
The brown recluse, Loxosceles reclusa, Sicariidae is a recluse spider with a necrotic venom. Similar to other recluse spider bites, their bite sometimes requires medical attention. The brown recluse is one of three spiders with medically significant venom in North America.

The recluse spiders, also known as brown spiders, fiddle-backs, violin spiders, and reapers, is a genus of spiders that was first described by R. T. Lowe in 1832. They are venomous spiders known for their bite, which sometimes produces a characteristic set of symptoms known as loxoscelism.

Sicariidae is a family of six-eyed venomous spiders known for their potentially necrotic bites. The family consists of three genera and about 160 species. Well known spiders in this family include the brown recluse spider and the six-eyed sand spider.

Loxosceles rufescens, the Mediterranean recluse spider, originated in the Mediterranean region as its name implies, but is now found worldwide.

A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin wound or severe pain.

Sicarius is a genus of recluse spiders that is potentially medically significant to humans. It is one of three genera in its family, all venomous spiders known for a bite that can induce loxoscelism. They live in deserts and arid regions of the Southern Hemisphere, and females use a mixture of sand and silk when producing egg sacs. Most are native to South America, with the exception of Central America's S. rugosus, known primarily for its self-burying behavior. The name is Latin for assassin.

The Chilean recluse spider is a highly venomous spider, Loxosceles laeta, of the family Sicariidae. In Spanish, it is known as araña de rincón, or "corner spider"; in Portuguese, as aranha-marrom or "brown spider". It is considered by many to be the most dangerous of recluse spiders, and its bites often result in serious systemic reactions, even death.
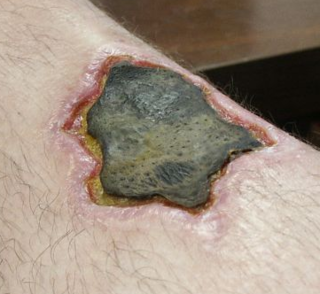
Loxoscelism is a condition occasionally produced by the bite of the recluse spiders. The area becomes dusky and a shallow open sore forms as the skin around the bite dies (necrosis). It is the only proven type of necrotic arachnidism in humans. While there is no known therapy effective for loxoscelism, there has been research on antibiotics, surgical timing, hyperbaric oxygen, potential antivenoms and vaccines. Because of the number of diseases that may mimic loxoscelism, it is frequently misdiagnosed by physicians.

The Natural History Museum is one of the museums under the directorship of the Finnish Museum of Natural History, part of the University of Helsinki, in Helsinki, Finland.
L. intermedia may refer to:

Loxosceles deserta, commonly known as the desert recluse, is a brown spider of the family Sicariidae.
The pathophysiology of a spider bite is due to the effect of its venom. A spider envenomation occurs whenever a spider injects venom into the skin. Not all spider bites inject venom – a dry bite, and the amount of venom injected can vary based on the type of spider and the circumstances of the encounter. The mechanical injury from a spider bite is not a serious concern for humans. Some spider bites do leave a large enough wound that infection may be a concern. However, it is generally the toxicity of spider venom that poses the most risk to human beings; several spiders are known to have venom that can cause injury to humans in the amounts that a spider will typically inject when biting.

Titiotus is a genus of American false wolf spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1897.
Loxosceles blanda, the big bend recluse, is a species of recluse spider in the family Sicariidae. It is found in the United States.
Loxosceles devia, the Texas recluse, is a species of recluse spider in the family Sicariidae. It is found in the United States and Mexico.

Loxosceles intermedia, the Brazilian brown recluse spider, is a highly venomous spider species in the family Sicariidae native to Brazil and Argentina.

Loxosceles gaucho commonly known in English as the gaucho spider. is a highly venomous recluse spider endemic to South America.
Loxosceles similis, is a species of a venomous recluse spider endemic to South America.
Loxosceles adelaida is a species of venomous recluse spider found in South America.











