
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.

The history of the graphical user interface, understood as the use of graphic icons and a pointing device to control a computer, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent code, but with basic elements in common that define the WIMP "window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.

Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, released on January 19, 1983. It is generally considered the first mass market personal computer operable through a graphical user interface (GUI). In 1983, a machine like the Lisa was still so expensive that it was primarily marketed to individual and small and medium-size businesses, as a groundbreaking new alternative to much bigger and more expensive mainframes or minicomputers such as from IBM, that either require additional, expensive consultancy from the supplier, hiring specially trained personnel, or at least, a much steeper learning curve to maintain and operate. Earlier GUI-controlled personal computers were not mass marketed; for example, the Xerox Alto was manufactured in several thousands only for Xerox and select partners through Xerox PARC from the early to mid 1970s.

The critical path method (CPM), or critical path analysis (CPA), is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. A critical path is determined by identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT).
Project management software (PMS) can help plan, organize, and manage resource tools and develop resource estimates. Depending on the sophistication of the software, it can manage estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, decision-making, quality management, time management and documentation or administration systems. Numerous PC and browser-based project management software and contract management software products and services are available.

A/UX is a Unix-based operating system from Apple Computer for Macintosh computers, integrated with System 7's graphical interface and application compatibility. It is Apple's first official Unix-based operating system, launched in 1988 and discontinued in 1995 with version 3.1.1. A/UX requires select 68k-based Macintosh models with an FPU and a paged memory management unit (PMMU), including the Macintosh II, SE/30, Quadra, and Centris series.
Claris International Inc., formerly FileMaker Inc., is a computer software development company formed as a subsidiary company of Apple Computer in 1987. It was given the source code and copyrights to several programs that were owned by Apple, notably MacWrite and MacPaint, in order to separate Apple's application software activities from its hardware and operating systems activities.

In software design, the look and feel of a graphical user interface comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces, as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes, and menus. The term can also refer to aspects of a non-graphical user interface, as well as to aspects of an API – mostly to parts of an API that are not related to its functional properties. The term is used in reference to both software and websites.

Apple Computer, Inc. v. Microsoft Corporation, 35 F.3d 1435, was a copyright infringement lawsuit in which Apple Computer, Inc. sought to prevent Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard from using visual graphical user interface (GUI) elements that were similar to those in Apple's Lisa and Macintosh operating systems. The court ruled that, "Apple cannot get patent-like protection for the idea of a graphical user interface, or the idea of a desktop metaphor [under copyright law]...". In the midst of the Apple v. Microsoft lawsuit, Xerox also sued Apple alleging that Mac's GUI was heavily based on Xerox's. The district court dismissed Xerox's claims without addressing whether Apple's GUI infringed Xerox's. Apple lost all claims in the Microsoft suit except for the ruling that the trash can icon and folder icons from Hewlett-Packard's NewWave windows application were infringing. The lawsuit was filed in 1988 and lasted four years; the decision was affirmed on appeal in 1994, and Apple's appeal to the U.S. Supreme Court was denied.

The Apple Macintosh—later rebranded as the Macintosh 128K—is the original Apple Macintosh personal computer. The Macintosh was the first successful mass-market all-in-one desktop personal computer with a graphical user interface, built-in screen, and mouse. It played a pivotal role in establishing desktop publishing as a general office function. The motherboard, a 9 in (23 cm) CRT monitor, and a floppy drive were housed in a beige case with integrated carrying handle; it came with a keyboard and single-button mouse. It sold for US$2,495. The Macintosh was introduced by a television commercial entitled "1984" shown during Super Bowl XVIII on January 22, 1984 and directed by Ridley Scott. Sales of the Macintosh were strong at its initial release on January 24, 1984, and reached 70,000 units on May 3, 1984. Upon the release of its successor, the Macintosh 512K, it was rebranded as the Macintosh 128K. The computer's model number was M0001.
Star Trek is the code name that was given to a secret prototype project, running a port of Macintosh System 7 and its applications on Intel-compatible x86 personal computers. The project, starting in February 1992, was conceived in collaboration between Apple Computer, who provided the majority of engineers, and Novell, who at the time was one of the leaders of cross-platform file-servers. The plan was that Novell would market the resulting OS as a challenge to Microsoft Windows, but the project was discontinued in 1993 and never released, although components were reused in other projects. The project was named after the Star Trek science fiction franchise with the slogan "To boldly go where no Mac has gone before".

Microsoft Project is a project management software product, developed and sold by Microsoft. It is designed to assist a project manager in developing a schedule, assigning resources to tasks, tracking progress, managing the budget, and analyzing workloads.
Many computer user interfaces use a control panel metaphor to give the user control of software and hardware features. The control panel consists of multiple settings including display settings, network settings, user account settings, and hardware settings. Control panels are also used by web applications for easy graphical configuration. Some services offered by control panels require the user to have admin rights or root access.

In computing, the trash, also known by other names such as dustbin, wastebasket, and others, is a graphical user interface desktop metaphor for temporary storage for files set aside by the user for deletion, but not yet permanently erased. The concept and name is part of Mac operating systems, a similar implementation is called the Recycle Bin in Microsoft Windows, and other operating systems use other names.
LisaProject is the first GUI-based project management software, conceived and programmed by Debra Willrett of SoloSoft for Apple's Lisa workstation.
Two major families of Mac operating systems were developed by Apple Inc.
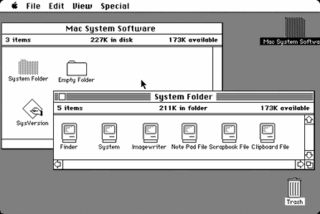
The Macintosh "System 1" is the first version of Apple Macintosh operating system and the beginning of the classic Mac OS series. It was developed for the Motorola 68000 microprocessor. System 1 was released on January 24, 1984, along with the Macintosh 128K, the first in the Macintosh family of personal computers. It received one update, "System 1.1" on December 29, 1984, before being succeeded by System 2.
Micro Planner X-Pert is a project management software package in continuous development since 1979.

Mac OS is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.
Comparison of user features of operating systems refers to a comparison of the general user features of major operating systems in a narrative format. It does not encompass a full exhaustive comparison or description of all technical details of all operating systems. It is a comparison of basic roles and the most prominent features. It also includes the most important features of the operating system's origins, historical development, and role.












