
Armillaria is a genus of fungi that includes the A. mellea species known as honey fungi that live on trees and woody shrubs. It includes about 10 species formerly categorized summarily as A. mellea. Armillarias are long-lived and form the largest living fungi in the world. The largest known organism covers more than 3.4 square miles (8.8 km2) in Oregon's Malheur National Forest and is estimated to be 2,500 years old. Some species of Armillaria display bioluminescence, resulting in foxfire.

Texas root rot is a disease that is fairly common in Mexico and the southwestern United States resulting in sudden wilt and death of affected plants, usually during the warmer months. It is caused by a soil-borne fungus named Phymatotrichopsis omnivora that attacks the roots of susceptible plants. It was first discovered in 1888 by Pammel and later named by Duggar in 1916.

Butt rot is a disease of plants, mostly trees, caused by fungi. The fungus attacks the moist, poorly protected undersurface of tree trunk's thickest part, where the end of the stem makes contact with the soil. It may affect the roots as well, causing a disease known as root rot. It then moves up into the interior of the plant, producing a roughly conical column of dead, rotted plant matter, up to one and a half meters long in severe cases. Such an infection is likely to impair the transport properties of the xylem tissue found at the center of the stem. It also weakens the stem and makes the plant more vulnerable to toppling. One particularly virulent species of fungus associated with butt rot is Serpula himantioides.

Phytophthora is a genus of plant-damaging oomycetes, whose member species are capable of causing enormous economic losses on crops worldwide, as well as environmental damage in natural ecosystems. The cell wall of Phytophthora is made up of cellulose. The genus was first described by Heinrich Anton de Bary in 1875. Approximately 210 species have been described, although 100–500 undiscovered Phytophthora species are estimated to exist.

Phytophthora cinnamomi, also known as cinnamon fungus, is a soil-borne water mould that produces an infection which causes a condition in plants variously called "dieback", "root rot", or, "ink disease".

Pythium is a genus of parasitic oomycetes. They were formerly classified as fungi. Most species are plant parasites, but Pythium insidiosum is an important pathogen of animals, causing pythiosis. The feet of the fungus gnat are frequently a vector for their transmission.
Root rot is a condition in which anoxic conditions in the soil or potting media around the roots of a plant cause them to rot. This occurs due to excessive standing water around the roots. It is found in both indoor and outdoor plants, although it is more common in indoor plants due to overwatering, heavy potting media, or containers with poor drainage. The leaves of plants experiencing root rot often yellow and die, and if allowed to continue, the condition can be fatal.
Fruit rot disease may refer to:

Rhizoctonia solani is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps are thin, effused, and web-like, but the fungus is more typically encountered in its anamorphic state, as hyphae and sclerotia. The name Rhizoctonia solani is currently applied to a complex of related species that await further research. In its wide sense, Rhizoctonia solani is a facultative plant pathogen with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It causes various plant diseases such as root rot, damping off, and wire stem. It can also form mycorrhizal associations with orchids.

Fusarium culmorum is a fungal plant pathogen and the causal agent of seedling blight, foot rot, ear blight, stalk rot, common root rot and other diseases of cereals, grasses, and a wide variety of monocots and dicots. In coastal dunegrass, F. culmorum is a nonpathogenic symbiont conferring both salt and drought tolerance to the plant.
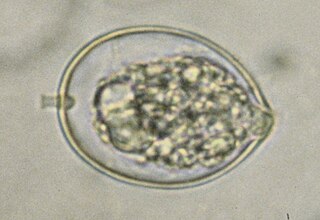
Phytophthora cactorum is a fungal-like plant pathogen belonging to the Oomycota phylum. It is the causal agent of root rot on rhododendron and many other species, as well as leather rot of strawberries.

Phytophthora cryptogea is a species of water mould in the family Pythiaceae. It is a plant pathogen that infects several species of cultivated plants, including over 40 species of cultivated flowers. It was first described as the cause of tomato foot rot in tomatoes
Pythium aphanidermatum is a soil borne plant pathogen. Pythium is a genus in the class Oomycetes, which are also known as water molds. Oomycetes are not true fungi, as their cell walls are made of cellulose instead of chitin, they are diploid in their vegetative state, and they form coenocytic hyphae. Also, they reproduce asexually with motile biflagelette zoospores that require water to move towards and infect a host. Sexually, they reproduce with structures called antheridia, oogonia, and oospores.
Pythium graminicola is a plant pathogen infecting cereals.

Ceratobasidium cornigerum is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps are thin, spread on the substrate out like a film (effused) and web-like. An anamorphic state is frequently obtained when isolates are cultured. Ceratobasidium cornigerum is saprotrophic, but is also a facultative plant pathogen, causing a number of economically important crop diseases, and an orchid endomycorrhizal associate. The species is genetically diverse and is sometimes treated as a complex of closely related taxa. DNA research shows the species actually belongs within the genus Rhizoctonia.
Pythium dissotocum is a plant pathogen infecting strawberry and rice.

Phellinus weirii is a species of fungus. It is the plant pathogen that causes laminated root rot in certain conifers, typically Douglas-fir and western redcedar. It is widespread in the Douglas-fir growing regions of British Columbia, Washington and Oregon.
Forest pathology is the research of both biotic and abiotic maladies affecting the health of a forest ecosystem, primarily fungal pathogens and their insect vectors. It is a subfield of forestry and plant pathology.

Collar rot is a symptomatically described disease that is usually caused by any one of various fungal and oomycete plant pathogens. It is present where the pathogen causes a lesion localized at or about the collet between the stem and the root. The lesions develop around the stem eventually forming a "collar". Observationally, collar rot grades into "basal stem rot", and with some pathogens is the first phase of "basal stem rot" often followed by "root rot". Collar rot is most often observed in seedings grown in infected soil. The pathogens that cause collar rot may be species or genera specific. But generalist pathogens such as Agroathelia rolfsii are known to attack over 200 different species. While bacteria caused collar rot is not common, trees infected with Fire blight may develop collar rot. Non-parasitic collar rot may be caused by winter damage.














