
Postal voting is voting in an election whereby ballot papers are distributed to electors or returned by post, in contrast to electors voting in person at a polling station or electronically via an electronic voting system. Historically, postal votes must be distributed and placed in return mail before the scheduled election day, it is sometimes referred to as a form of early voting. It can also be used as an absentee ballot. However, in recent times the model in the US has morphed, in municipalities that use postal voting exclusively, to be one of ballots being mailed out to voters, but the return method taking on alternatives of return by mail or dropping off the ballot in person via secure drop boxes and/or voting centers.

Voter registration in the United States is the voter registration that is required for voting in federal, state and local elections in the United States. The only exception is North Dakota, which does not require registration, although North Dakota law allows cities to register voters for city elections. Voter registration takes place at the county level in many states and at the municipal level in several states. Most states set cutoff dates for voter registration, ranging from 2 to 4 weeks before an election; while a third of states have Election Day or "same-day" voter registration which enables eligible citizens to register or update their registration when they vote before or on Election Day.
Instant-runoff voting (IRV) is used for state and congressional elections in Maine and for local elections in 11 cities, where it is often called "ranked-choice voting." Those cities include San Francisco, California; Oakland, California; Berkeley, California; San Leandro, California; Takoma Park, Maryland; Basalt, Colorado; Telluride, Colorado; St. Paul, Minnesota; Minneapolis, Minnesota; Santa Fe, New Mexico, and Portland, Maine. It is pending implementation in several additional cities, including in 2019 in Las Cruces, New Mexico and St. Louis Park, Minnesota. IRV is commonly used for student government and other non-governmental elections, but it has been proposed for Democratic primaries.

Matthew Dunlap is an American politician from Maine. A Democrat, Dunlap is the Secretary of State of Maine, serving since January 7, 2013, and previously served in that same post from 2005 to 2011. In 2012, he sought to become his party's nominee to replace retiring Olympia Snowe, but lost in the primary to State Senator Cynthia Dill. Prior to his first election as Secretary of State in 2005, he represented Old Town in the Maine House of Representatives for four terms beginning in 1996.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Maine since December 29, 2012. A bill for the legalization of such marriages was approved by voters, 53-47 percent, on November 6, 2012, as Maine, Maryland and Washington became the first U.S. states to legalize same-sex marriage by popular vote. Election results were certified by the Maine Secretary of State's office and the Governor of Maine on November 29.

Paul Richard LePage is an American businessman and politician who was the 74th Governor of Maine, from 2011 to 2019. A member of the Republican Party, LePage served two terms as a city councilor in Waterville, Maine, before being elected Mayor of Waterville in 2003, serving until 2011.

Maine Question 1 was a voter referendum conducted in Maine in 2009 that rejected a bill legalizing same-sex marriage in the state. The measure passed 53%–47% on November 3, 2009.

Bruce Lee Poliquin is an American businessman and politician. A Republican, he represented Maine's 2nd congressional district in the United States House of Representatives from 2015 to 2019. Poliquin was first elected to Congress in the 2014 general election. From 2010 to 2012, he was the Maine State Treasurer. He was a candidate for the Republican nomination for the U.S. Senate in 2012, finishing second in the primary election. In January 2017, at the start of the 115th United States Congress, Poliquin was the only Republican representing a U.S. House district in New England.

Maine Question 1 was a voter referendum on an initiated state statute that occurred November 6, 2012. The title of the citizen initiative is "An Act to Allow Marriage Licenses for Same-Sex Couples and Protect Religious Freedom". The question that appeared on the ballot was: "Do you want to allow the State of Maine to issue marriage licenses to same-sex couples?"

Voter ID laws in the United States are laws that require a person to provide some form of official identification before they are permitted to register to vote, receive a ballot for an election, or to actually vote in elections in the United States.

Maine Question 1 (MQ1), "An Act To Prohibit the Use of Dogs, Bait or Traps When Hunting Bears Except under Certain Circumstances", was a citizen-initiated referendum measure in Maine, which was voted on in the general election of November 4, 2014. As the Maine Legislature declined to act on the proposed statute, it was automatically placed on the ballot. The proposal was defeated by 320,873 "No" votes to 279,617 "Yes".

Maine Question 1, "An Act To Strengthen the Maine Clean Election Act, Improve Disclosure and Make Other Changes to the Campaign Finance Laws", was a citizen-initiated referendum measure in Maine, which appeared on the November 3, 2015 statewide ballot. As the Maine Legislature did not exercise its ability to pass the bill on its own, it was placed on the ballot and approved by Maine voters.

Maine Question 1 was a people's veto referendum that appeared on the June 12, 2018 statewide ballot. It sought to reject a law passed by the Maine Legislature that suspended the implementation of ranked choice voting, authorized by Maine voters in a previous referendum, for use in Maine elections until and if an amendment to the Maine Constitution is passed to expressly permit it; failing that, the law would be automatically repealed in 2021. It qualified because supporters of the original referendum collected the necessary number of signatures from registered Maine voters. This vote coincided with primary elections in which party nominees for governor, U.S. Senate, U.S. House, and the Maine Legislature were chosen to run in general elections on November 6.

Maine Question 5, formally An Act to Establish Ranked-Choice Voting, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that qualified for the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot and was approved by a margin of 52% to 48%. It would change how most Maine elections will be conducted from a plurality voting system to a ranked-choice voting system. It appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the legislature, five other ballot questions, and various local elections. Maine would be the first state to use such a system for its statewide elections for governor and U.S. Senate if implemented.

Maine Question 4, formally An Act to Raise the Minimum Wage, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that appeared on the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It sought to increase Maine's minimum wage from $7.50 per hour to $12 an hour by 2020, as well as increasing the minimum wage for tipped employees gradually to the same level by 2024. It would also index increases after 2024 to inflation. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the Legislature, other statewide ballot questions, and various local elections. Efforts to place a competing, more moderate proposal alongside the citizen-initiated bill were unsuccessful.

Maine Question 3, formally An Act to Require Background Checks for Gun Sales, was a citizen-initiated referendum question that appeared on the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It sought to require a background check for virtually all gun transfers in Maine, with some exceptions. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two United States House seats, the Maine Legislature, other statewide ballot questions, and various local elections.

Maine Question 2, formally An Act to Establish The Fund to Advance Public Kindergarten to Grade 12 Education, was a citizen-initiated referendum question that appeared on the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It sought to increase state aid to public schools by instituting a surcharge of 3% on Maine income taxes for those with income above $200,000 a year. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the Legislature, and various local elections.
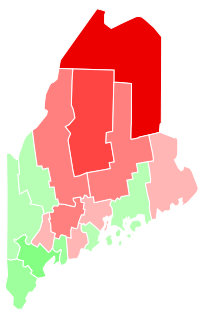
Maine Question 1, formally An Act to Legalize Marijuana, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that qualified for the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It was qualified for the ballot after a Maine Superior Court judge ordered that petitions rejected by the Maine Secretary of State be reconsidered. The proposal seeks to legalize the recreational use of marijuana in Maine for those over the age of 21, and institute a 10 percent tax on its sale. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it will appear on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the Legislature, other statewide ballot questions, and various local elections.

Maine Question 2, formally titled "An Act To Enhance Access to Affordable Health Care", is a citizen-initiated ballot measure that has qualified for the November 7, 2017 statewide ballot. It seeks to expand Medicaid eligibility under the terms of the Affordable Care Act, something which has been vetoed six times by Maine Gov. Paul LePage.

Maine Question 1, formally An Act To Allow Slot Machines or a Casino in York County, was a citizen-initiated referendum question that appeared on the November 7, 2017, statewide ballot in Maine. It sought to award a license for the construction and operation of a casino in York County, Maine by a qualified entity as spelled out in the proposed law, with tax revenue generated by the casino to go to specific programs. The wording of the proposed law effectively permitted only one company, Capital 7, to be awarded the license. The ballot measure was defeated, with 83% of voters opposing it.













