
Lymantria dispar, the gypsy moth, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. Lymantria dispar covers many subspecies, subspecies identification such as L. d. dispar or L. d. japonica leaves no ambiguity in identification. Lymantria dispar subspecies have a range which covers in Europe, Africa, Asia, North America and South America.

The Lymantriinae are a subfamily of moths of the family Erebidae.

The black arches or nun moth is a small Palaearctic moth. It is considered a forest pest.

Cybosia is a monotypic moth genus in the subfamily Arctiinae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819. Its only species, Cybosia mesomella, the four-dotted footman, was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Dasychira mendosa, the brown tussock moth or hairy tussock moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1823. It is found in India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Taiwan, Thailand and Australia.

Udea ferrugalis, the rusty dot pearl, is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. The species was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1796.

Wittia sororcula, the orange footman, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Johann Siegfried Hufnagel in 1766. It is found in Europe, Anatolia and further east across the Palearctic to southern Siberia and the Amur basin to China.

Lymantria is a genus of tussock moths in the family Erebidae. They are widely distributed throughout Europe, Japan, India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Java, and Celebes. It was described by Jacob Hübner in 1819.

Laelia coenosa is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in North Africa, southern and central Europe, through Russia and eastern Asia up to Japan.
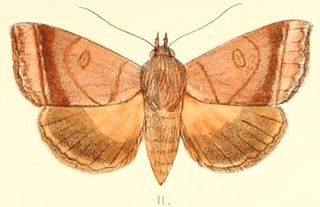
Ophiusa trapezium is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka to Queensland, the Bismarck Islands and New Caledonia. Adults are fruit piercers.

Eucyclodes gavissima, the Oriental orange banded green geometer moth, is a species of moth of the family Geometridae described by Francis Walker in 1861. It is found in the Indian subregion, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, western China, Taiwan, Sumatra and Borneo.

Archips cerasivorana, the ugly-nest caterpillar moth, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. The caterpillars of this species are known to create nests by tying the leaves of their host plant together. Within the nests, they live and feed off the leaves that have been tied together. The larvae are brownish or greenish yellow with a shiny dark brown head. Larvae can be found from May to July. The species overwinters as an egg, and pupation takes place within the nest. Caterpillars are seen follow one another in trails, a behavior prompted by the release of signaling pheromones from their spinnerets.

Lymantria xylina is a moth in the family Erebidae. It is found in Japan, Taiwan and China.

Orgyia postica, the cocoa tussock moth or hevea tussock moth, is a species of moth of the subfamily Lymantriinae of family Erebidae found from the Oriental tropics of India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Borneo, Java, New Guinea and Taiwan. It was described by Francis Walker in 1855.

Ethmia nigritaenia is a moth in the family Depressariidae. It is found from southern Mexico, Guatemala and Honduras to north-western Costa Rica.

Lymantria dispar asiatica, the Asian gypsy moth, is a moth in the family Erebidae of Eurasian origin. It is similar to Lymantria dispar dispar in appearance, but adult females can fly. It is classified as a pest and is host to over 500 species of trees, shrubs and plants.

Somena scintillans,the yellow tail tussock moth, is a moth in the family Erebidae described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found in northern India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar and the Andaman Islands. Though considered a minor pest, larva can sporadically be a serious pest.
Prabhasa monastyrskii is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Vladimir Viktorovitch Dubatolov in 2012. It is found in Vietnam.

Lymantria grisea is a species of moth of the family Erebidae.
Spilarctia castanea is a moth in the family Erebidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1893. It is found in Sri Lanka.


















