Related Research Articles

The metropolitan counties are a type of county-level administrative division of England. There are six metropolitan counties, which each cover large urban areas, with populations between 1 and 3 million. They were created in 1974 and are each divided into several metropolitan districts or boroughs.

Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East Riding of Yorkshire, West Riding of Yorkshire, and the northern part of Lindsey, Lincolnshire. The county council's headquarters was County Hall at Beverley, inherited from East Riding County Council. Its largest settlement and only city was Kingston upon Hull. The county stretched from Wold Newton in its northern tip to a different Wold Newton at its most southern point.
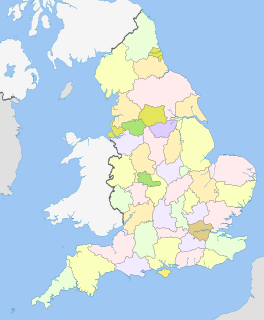
The counties of England are areas used for different purposes, which include administrative, geographical, cultural and political demarcation. The term 'county' is defined in several ways and can apply to similar or the same areas used by each of these demarcation structures. These different types of county each have a more formal name but are commonly referred to just as 'counties'. The current arrangement is the result of incremental reform.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74 and is surpassed only by the European Communities Act 1972 which took the United Kingdom into the European Communities.

Metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties are one of the four levels of subdivisions of England used for the purposes of local government outside Greater London and the Isles of Scilly. As originally constituted, the metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties each consisted of multiple districts, had a county council and were also the counties for the purposes of Lieutenancies. Later changes in legislation during the 1980s and 1990s have allowed counties without county councils and 'unitary authority' counties of a single district. Counties for the purposes of Lieutenancies are now defined separately, based on the metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties.
In England, an unparished area is an area that is not covered by a civil parish. Most urbanised districts of England are either entirely or partly unparished. Many towns and some cities in otherwise rural districts are also unparished areas and therefore no longer have a town council or city council. Some cities and towns which are unparished areas in larger districts have charter trustees to maintain a historic charter, such as city status or simply the mayoralty of a town.
Successor parishes are civil parishes with a parish council created by the Local Government Act 1972 in England. They replaced, with the same boundaries, a selected group of urban districts and municipal boroughs that were abolished in 1974. Most successor parish councils exercised the right to call themselves towns. A total of 300 successor parishes were formed from the former area of 78 municipal boroughs and 221 urban districts. Civil parishes are not permitted to cross district or county boundaries, and where the creation of a successor parish would cause this to happen, either only part of the former area became a parish or two parishes were formed.

Unitary authorities of England are local authorities that are responsible for the provision of all local government services within a district. They are constituted under the Local Government Act 1992, which amended the Local Government Act 1972 to allow the existence of counties that do not have multiple districts. They typically allow large towns to have separate local authorities from the less urbanised parts of their counties and provide a single authority for small counties where division into districts would be impractical. Unitary authorities do not cover all of England. Most were established during the 1990s, though further tranches were created in 2009 and 2019–20. Unitary authorities have the powers and functions that are elsewhere separately administered by councils of non-metropolitan counties and the non-metropolitan districts within them.

The Local Government Commission for England was the body responsible for reviewing the structure of local government in England from 1992 to 2002. It was established under the Local Government Act 1992, replacing the Local Government Boundary Commission for England. The Commission could be ordered by the Secretary of State to undertake "structural reviews" in specified areas and recommend the creation of unitary authorities in the two-tier shire counties of England. The Commission, chaired by John Banham, conducted a review of all the non-metropolitan counties of England from 1993 to 1994, making various recommendations on their future.
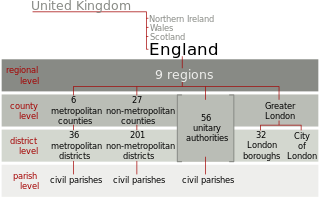
The history of local government in England is one of gradual change and evolution since the Middle Ages. England has never possessed a formal written constitution, with the result that modern administration is based on precedent, and is derived from administrative powers granted to older systems, such as that of the shires.

The administrative boundaries of Worcestershire, England have been fluid for over 150 years since the first major changes in 1844. There were many detached parts of Worcestershire in the surrounding counties, and conversely there were islands of other counties within Worcestershire. The 1844 Counties Act began the process of eliminating these, but the process was not completed until 1966, when Dudley was absorbed into Staffordshire.

Fernhill is a hamlet close to Gatwick Airport in West Sussex, England. Its fields and farmhouses formerly straddled the county boundary between Surrey and West Sussex, but since 1990 the whole area has been part of the county of West Sussex and the borough of Crawley. Fernhill is bounded on three sides by motorways and the airport. A fatal aeroplane crash occurred here in 1969.
References
- Final Report 1971-1992 (PDF). Local Government Boundary Commission For England. 1992. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 June 2012. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ↑ Local government in England and Wales: A Guide to the New System. London: HMSO. 1974. p. 4. ISBN 0-11-750847-0.
- ↑ Wise, M J (December 1969). "Review: The Future of Local Government in England: The Redcliffe-Maud Report". The Geographical Journal. 135 (4): 583–587. doi:10.2307/1795107. JSTOR 1795107.
- ↑ "1970 Conservative Party Manifesto". conservativemanifesto.com. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 "Sir Edmund Compton is boundaries chief". The Times. 26 November 1971. p. 3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Local Government Boundary Commission for England Designate". Hansard 1803–2005. Parliament of the United Kingdom. 25 November 1971. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ "Local Government Act 1972 c.70: Schedule 7 – Constitution and Proceedings of the Local Government Boundary Commission for England". UK Statute Law Database. Office of Public Sector Information . Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ↑ Tam Dalyell (14 March 1994). "Obituary: Sir Edmund Compton". The Independent .
- ↑ "Obituary: Sir Nicholas Morrison". The Times . 16 July 1981. p. 14.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Annex A – Commission Chairmen, Deputy Chairmen, members and Secretaries, Final Report p.37
- ↑ "Obituary: Sir Geoffrey Ellerton". The Independent . 22 August 2005.
- ↑ "Obituary: Mr J M Rankin, QC". The Times . 14 August 1980. p. 14.
- 1 2 "Latest appointments". The Times . 1 December 1982. p. 14.
- ↑ "Professor Michael D I Chisholm ScD". Geography Department, University of Cambridge . Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ "Latest appointments". The Times . 4 December 1981. p. 12.
- 1 2 "Appointments". The Times . 4 March 1988.
- ↑ "Appointments". The Times . 9 November 1987.
- ↑ "Appointments". The Times . 3 October 1990.
- ↑ "Councils offered five more months before changes". The Times . 18 February 1872. p. 3.
- 1 2 "Boundary commission reduces local councils by 672". The Times . 27 April 1972. p. 1.
- ↑ "Boundary Changes. Big cut in number of councils proposed". The Times . 27 April 1872. p. 4.
- ↑ "Boundary plea by 12,000". The Times . 22 June 1972. p. 3.
- ↑ Frank Roberts (26 June 1972). "Boundary team to review submissions". The Times . p. 2.
- ↑ "Some proposed districts too big, councils say". The Times . 12 September 1972. p. 3.
- ↑ "Many enlarged districts will be less unwieldy or remote". The Times . 22 November 1972. p. 4.
- ↑ The English Non-metropolitan Districts (Definition) Order 1972
- ↑ "Ward schemes for new local councils". The Times . 24 November 1972. p. 10.
- ↑ "Changes in local government units may cause some famous names to disappear". The Times . 2 January 1973. p. 2.
- ↑ Christopher Warman (13 August 1973). "Councils want their names changed". The Times . p. 2.
- ↑ Local Government Boundary Commission for England: report number 2. Proposals for names for non-metropolitan districts, March 1973
- ↑ Frank Roberts (28 March 1973). "Administrative map loses some famous names". The Times . p. 6.
- ↑ Local Government Boundary Commission for England (1973). Report No.2 (PDF). London: HMSO. ISBN 011700135X . Retrieved 5 May 2017.
- ↑ Frank Roberts (21 June 1973). "Way will soon open for urban districts to set up their own new-style town councils". The Times . p. 4.
- ↑ Frank Roberts (27 November 1973). "More small towns get parish status". The Times . p. 13.
- 1 2 3 "Part IV: Changes in Local Government Areas". Local Government Act 1972. Wikisource . Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ↑ "Electoral Equality in Boundary Reorganisation". The Times . 28 January 1978. p. 5.
- ↑ "Boundary work delayed by council's appeal". The Times . 4 February 1978. p. 3.
- ↑ "Approach of Boundary Commission upheld". The Times . 28 July 1978. p. 12.
- ↑ "Abolition of county is rejected". The Times . 8 March 1990.
- ↑ "Proposal to abolish unloved county; Humberside". The Times . 29 November 1990.
- ↑ Local Government Act 1992. 1992 c. 19. part II.
- ↑ https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm199293/cmhansrd/1993-11-02/Writtens-3.html
|chapter-url=missing title (help). Parliamentary Debates (Hansard) . House of Commons. 2 November 1993. col. 104–105.