
The Sri Lankan Civil War was a civil war fought in Sri Lanka from 1983 to 2009. Beginning on 23 July 1983, it was an intermittent insurgency against the government by the Velupillai Prabhakaran-led Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. The LTTE fought to create an independent Tamil state called Tamil Eelam in the north-east of the island, due to the continuous discrimination and violent persecution against Sri Lankan Tamils by the Sinhalese-dominated Sri Lanka government.
The Kent and Dollar Farm massacres were the first massacres of Sinhalese civilians carried out by the LTTE during the Sri Lankan Civil War. The massacres took place on 30 November 1984, in two tiny farming villages in the Mullaitivu district in north-eastern Sri Lanka. The Sri Lankan government labeled this as an attack on civilians by the LTTE.
The Kokkilai massacre was carried out by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam.
The Anuradhapura massacre occurred in Sri Lanka in 1985 and was carried out by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. This was the largest massacre of Sinhalese civilians by the LTTE to date; it was also the first major operation carried out by the LTTE outside a Tamil majority area. Initially, EROS claimed responsibility for the massacre, but it later retracted the statement, and joined the PLOTE in denouncing the incident. The groups later accused the LTTE for the attack. Since then, no Tamil militant group has admitted to committing the massacre. However, state intelligence discovered that the operation was ordered by the LTTE's leader Velupillai Prabhakaran. He assigned the massacre to the LTTE Mannar commander Victor and it was executed by Victor's subordinate Anthony Kaththiar. The LTTE claimed the attack was in revenge of the 1985 Valvettiturai massacre, where the Sri Lanka Army killed 70 Tamil civilians in Prabhakaran's hometown.
The Palliyagodella massacre was carried out by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) against the mostly Muslim population of the Palliyagodella village located on border region of the northern part of Sri Lanka that were controlled by the Tigers at the time. This was the largest massacre of Muslim civilians by the LTTE to date. Village eyewitnesses claim that some 285 men, women and children, around a third of the population, were killed by a 1,000 strong force of the Tamil Tigers; however, the Sri Lankan government states that the LTTE massacred 166 to 171. All but 40 of the victims of the Palliyathidal massacre were Muslim; the rest were Sinhalese.
The Gonagala Massacre was a massacre that occurred on 18 September 1999, in the small village of Gonagala, located in the Ampara District of Sri Lanka. According to reports, over 50 men, women and children were hacked to death in the middle of the night. The massacre is attributed to the LTTE, which is banned as a terrorist organisation by a number of countries including the United States, the United Kingdom and the European Union.
The Kebithigollewa massacre occurred on 15 June 2006 when 60 civilians were killed by an Claymore mine attack on a bus. The U.S and the SLMM claimed that LTTE was the perpetrator.
The Kallarawa massacre was carried out by the LTTE, an organisation which has been banned in 33 countries including the US, Australia, EU, India and Canada due to its terrorist activities.
The October 1995 massacres were carried out by the LTTE, an organization which has been banned in 33 countries including the US, Australia, EU, India and Canada due to its terrorist activities.
Eelam War I is the name given to the initial phase of the armed conflict between the government of Sri Lanka and the LTTE.

Eelam War II is the name given to the second phase of armed conflict between Sri Lankan military and the separatist Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. The war started after the failure of peace talks between the Premadasa government and the LTTE. This phase of the war was initiated by the LTTE who massacred almost 600 Sinhalese and Muslim police personnel after they were ordered by the Premadasa government to surrender to the LTTE. The truce was broken on June 10, 1990 when the LTTE in October expelled all the 28,000 Muslims residing in Jaffna.
Eelam War III is the name given to the third phase of armed conflict between the Sri Lankan military and the separatist Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE).
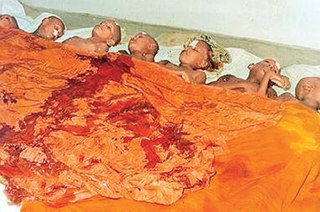
The Aranthalawa massacre was the massacre of 33 Buddhist monks, most of them young novice monks, and four civilians by cadres of the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam organization on June 2, 1987, close to the village of Aranthalawa, in the Ampara District of Eastern Sri Lanka. The massacre is among the most notorious and devastating atrocities committed by the LTTE during the history of the Sri Lankan Civil War, and continues to be commemorated 35 years on.

The 1989 Valvettiturai massacre occurred on 2 and 3 August 1989 in the small coastal town of Valvettiturai, on the Jaffna Peninsula in Sri Lanka. Sixty-four Sri Lankan Tamil civilians were killed by soldiers of the Indian Peace Keeping Force. The massacre followed an attack on the soldiers by rebel Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam cadres. The rebel attack had left six Indian soldiers, including an officer, dead, and another 10 injured. Indian authorities claimed that the civilians were caught in crossfire. Journalists such as Rita Sebastian of the Indian Express, David Husego of the Financial Times and local human rights groups such as the University Teachers for Human Rights have reported quoting eyewitness accounts that it was a massacre of civilians. George Fernandes, who later served as defense minister of India (1998–2004), called the massacre India’s My Lai.
The war was waged for over a quarter of a century, with an estimated 70,000 killed by 2007. Immediately following the end of war, on 20 May 2009, the UN estimated a total of 80,000–100,000 deaths. However, in 2011, referring to the final phase of the war in 2009, the Report of the Secretary-General's Panel of Experts on Accountability in Sri Lanka stated, "A number of credible sources have estimated that there could have been as many as 40,000 civilian deaths." The large majority of these civilian deaths in the final phase of the war were said to have been caused by indiscriminate shelling by the Sri Lankan Armed Forces.
The Aluth Oya massacre was the massacre of 127 Sinhalese civilians, including children and women, by the cadres of Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam organization on April 17, 1987, near the village of Aluth Oya, on the Habarana Trincomalee road in North Central Province of Sri Lanka. This massacre is considered one of the most notorious and devastating atrocities committed by the LTTE during the history of the Sri Lankan Civil War.

The 1987 Eastern Province massacres were a series of massacres of the Sinhalese population in the Eastern Province of Sri Lanka by Tamil mobs and Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) during the Sri Lankan Civil War. Though they began spontaneously, they became more organized, with the LTTE leading the violence. Over 200 Sinhalese were killed by mob and militant violence, and over 20,000 fled the Eastern Province. The violence has been described as having had the appearance of a pogrom.




