A location-based service (LBS) is a general term denoting software services which utilize geographic data and information to provide services or information to users. LBS can be used in a variety of contexts, such as health, indoor object search, entertainment, work, personal life, etc. Commonly used examples of location based services include navigation software, social networking services, location-based advertising, and tracking systems. LBS can also include mobile commerce when taking the form of coupons or advertising directed at customers based on their current location. They include personalized weather services and even location-based games.
A waypoint is an intermediate point or place on a route or line of travel, a stopping point or point at which course is changed, the first use of the term tracing to 1880. In modern terms, it most often refers to coordinates which specify one's position on the globe at the end of each "leg" (stage) of an air flight or sea passage, the generation and checking of which are generally done computationally.

Wireless communication — otherwise known as “over the air” —is the electromagnetic transfer of information between two or more points that are not connected by an electrical conductor. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications include the use of other electromagnetic wireless technologies, such as light, magnetic, or electric fields or the use of sound.

A cell site, cell tower, or cellular base station is a cellular-enabled mobile device site where antennae and electronic communications equipment are placed—typically on a radio mast, tower, or other raised structure—to create a cell in a cellular network. The raised structure typically supports antenna and one or more sets of transmitter/receivers transceivers, digital signal processors, control electronics, a GPS receiver for timing, primary and backup electrical power sources, and sheltering.

A cellular network or mobile network is a communication network where the last link is wireless. The network is distributed over land areas called "cells", each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, but more normally, three cell sites or base transceiver stations. These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice, data, and other types of content. A cell typically uses a different set of frequencies from neighbouring cells, to avoid interference and provide guaranteed service quality within each cell.
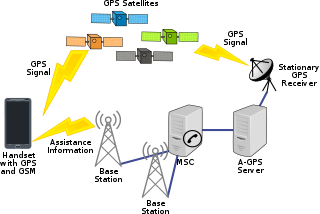
Assisted GPS or Augmented GPS is a system that often significantly improves the startup performance—i.e., time-to-first-fix (TTFF)—of a GPS satellite-based positioning system. A-GPS is extensively used with GPS-capable cellular phones, as its development was accelerated by the U.S. FCC's 911 requirement to make cell phone location data available to emergency call dispatchers.

Mobile phone tracking is a process for identifying the location of a mobile phone, whether stationary or moving. Localization may be effected by a number of technologies, such as using multilateration of radio signals between (several) cell towers of the network and the phone, or simply using GPS. To locate a mobile phone using multilateration of radio signals, it must emit at least the idle signal to contact the next nearby antenna tower, but the process does not require an active call. The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is based on the phone's signal strength to nearby antenna masts.
Radiolocating is the process of finding the location of something through the use of radio waves. It generally refers to passive uses, particularly radar—as well as detecting buried cables, water mains, and other public utilities. It is similar to radionavigation, but radiolocation usually refers to passively finding a distant object rather than actively one's own position. Both are types of radiodetermination. Radiolocation is also used in real-time locating systems (RTLS) for tracking valuable assets.

Real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning is a satellite navigation technique used to enhance the precision of position data derived from satellite-based positioning systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, NavIC and BeiDou. It uses measurements of the phase of the signal's carrier wave in addition to the information content of the signal and relies on a single reference station or interpolated virtual station to provide real-time corrections, providing up to centimetre-level accuracy. With reference to GPS in particular, the system is commonly referred to as carrier-phase enhancement, or CPGPS. It has applications in land survey, hydrographic survey, and in unmanned aerial vehicle navigation.

A tracking system is used for the observing of persons or objects on the move and supplying a timely ordered sequence of location data for further processing.
gpsOne is the brand name for a cellphone chipset manufactured by Qualcomm for mobile phone tracking. It uses A-GPS or Assisted-GPS to locate the phone more quickly, accurately and reliably than by GPS alone, especially in places with poor GPS reception.
Proximity marketing is the localized wireless distribution of advertising content associated with a particular place. Transmissions can be received by individuals in that location who wish to receive them and have the necessary equipment to do so.
Skyhook is a mobile location services company based in Boston, MA that specializes in location positioning, context and intelligence. Founded in 2003, Skyhook originally began by geolocating Wi-Fi access points and evolved with the idea that hybrid positioning technology, which incorporates Wi-Fi, GPS, cell towers, IP address and device sensors, could improve device location. The firm expanded their product set in 2015 to deliver advertising segments and behavioral insights; emphasizing data privatization and security for their advertising technology and mobile app customers. In 2016, the firm introduced Precision Location to power Wearables and the Internet of Things, and launched products Personas and Context Accelerator to help brands reach out to mobile consumers.
An indoor positioning system (IPS) is a network of devices used to locate people or objects where GPS and other satellite technologies lack precision or fail entirely, such as inside multistory buildings, airports, alleys, parking garages, and underground locations. A large variety of techniques and devices are used to provide indoor positioning ranging from reconfigured devices already deployed such as smartphones, WiFi and Bluetooth antennas, digital cameras, and clocks; to purpose built installations with relays and beacons strategically placed throughout a defined space. IPS has broad applications in commercial, military, retail, and inventory tracking industries. There are several commercial systems on the market, but no standards for an IPS system. Instead each installation is tailored to spatial dimensions, building materials, accuracy needs, and budget constraints. Lights, radio waves, magnetic fields, acoustic signals, and behavioral analytics are all used in IPS networks. IPS can achieve position accuracy of 2cm, which is on par with RTK enabled GNSS receivers that can achieve 2cm accuracy outdoors.

Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by a radio receiver connected to another antenna. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing and other applications.
Real-time geotagging is a name given to the automatic technique of acquiring media, associating a specific location with the media, transferring the media to an online map and publishing the media in real time. It is thus an extension of an automatic geotagging process, requiring an in-built or attached location acquisition device, but also requires communication with a wireless data transfer device. Several modern cell phones and digital cameras already integrate camera, aGPS, and wireless data transfer into one device, thus directly producing a geotagged photograph. Real-time geotagging is sometimes referred to as "mobile geotagging" or "autogeotagging", but this does not imply the real-time publishing step.

A Satellite navigation device, colloquially called a GPS receiver, or simply a GPS, is a device that is capable of receiving information from GNSS satellites and then to calculate the device's geographical position. Using suitable software, the device may display the position on a map, and it may offer routing directions. The Global Positioning System (GPS) is one of a handful of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) made up of a network of a minimum of 24, but currently 30, satellites placed into orbit by the U.S. Department of Defense.

Navizon, Inc. is a provider of location-based services and products. Navizon was an early developer of technology that makes it possible to determine the geographic position of a mobile device using as reference the location of cell phone towers and Wi-Fi-based wireless access points instead of GPS. Navizon also developed technology for locating mobile devices indoors with room and floor-level accuracy.
Real-time locating systems (RTLS) are used to automatically identify and track the location of objects or people in real time, usually within a building or other contained area. Wireless RTLS tags are attached to objects or worn by people, and in most RTLS, fixed reference points receive wireless signals from tags to determine their location. Examples of real-time locating systems include tracking automobiles through an assembly line, locating pallets of merchandise in a warehouse, or finding medical equipment in a hospital.
Locata Corporation is a privately held technology company headquartered in Canberra, Australia, with a fully owned subsidiary in Las Vegas, Nevada. Locata has invented a local positioning system that can either replace or augment Global Positioning System (GPS) signals when they are blocked, jammed or unreliable. Government, commercial and other organizations use Locata to determine accurate positioning as a local backup to GPS.








