
Hipposideros is one of the most diverse genera of bats, with more than 70 species. They are collectively called roundleaf bats after the shape of their nasal ornament. It is the type genus of the family Hipposideridae. It is divided into species groups based on morphology.

The rufous trident bat, Persian trident bat, or triple nose-leaf bat is a species of bat in the genus Triaenops. It occurs in southwestern Pakistan, southern Iran, the United Arab Emirates, Oman, and Yemen. In the last country, it occurs together with the much smaller Triaenops parvus. Populations from Madagascar and mainland Africa have also been assigned to T. persicus, but are referable to the species Triaenops menamena and Triaenops afer, respectively. Madagascar populations have also been referred to as Triaenops rufus, but this name is a synonym of T. persicus.
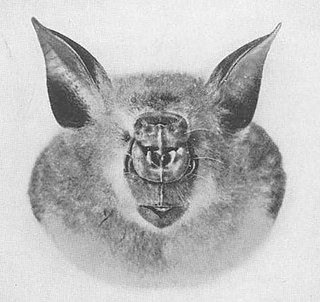
The giant roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae found in western tropical Africa. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and caves. The species was formerly considered part of M. commersoni, which is now viewed as being restricted to Madagascar. Both commersoni and it were formerly placed in the genus Hipposideros, but moved to the resurrected Macronycteris in 2017 on the basis of molecular evidence. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The São Tomé leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to the island of São Tomé, in the Gulf of Guinea off the western coast of Africa. The bat's natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and caves.

Rhinonicteris is a genus of leaf-nosed microbats, represented by fossil taxa found at Riverleigh in Queensland and the extant species Rhinonicteris aurantia, which occurs in the north and west of the Australian continent.
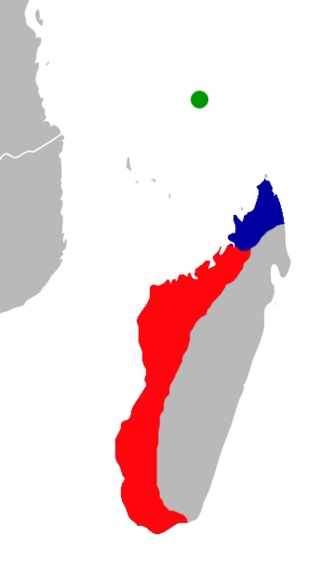
Grandidier's trident bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops.
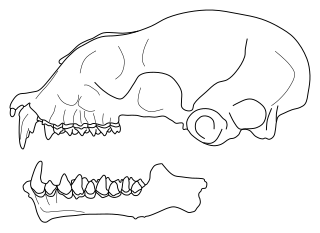
Triaenops is a genus of bat in the family Rhinonycteridae. It is classified in the tribe Triaenopini, along with the closely related genus Paratriaenops and perhaps the poorly known Cloeotis. The species of Paratriaenops, which occur on Madagascar and the Seychelles, were placed in Triaenops until 2009. Triaenops currently contains the following species:

Paratriaenops furcula, also known as Trouessart's trident bat, is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops. A related species, Paratriaenops pauliani, occurs in the Seychelles.

The Hipposideridae are a family of bats commonly known as the Old World leaf-nosed bats. While it has often been seen as a subfamily, Hipposiderinae, of the family Rhinolophidae, it is now more generally classified as its own family. Nevertheless, it is most closely related to Rhinolophidae within the suborder Yinpterochiroptera.

Triaenops goodmani is an extinct bat from Madagascar in the genus Triaenops. It is known from three lower jaws collected in a cave at Anjohibe in 1996, and described as a new species in 2007. The material is at most 10,000 years old. A bat humerus from the same site could not be identified as either T. goodmani or the living T. menamena. T. goodmani is identifiable as a member of Triaenops or the related genus Paratriaenops by a number of features of the teeth, such as the single-cusped, canine-like fourth premolar and the presence of a gap between the entoconid and hypoconulid cusps on the first two molars. T. goodmani is larger than the living species of Triaenops and Paratriaenops on Madagascar, and on the first molar the protoconid cusp is only slightly higher than the hypoconid, not much higher as in the other species.

Triaenops menamena is a bat in the genus Triaenops found on Madagascar, mainly in the drier regions. It was known as Triaenops rufus until 2009, when it was discovered that that name had been incorrectly applied to the species. Triaenops rufus is a synonym of Triaenops persicus, a Middle Eastern species closely related to T. menamena— the Malagasy species had previously been placed as a subspecies of T. persicus by some authors. Triaenops menamena is mostly found in forests, but also occurs in other habitats. It often roosts in large colonies and eats insects such as butterflies and moths. Because of its wide range, common occurrence, and tolerance of habitat degradation, it is not considered to be threatened.

The striped leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat native to eastern and southern Africa. It was formerly considered part of M. commersoni, which is now viewed as being restricted to Madagascar. Both commersoni and it were formerly placed in the genus Hipposideros, but moved to the resurrected Macronycteris in 2017 on the basis of molecular evidence.

Paratriaenops is a genus in the bat family Hipposideridae. It is classified in the tribe Triaenopini, along with the closely related genus Triaenops and perhaps the poorly known Cloeotis. The species of Paratriaenops were placed in Triaenops until 2009. Paratriaenops currently contains the following species:

Paratriaenops pauliani is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to Aldabra Atoll of the western Seychelles, where it was found on Picard Island. It was formerly considered to be part of the species Triaenops furculus, known from Madagascar, and was initially assigned as a new species within the genus Triaenops. Later it as well as T. furculus were placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops. A related species, Paratriaenops auritus, also of Madagascar, was similarly reassigned.

Commerson's roundleaf bat, also known as Commerson's leaf-nosed bat, is a species of bat endemic to Madagascar. It is named after French naturalist Philibert Commerson (1727-1773). Bat populations of Africa or São Tomé and Príncipe formerly considered part of this species are now classified separately as M. gigas, M. thomensis or M. vittata, while one from Madagascar was split off to become M. cryptovalorona. It was formerly placed in the genus Hipposideros, but moved to the resurrected Macronycteris in 2017 on the basis of molecular evidence.

Rhinonycteridae is a family of bats, within the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. The type species, the orange nose-leafed species group Rhinonicteris aurantia, is found across the north of Australia.
Doryrhina is a genus of bats belonging to the family Hipposideridae. The best known species, Doryrhina cyclops, was long placed in the diverse genus Hipposideros, but a 2017 study found that it did not form a monophyletic group with true Hipposideros. Consequently, it was placed in a separate genus, Doryrhina. A second species, Doryrhina camerunensis, has not been studied genetically, but it is generally thought to be related to D. cyclops, so it was also moved to Doryrhina.











