
In Hinduism, kundalini is a form of divine feminine energy believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the muladhara. It is an important concept in Śhaiva Tantra, where it is believed to be a force or power associated with the divine feminine or the formless aspect of the Goddess. This energy in the body, when cultivated and awakened through tantric practice, is believed to lead to spiritual liberation. Kuṇḍalinī is associated with the goddess Parvati or Adi Parashakti, the supreme being in Shaktism, and with the goddesses Bhairavi and Kubjika. The term, along with practices associated with it, was adopted into Hatha Yoga in the 9th century. It has since then been adopted into other forms of Hinduism as well as modern spirituality and New Age thought.

Kundalini yoga is a spiritual practice in the yogic and tantric traditions of Hinduism, centered on awakening the kundalini energy. This energy, often symbolized as a serpent coiled at the root chakra at the base of the spine, is guided upward through the chakras until it reaches the crown chakra at the top of the head. This leads to the blissful state of samadhi, symbolizing the union of Shiva and Shakti. Most yoga schools use pranayama, meditation, and moral code observation to raise the kundalini.

Hatha yoga is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ haṭha literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century Amṛtasiddhi, comes from a tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of hatha are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward.

Muladhara or the root chakra is one of the seven primary chakras according to Hindu tantrism. It is symbolized by a lotus with four petals and the colour pink or red.

Vishuddha, or Vishuddhi, or throat chakra is the fifth primary chakra according to the Hindu tradition of tantra. The residing Deity of this chakra is Panchavaktra Shiva, with 5 heads and 4 arms, and the Shakti is Shakini.

A mudra is a symbolic or ritual gesture or pose in Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. While some mudras involve the entire body, most are performed with the hands and fingers.

The Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā is a classic fifteenth-century Sanskrit manual on haṭha yoga, written by Svātmārāma, who connects the teaching's lineage to Matsyendranath of the Nathas. It is among the most influential surviving texts on haṭha yoga, being one of the three classic texts alongside the Gheranda Samhita and the Shiva Samhita.

Nāḍī is a term for the channels through which, in traditional Indian medicine and spiritual theory, the energies such as prana of the physical body, the subtle body and the causal body are said to flow. Within this philosophical framework, the nadis are said to connect at special points of intensity, the chakras. All nadis are said to originate from one of two centres; the heart and the kanda, the latter being an egg-shaped bulb in the pelvic area, just below the navel. The three principal nadis run from the base of the spine to the head, and are the ida on the left, the sushumna in the centre, and the pingala on the right. Ultimately the goal is to unblock these nadis to bring liberation.
Bindu is a Sanskrit word meaning "point", "drop" or "dot".

The Bihar School of Yoga is a modern school of yoga founded and developed by Sri Swami Satyananda Saraswati in Munger, Bihar, India, in 1963. The system of yoga taught at the Bihar School of Yoga is recognized worldwide as Bihar Yoga or the Satyananda Yoga tradition. In 2019, the Bihar School of Yoga was awarded the Prime Minister’s Award for Outstanding Contribution Towards Promotion and Development of Yoga.
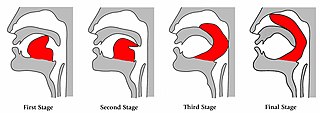
Khecarī mudrā is a hatha yoga practice carried out by curling the tip of the tongue back into the mouth until it reaches above the soft palate and into the nasal cavity. The tongue is made long enough to do this with many months of daily tongue stretching and, in some versions of the practice, by gradually severing the frenulum of the tongue with a sharp implement over a period of months.

Siddhasana or Accomplished Pose is an ancient seated asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise suitable for meditation. The names Muktasana and Burmese position are sometimes given to the same pose, sometimes to an easier variant, Ardha Siddhasana. Svastikasana has each foot tucked as snugly as possible into the fold of the opposite knee.
Shiva Samhita is a Sanskrit text on yoga, written by an unknown author. The text is addressed by the Hindu ascetic Shiva to his consort Parvati. The text consists of five chapters, with the first chapter a treatise that summarizes nondual Vedanta philosophy with influences from the Sri Vidya school of South India. The remaining chapters discuss yoga, the importance of a guru (teacher) to a student, various asanas, mudras and tantra.

A bandha is a kriyā in Hatha Yoga, being a kind of internal mudra described as a "body lock," to lock the vital energy into the body. Bandha literally means bond, fetter, or "catching hold of".
The Joga Pradīpikā is a hatha yoga text by Ramanandi Jayatarama written in 1737 in a mixture of Hindi, Braj Bhasa, Khari Boli and forms close to Sanskrit. It presents 6 cleansing methods, 84 asanas, 24 mudras and 8 kumbhakas. The text is illustrated in an 1830 manuscript with 84 paintings of asanas, prepared about a hundred years after the text.
Vajroli mudra, the Vajroli Seal, is a practice in Hatha yoga which requires the yogi to preserve his semen, either by learning not to release it, or if released by drawing it up through his urethra from the vagina of "a woman devoted to the practice of yoga".
The Amṛtasiddhi, written in a Buddhist environment in about the 11th century, is the earliest substantial text on what became haṭha yoga, though it does not mention the term. The work describes the role of bindu in the yogic body, and how to control it using the Mahamudra so as to achieve immortality (Amṛta). The implied model is that bindu is constantly lost from its store in the head, leading to death, but that it can be preserved by means of yogic practices. The text has Buddhist features, and makes use of metaphors from alchemy.

The Vivekamārtaṇḍa is an early Hatha yoga text, the first to combine tantric and ascetic yoga. Attributed to Goraknath, it was probably written in the 13th century. It emphasises mudras as the most important practice. The name means "Sun of Discernment". It teaches khecarīmudrā, mahāmudrā, viparītakaraṇī and the three bandhas. It teaches six chakras and the raising of Kundalinī by means of "fire yoga" (vahniyogena).

The Amaraugha and the Amaraugha Prabodha are recensions of a 12th century Sanskrit text on haṭha yoga, attributed to Gorakṣanātha. The Amaraugha Prabodha is the later recension, with the addition of verses from other texts and assorted other materials. The text's physical practices imply a Buddhist origin for haṭha yoga.

The Gorakṣaśataka is an early text on Haṭha yoga text from the 11th-12th century, attributed to the sage Gorakṣa. It was the first to teach a technique for raising Kundalini called "the stimulation of Sarasvati", along with elaborate pranayama, breath control. It was written for an audience of ascetics.

















