
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time.

The Rotaliida are an order of Foraminifera, characterized by multilocular tests (shells) composed of bilamellar perforate hyaline lamellar calcite that may be optically radial or granular.

Fattail scorpion or fat-tailed scorpion is the common name given to scorpions of the genus Androctonus, one of the most dangerous groups of scorpion species in the world. The genus was first described in 1828 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

Montipora is a genus of Scleractinian corals in the phylum Cnidaria. Members of the genus Montipora may exhibit many different growth morphologies. With eighty five known species, Montipora is the second most species rich coral genus after Acropora.

Chromodorididae, or chromodorids, are a taxonomic family of colourful, sea slugs; dorid nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Doridoidea. “Chromodorid nudibranchs are among the most gorgeously coloured of all animals.” The over 360 described species are primarily found in tropical and subtropical waters, as members of coral reef communities, specifically associated with their sponge prey. The chromodorids are the most speciose family of opisthobranchs. They range in size from <10mm to over 30 cm, although most species are approximately 15–30 mm in size.

Trochoidea is a genus of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Helicellinae of the family Geomitridae. The name means "those that are shaped like a top".

Polinices is a genus of predatory sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Polinicinae of the family Naticidae, commonly known as moon snails.

Peridinium is a genus of motile, marine and freshwater dinoflagellates. Their morphology is considered typical of the armoured dinoflagellates, and their form is commonly used in diagrams of a dinoflagellate's structure. Peridinium can range from 30 to 70 μm in diameter, and has very thick thecal plates.
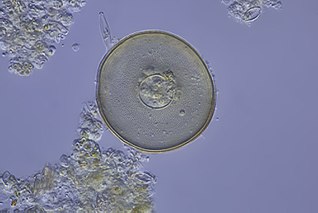
Arcella is a genus of testate amoebae in the order Arcellinida, usually found in freshwaters and mosses, and rarely in soils. A key characteristic of Arcella is the circular test with a hole on its center from where finger-like pseudopods emerge. It is one of the largest testacean genera.

Herbert Ehrenberg was a German politician.
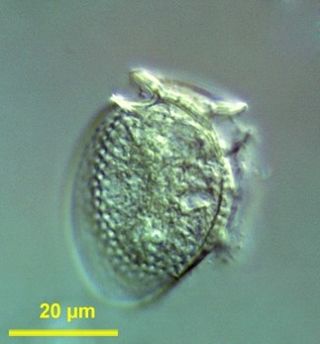
Dinophysis is a genus of dinoflagellates common in tropical, temperate, coastal and oceanic waters. It was first described in 1839 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

Corynactis is a genus of colonial anthozoans similar in appearance to sea anemones and in body format to scleractinian stony corals. These animals are cnidarians in the family Corallimorphidae. Large unidentified polyps of this genus feed on the crown-of-thorns seastar Acanthaster planci and may help control the crown-of-thorns population.
Riedelia is a genus of diatoms known from the fossil record, comprising approximately eight species. Many of the species were originally described under the closely allied genus Hemiaulus. Paleontologists Hans-Joachim Schrader and Juliane Fenner, working with fossil specimens obtained from Leg 38 of the Deep Sea Drilling Program in the Norwegian and Greenland Seas, decided that several previous descriptions of diatoms belonging to Hemiaulus were rightfully placed on Riedelia. Schrader and Fenner note that while Hemiaulus diatoms have polygonal areolated valves, Riedelia valves are punctate with isolated punctae. Additionally, Riedelia typically have two spines, while Hemiaulus have only one. These characteristics were used to justify the placement of these species in Riedelia.

Dileptus is a genus of unicellular ciliates in the class Litostomatea. Species of Dileptus occur in fresh and salt water, as well as mosses and soils. Most are aggressive predators equipped with long, mobile proboscides lined with toxic extrusomes, with which they stun smaller organisms before consuming them. 13 species and subspecies of Dileptus are currently recognized.

Lobophyllia, commonly called lobed brain coral or lobo coral, is a genus of large polyp stony corals. Members of this genus are sometimes found in reef aquariums.
Cymatosira is a genus of diatoms in the family Cymatosiraceae. It is the type genus of its family.

Eucampia is a genus of marine centric diatoms. It was first described by Ehrenberg in 1839.

Diploneis is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Diploneidaceae.















