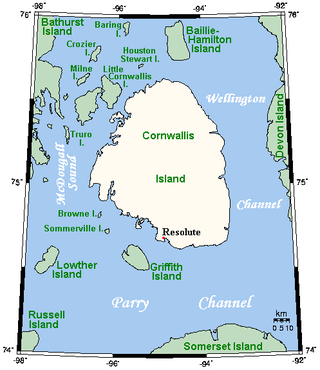
Cornwallis Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, part of the Arctic Archipelago, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut in the Canadian Arctic. It lies to the west of Devon Island, the largest uninhabited island in the world, and at its greatest length is about 113 km (70 mi). At 6,995 km2 (2,701 sq mi) in size, it is the 96th largest island in the world, and Canada's 21st largest island. Cornwallis Island is separated by the Wellington Channel from Devon Island, and by the Parry Channel from Somerset Island to the south. Northwest of Cornwallis Island lies Little Cornwallis Island, the biggest of a group of small islands at the north end of McDougall Sound, which separates Cornwallis Island from nearby Bathurst Island.

Kitikmeot Region is an administrative region of Nunavut, Canada. It consists of the southern and eastern parts of Victoria Island with the adjacent part of the mainland as far as the Boothia Peninsula, together with King William Island and the southern portion of Prince of Wales Island. The regional centre is Cambridge Bay.

King William Island is an island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, which is part of the Arctic Archipelago. In area it is between 12,516 km2 (4,832 sq mi) and 13,111 km2 (5,062 sq mi) making it the 61st-largest island in the world and Canada's 15th-largest island. Its population, as of the 2021 census, was 1,349, all of whom live in the island's only community, Gjoa Haven.

Hay River, known as "the Hub of the North", is a town in the Northwest Territories, Canada, located on the south shore of Great Slave Lake, at the mouth of the Hay River. The town is separated into two sections, a new town and an old town with the Hay River/Merlyn Carter Airport between them. The town is in the South Slave Region, and along with Fort Smith, the town is home to one of the two regional offices.

Arviat is a predominantly Inuit hamlet located on the western shore of Hudson Bay in the Kivalliq Region of Nunavut, Canada. Arviat is derived from the Inuktitut word arviq meaning "Bowhead whale". Earlier in history, its name was Tikirajualaaq, and Ittaliurvik,.

Resolute or Resolute Bay is an Inuit hamlet on Cornwallis Island in Nunavut, Canada. It is situated at the northern end of Resolute Bay and the Northwest Passage and is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region.

Kinngait, known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.

Kugluktuk, formerly known as Coppermine until 1 January 1996, is a hamlet located at the mouth of the Coppermine River in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada, on Coronation Gulf, southwest of Victoria Island. It is the westernmost community in Nunavut, near the border with the Northwest Territories.

Naujaat, Anglicised and officially known until 2 July 2015 as Repulse Bay, is an Inuit hamlet situated on the Arctic Circle. It is located on the shores of Hudson Bay, at the south end of the Melville Peninsula, in the Kivalliq Region of Nunavut, Canada.

Taloyoak or Talurjuaq, formerly known as Spence Bay until 1 July 1992, although the body of water on which it is situated continues to be known as Spence Bay — same as the body of water on which Iqaluit is situated continues to be known as Frobisher Bay — is located on the Boothia Peninsula, in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. The community is served only by air and by annual supply sealift. Taloyoak, the northernmost community in mainland Canada, in Inuktitut means "large blind", referring to a stone caribou blind or a screen used for caribou hunting. The community is situated 460 km (290 mi) east of the regional centre of Cambridge Bay, 1,224 km (761 mi) northeast of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Apex is a small community in Iqaluit located on Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. It is about 5 km (3.1 mi) southeast of Iqaluit on a small peninsula separating Koojesse (Kuujussi) Inlet from Tarr Inlet. Historically Apex was the place where most Inuit lived when Iqaluit was a military site and off-limits to anyone not working at the base. The community is accessed by bridge or causeway, and bordered by a local creek (kuujuusi) and waterfall (kugluktuk). Located here are the women's shelter, a church, Nanook Elementary School, and a bed-and-breakfast, along with housing for about 60 families.


























