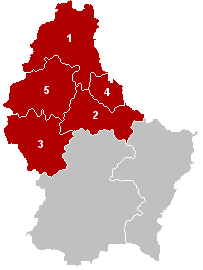
The District of Diekirch was one of three districts of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Immediately prior to its abolition on 3 October 2015, it contained five cantons divided into 43 communes:
To its west, the district of Diekirch bordered the Belgian province of Luxembourg in the region of Wallonia, whilst to its north was the Belgian providence of Liège. To its south was located the district ofGrevenmacher. The German State of Rhineland-Palatinate bordered Diekirch to its east. It had a per capita income of $49,000.