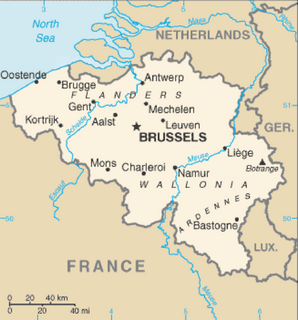
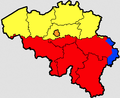
| Liège German: Lüttich Dutch: Luik | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Province of Belgium | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Coordinates: 50°38′N05°34′E / 50.633°N 5.567°E Coordinates: 50°38′N05°34′E / 50.633°N 5.567°E | |||
| Country | |||
| Region | |||
| Capital | Liège | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Hervé Jamar | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 3,844 km2 (1,484 sq mi) | ||
| Population (1 January 2017) [1] | |||
| • Total | 1,102,531 | ||
| • Density | 290/km2 (740/sq mi) | ||
| Website | Official site | ||
Liège (French: [ljɛʒ] ; Walloon : Lîdje; Dutch : Luik, IPA: [lœyk] (![]()
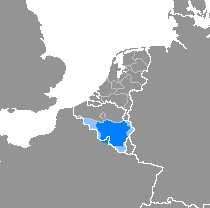
Walloon is a Romance language that is spoken in much of Wallonia in Belgium, in some villages of Northern France and in the northeast part of Wisconsin until the mid 20th century and in some parts of Canada. It belongs to the langue d'oïl language family, whose most prominent member is the French language. The historical background of its formation was the territorial extension since 980 of the Principality of Liège to the south and west.

Dutch(

German is a West Germanic language that is mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, South Tyrol (Italy), the German-speaking Community of Belgium, and Liechtenstein. It is also one of the three official languages of Luxembourg and a co-official language in the Opole Voivodeship in Poland. The languages which are most similar to German are the other members of the West Germanic language branch: Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German/Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, and Yiddish. There are also strong similarities in vocabulary with Danish, Norwegian and Swedish, although those belong to the North Germanic group. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language, after English.
Contents
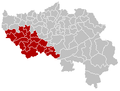
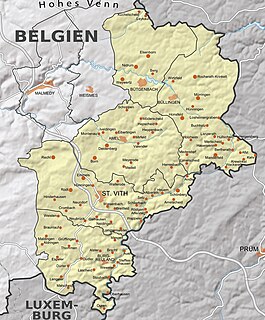
It borders (clockwise from the north) Limburg in the Netherlands, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany, Diekirch in Luxembourg, and in Belgium the provinces of Luxembourg, Namur, Walloon Brabant (Wallonia), as well as those of Flemish Brabant and Limburg (Flanders).

Limburg is the southernmost of the 12 provinces of the Netherlands. It is in the southeastern part of the country, stretched out from the north, where it touches the province of Gelderland, to the south, where it internationally borders Belgium. Its northern part has the North Brabant province to its west. Its long eastern boundary is the international border with the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Much of the west border runs along the River Maas, bordering the Flemish province of Limburg, and a small part of the Walloon province of Liège. On the south end, it has borders with the Flemish exclave of Voeren and its surrounding part of Liège, Wallonia. The Vaalserberg is on the extreme south-eastern point, marking the tripoint of Netherlands, Germany and Belgium.

The Netherlands is a country located mainly in Northwestern Europe. The European portion of the Netherlands consists of twelve separate provinces that border Germany to the east, Belgium to the south, and the North Sea to the northwest, with maritime borders in the North Sea with Belgium, Germany and the United Kingdom. Together with three island territories in the Caribbean Sea—Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba— it forms a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The official language is Dutch, but a secondary official language in the province of Friesland is West Frisian.

North Rhine-Westphalia is a state of Germany.
It is an area of Walloon and German ethnicity.
The capital of the province is the city of the same name, Liège.

Liège is a major Walloon city and municipality and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.