Iqaluit is the capital of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is the territory's largest community and its only city. It was known as Frobisher Bay from 1942 to 1987, after the large bay on the coast on which the city is situated. The northernmost city in Canada, its traditional Inuktitut name was restored in 1987.

The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and the adjacent subarctic regions as far south as Labrador. The Inuit languages are one of the two branches of the Eskimoan language family, the other being the Yupik languages, which are spoken in Alaska and the Russian Far East. Most Inuit people live in one of three countries: Greenland, a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark; Canada, specifically in Nunavut, the Inuvialuit Settlement Region of the Northwest Territories, the Nunavik region of Quebec, and the Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut regions of Labrador; and the United States, specifically in northern and western Alaska.

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km²; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.

Pond Inlet is a small, predominantly Inuit community in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada, located on northern Baffin Island. To the Inuit the name of the place "is and always has been Mittimatalik." The Scottish explorer Sir John Ross had named an arm of the sea that separates Bylot Island from Baffin Island as Pond's Bay, and the hamlet now shares that name. On 29 August 1921, the Hudson's Bay Company opened its trading post near the Inuit camp and named it Pond Inlet, marking the expansion of its trading empire into the High Arctic.

Ukkusiksalik National Park is a national park in Nunavut, Canada. It covers 20,885 km2 (8,064 sq mi) of tundra and coastal mudflats south of the Arctic Circle and the hamlet of Naujaat, from Hudson Bay's Roes Welcome Sound towards the western Barrenlands and the source of Brown River. The park surrounds Wager Bay, a 100 km (62 mi)-long inlet on the Hudson Bay. Although the smallest of Nunavut's four national parks, it is the sixth largest in Canada. Its name relates to steatite found there: Ukkusiksalik means "where there is material for the stone pot".

Rankin Inlet is an Inuit hamlet on the Kudlulik Peninsula in Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest hamlet and second-largest settlement in Nunavut, after the territorial capital, Iqaluit. On the northwestern Hudson Bay, between Chesterfield Inlet and Arviat, it is the regional centre for the Kivalliq Region.
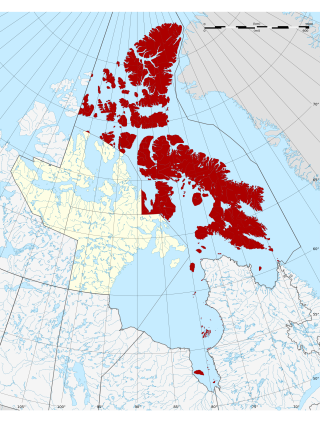
The Qikiqtaaluk Region, Qikiqtani Region or the Baffin Region is the easternmost, northernmost, and southernmost administrative region of Nunavut, Canada. Qikiqtaaluk is the traditional Inuktitut name for Baffin Island. Although the Qikiqtaaluk Region is the most commonly used name in official contexts, several notable public organizations, including Statistics Canada prior to the 2021 Canadian census, use the older term Baffin Region.

Inuktitut, also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, to some extent in northeastern Manitoba as well as the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. It is one of the aboriginal languages written with Canadian Aboriginal syllabics.

Cambridge Bay is a hamlet located on Victoria Island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest settlement on Victoria Island. Cambridge Bay is named for Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, while the traditional Inuinnaqtun name for the area is Ikaluktutiak or Iqaluktuuttiaq meaning "good fishing place".

Kinngait, known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
Tagak Curley is an Inuit leader, politician and businessman from Nunavut. As a prominent figure in the negotiations that led to the creation of Nunavut, Tagak is considered a living father of confederation in Canada. He was born in a hunting camp at Coral Harbour, Northwest Territories.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Inuit are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.

The Inuit are an indigenous people of the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America. The ancestors of the present-day Inuit are culturally related to Iñupiat, and Yupik, and the Aleut who live in the Aleutian Islands of Siberia and Alaska. The term culture of the Inuit, therefore, refers primarily to these areas; however, parallels to other Eskimo groups can also be drawn.

Apex is a small community in Iqaluit located on Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. It is about 5 km (3.1 mi) southeast of Iqaluit on a small peninsula separating Koojesse (Kuujussi) Inlet from Tarr Inlet. Historically Apex was the place where most Inuit lived when Iqaluit was a military site and off-limits to anyone not working at the base. The community is accessed by bridge or causeway, and bordered by a local creek (kuujuusi) and waterfall (kugluktuk). Located here are the women's shelter, a church, Nanook Elementary School, and a bed-and-breakfast, along with housing for about 60 families.

Inuit Nunangat refers to the land, water, and ice of the homeland of Inuit in Canada. This Arctic homeland consists of four northern Canadian regions called the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, the territory Nunavut (ᓄᓇᕗᑦ), Nunavik (ᓄᓇᕕᒃ) in northern Quebec, and Nunatsiavut of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Utkuhiksalik, Utkuhikhalik, Utkuhikhaliq, Utkuhiksalingmiutitut, Utkuhiksalingmiutut, Utkuhiksalingmiut Inuktitut, Utku, Gjoa Haven dialect, is a sub-dialect of Natsilingmiutut (Nattiliŋmiut) dialect of Inuvialuktun language once spoken in the Utkuhiksalik area of Nunavut, and now spoken mainly by elders in Uqsuqtuuq and Qamani'tuaq on mainland Canada. It is generally written in Inuktitut syllabics.
Qaummaarviit Territorial Park is located 12 km (7.5 mi) west of Iqaluit in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Situated on a small island near Peterhead Inlet, it is thought that the island was inhabited by the Thule people in the early part of the 13th century.

Qausuittuq National Park is a national park located on northwest Bathurst Island in Nunavut. It was established on September 1, 2015, becoming Canada's 45th national park.

Simonie Michael was a Canadian politician from the eastern Northwest Territories who was the first Inuk elected to a legislature in Canada. Before becoming involved in politics, Michael worked as a carpenter and business owner, and was one of very few translators between Inuktitut and English. He became a prominent member of the Inuit co-operative housing movement and a community activist in Iqaluit, and was appointed to a series of governing bodies, including the precursor to the Iqaluit City Council.